
The ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity is shaped by a dedicated group of individuals. These pioneers, through their research, entrepreneurship, and tireless efforts, have left a significant mark on the industry.
From seasoned security leaders steering the helm of major companies, to passionate bloggers, journalists, podcasters, and authors, this diverse group offers a wealth of perspectives on the ever-present fight against cybercrime.
Veterans with decades of experience share the stage with innovative minds constantly pushing boundaries. Whether it's investigative journalists uncovering cybercrime rings, ethical hackers forging new defensive strategies, or company founders shaping the future of online safety, these influencers are united in a common cause.
They leverage social media to not only stay updated on the latest threats but also advocate for increased awareness and education. This list compiles the top 30 most influential cybersecurity influencers who actively share their expertise online. If you're interested in cybersecurity, following and engaging with these influential figures is a surefire way to stay informed and inspired.
Top 30 Cybersecurity Influencers of 2024
[caption id="attachment_68576" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alexandre Blanc is a renowned Cybersecurity dvisor, ISO/IEC 27001 and 27701 Lead Implementer, and a recognised security expert. With a track record of holding successful cybersecurity events, Blanc serves as an Independent Strategic and Security Advisor, providing invaluable counsel to various organisations. His expertise spans incident response management, digital transformations, and dark web investigations.
Recognised as a LinkedIn Top Voice in Technology and named among the top security experts with over 75k followers on LinkedIn, Blanc's insights are highly sought-after in the cybersecurity community. Through publications, speaking engagements, and advisory roles, he continues uplift the IT and security industry.
[caption id="attachment_68502" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alissa Abdullah, PhD, is a distinguished senior information technology and cybersecurity executive with a rich background spanning Fortune 100 companies, the White House, and the government intelligence community. Currently serving as Deputy Chief Security Officer for Mastercard, she brings over 20 years of experience in IT strategy, fiscal management, and leading large government programmes.
Abdullah's strategic leadership extends beyond her corporate role; she serves as a board member for organisations like Girls in Tech, Inc. and Smartsheet, while also lecturing at the University of California, Berkeley. With a PhD in Information Technology Management, and over 17k followers on LinkedIn, she is a recognised authority in cybersecurity and IT leadership.
[caption id="attachment_68503" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Jane Frankland is a prominent figure in cybersecurity with a career spanning over two decades of experience in the field. As a cybersecurity influencer and LinkedIn Top Voice, she has established herself as an award-winning leader, coach, board advisor, author, and speaker.
Frankland's expertise lies in bridging the gap between business strategy and technical cybersecurity needs, enabling smoother and more effective engagements. With a portfolio career, she works with major brands as an influencer, leadership coach, and board advisor. Additionally, Frankland is deeply involved in initiatives promoting diversity and inclusion in cybersecurity, aligning her work with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
[caption id="attachment_68504" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Mark Lynd is a globally recognised cybersecurity strategist, and keynote speaker in cybersecurity and AI. With over 25 years of experience, including four stints as a CIO & CISO for global companies, he excels in technology, cybersecurity, and AI.
Currently, he serves as the Head of Executive Advisory & Corporate Strategy at Netsync, a global technology reseller, where he concentrates on cybersecurity, AI, data center, IoT, and digital transformation. Lynd's accolades include being ranked globally for security and AI thought leadership, and he's authored acclaimed books and eBooks.
He holds a Bachelor of Science from the University of Tulsa and is a proud military veteran.
[caption id="attachment_68505" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Naomi Buckwalter is an accomplished Information Security Leader, Nonprofit Director, Keynote Speaker, and LinkedIn Learning Instructor. With extensive experience in directing information security programmes, she has notably served as Director of Product Security at Contrast Security and Director of Information Security & IT at Beam Dental. Buckwalter's expertise encompasses compliance, risk management, and security operations.
She is also the Founder & Executive Director of the Cybersecurity Gatebreakers Foundation, aiming to revolutionise cybersecurity hiring practices. With a background in computer science and over 99K followers on LinkedIn, she is recognised for her contributions as a cybersecurity thought leader and advocate for diversity in tech.
[caption id="attachment_68506" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Australian
Cyber Conference 2024[/caption]
Raj Samani is currently a Chief Scientist at Rapid7 and has experience in this industry spanning 20 years. He has worked with law enforcement and is also advisor to the European Cybercrime Centre. Samani is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences, a published author, and continues to make appearances in podcasts where he discusses his expertise surrounding threat intelligence, cyber defence strategies, and emerging threats.
With his following of over 15.2k followers on LinkedIn and 14.4k on Twitter, Samani is influential to his followers due to the cybersecurity related articles, updates and insights he shares, often engaging not only cybersecurity enthusiasts but also professionals.
[caption id="attachment_68507" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: BankInfoSecurity[/caption]
Tyler Cohen Wood is a prominent and respected figure in the cybersecurity field. Currently the co-founder of Dark Cryptonite, a Special Comms method of cybersecurity, Woods has over 20 years of experience in the intelligence community. Woods previously served as Senior Intelligence Officer at the Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA) and Cyber Branch Chief at the DIA's Science and Technology Directorate.
Woods is also a keynote speaker and provides insight into global cyber threats and national security due to her knowledge on digital privacy and national security. Woods has a following of over 27k on LinkedIn, attention she’s garnered due to her ability to share insightful commentary on cybersecurity issues which explains complex technical concepts easily for all types of audiences.
[caption id="attachment_68509" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Experience McIntire[/caption]
Theresa Payton was the first ever female Chief Information Officer for the White House from 2006-2008, serving under George W. Bush, and is now the CEO of her company Fortalice Solutions which she founded in 2008.
Payton is best known for consulting as that is the purpose of her company, providing services like risk assessments, incident response, and digital forensics to government agencies and different industries and businesses about cybersecurity strategy and best IT practices.
Payton has over 25k followers on LinkedIn and this is due to her continuous and avid blogging exposing cybercrimes and tackling cybersecurity on her companies page.
[caption id="attachment_68510" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Bill Brenner is an experienced professional in the cybersecurity field and has ventured into many areas including journalist, editor, and community manager. His work has focused on cybersecurity education and awareness.
Brenner is currently the Vice President of Custom and Research Content Strategy at CyberRisk Alliance. Brenners 15.7k followers on Twitter come from his influence surrounding articles posted on CS Media and Techtarget which are informative and relevant to cybersecurity professionals.
[caption id="attachment_68511" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: BH Consulting[/caption]
Brian Honan is the CEO of BH Consulting and has over 30 years of experience in cybersecurity. He was formerly a special advisor on cyber security to Europol’s Cyber Crime Centre, along with being an advisor to the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security.
Honan’s work in consultancy is not just aimed at government agencies but also multinational corporations, and small businesses. Honan advocates highly for education in the field and is a founding member of the Irish Reporting and Information Security Service (IRISS-CERT).
His following of 36.2k on Twitter can be attested to the articles and blogs he’s written and posted along with presentations at industry conferences worldwide.
[caption id="attachment_68513" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Magda Chelly is the first Tunisian woman to be on the advisory board of Blackhat. She has over 10 years of experience in security architecture, risk management, and incident response. Chelly is also a published author and is also known to be a keynote speaker who can deliver her talks in five different languages.
She is currently the Managing Director at Responsible Cyber where she helps organisations implement effective cybersecurity strategies, while also being the founder of Women of Security (WoSEC) Singapore which aims to encourage women to join the field of cybersecurity.
Chelly has over 57k followers on LinkedIn due to her posts on cybersecurity, but also her diversity initiatives which make her an advocate in the field.
[caption id="attachment_68514" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Facebook[/caption]
Marcus J Carey is a former Navy Cryptologist who is now in cybersecurity innovation. He has worked many roles including penetration tester, security researcher, and security engineer, all of which helped to gain new and revolutionary insights into offensive and defensive cybersecurity techniques.
Carey is famous for the books he has written surrounding hackers and cybersecurity and is an established CEO of Threatcare, a cybersecurity company focused on providing proactive threat detection and risk assessment solutions.
His 52.4k Twitter followers stem from the expertise he shares on social media and his importance in educating future professionals in the field. He is also sought after for speaking in industry conferences.
[caption id="attachment_68515" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Penguin Random House[/caption]
Andy Greenberg is currently a senior writer at Wired magazine, and has written many articles investigating high-profile cyber incidents, hacking groups, and emerging cybersecurity threats.
Greenberg's reports often focus on the details of cyberattacks and looks at the broader implications for people, the government, and the industry as a whole.
His 70.4k followers on Twitter are influenced by his updates and in-depth articles exploring the world of cybersecurity, not only informing the general public but also professionals about the hazards.
[caption id="attachment_68516" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Paul Asadoorian is a professional in the cybersecurity field for over 20 years, but his following comes from his blogs and podcasts. He’s best known as the founder and host of Security Weekly where Asadoorian brings together experts and practitioners from the cybersecurity field to discuss latest news and research in the field such as network security, application security, incident response, etc.
Additionally, he is also the founder and CEO of Offensive Countermeasures, a company that helps cybersecurity professionals enhance their skills and stay ahead of evolving threats. His 77.3k followers on Twitter are mostly due to his large social media presence as a podcaster and his posts surrounding resources , opinions, and promotion of Security Weekly.
[caption id="attachment_68518" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source:[/caption]
Nicole Perlroth is a Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist who covers cybersecurity and digital espionage for The New York Times. She is regarded for her intensive reporting on cyber threats, hacking incidents, and the intersection of technology and national security.
Perlroth has also written a book on the cyberweapons arms race. With 91.5k followers on Twitter, Perlroth shares her own articles, as well as insights and updates related to cybersecurity and technology which creates engagement for her from both cybersecurity professionals and general readers interested in security.
[caption id="attachment_67630" align="alignnone" width="523"]

Source: Smashing Security[/caption]
Graham Cluley is an author and blogger who has written books on cybersecurity and continues to be avid in sharing news and stories on cybersecurity through the written word and speech. Currently, Graham Cluley is an independent cybersecurity analyst, writer, and public speaker.
He also runs a podcast where he discusses internet threats and safety in an entertaining, engaging and informative way. Cluley’s 112.9k Twitter followers are updated with his podcast, tweets and YouTube videos which explain cybersecurity topics and how to tackle them in a way patented to the general users of the internet.
[caption id="attachment_68522" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Rachel Tobac is an ethical hacker who helps companies keep safe through her work as CEO of SocialProof Security, which she co-founded. The company focuses on educating employees to recognize and deal with cyberattacks. She has a background in behavioural psychology and uses it to improve cybersecurity awareness and defences in the general public.
Tobac also works with the non-profit Women in Security and Privacy (WISP) where she helps women advance in the security field and often speaks for underrepresented groups to pursue a career in cybersecurity. Tobac’s 106k strong following on Twitter is due to her activism and due to the tips and updates she shares related to the industry, with some posts being popular for starting debates amongst professionals.
[caption id="attachment_68523" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: SANS Cyber Security Certifications & Research[/caption]
Katie Moussouris is the Founder of Luta Security which encompasses her aims surrounding vulnerability disclosure and safer and responsible research in security. She is a leading figure in both the aspects and has 20 years of experience on the field. Some of Moussouris’s leading work is the Microsoft's bug bounty programme, which she developed and was one of the first-of-its-kind in the industry.
She also advocates for vulnerability disclosure, which merits more transparency between security researchers and organisations. Moussouris’s 115.5k followers come from her revolutionary developments. She is a frequent speaker at cybersecurity conferences and events. She often posts and talks about her advocacy for ethical hacking and responsible security practices along with her expertise on vulnerability disclosure and bug bounty programmes.
[caption id="attachment_68524" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Brooks is the president of his consulting company where he advises clients on cybersecurity strategy, risk assessment, and business development. Along with that, he is a featured author in many technology and cybersecurity blogs.
Brooks has previously worked in advisory roles with corporations and also at government agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security and the Defence Intelligence Agency.
Brooks’ 116k LinkedIn followers are due to his regular contributions to industry research and news, media articles. Along with that, he is a popular keynote speaker who shares his expertise on a wide range of cybersecurity topics.
[caption id="attachment_68525" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Miessler is the founder and CEO of Unsupervised Learning where he writes informative articles and tackles relevant issues surrounding cybersecurity and what the world after AI means for human beings.
Miesslers following of 139.4k on Twitter comes from professionals in the field and novice enthusiasts engaging with his content and discussions due to his experience in the field. He also avidly shares articles, podcasts, bringing his audience up to speed with cybersecurity.
[caption id="attachment_68526" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: iTWire[/caption]
Kevin Beaumont is an experienced professional who has worked in various cybersecurity roles, including security engineer and consultant. He also specialises in threat detection and incident response. Kevin is now the Head of Cybersecurity Operations at Arcadia Ltd. along with being a cybersecurity researcher who runs his own platform where he discusses cybersecurity.
Beaumont appeals to newer, younger cybersecurity enthusiasts with around 150.9k followers on Twitter due to his engagement with trolling on the internet. Additionally, he writes articles for Medium where he informs about cybercrime issues such as Microsoft Windows vulnerability.
[caption id="attachment_68527" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: hacks4pancakes[/caption]
Lesley Carhart is currently a threat analyst and principal responder at Dragos, a company which works to protect industrial control systems from cyber threats, and has experience as a security analyst, incident responder and threat hunter.
Her work in both the public and private sectors allowed her to gain valuable insights into cybersecurity issues across different industries. Her following of 168k comes from her works such as blogger and speaker who offers career advice in the field of cybersecurity. She also speaks about topics such as industrial control, ransomware attacks and more.
[caption id="attachment_68528" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Wikipedia[/caption]
Schneier is a specialist in computer security and privacy along with being a cryptographer. Schneier is regarded as one of the most influential people in his field of cryptography and has written numerous books on cybersecurity, some of which are considered seminal works in the field.
He has also written articles about security and privacy for magazines such as Wired. Schneier’s following of 147.1k comes from being acknowledged as impactful in his field but also due to his blog where he addresses the prevalence of hacking and other cyber dangers intersecting with our everyday lives.
[caption id="attachment_68530" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eugene Kaspersky is an individual most impactful in the cybersecurity, best known as the CEO of Kaspersky Lab, a company he co-founded in 1997 which identified government-sponsored cyberwarfare. Kaspersky’s following of 187.5k comes from how Kaspersky Lab has grown into a global cybersecurity powerhouse, offering a wide range of products and services, along with his advocacy for cybersecurity education.
Kaspersky is also a keynote speaker on emerging threats, and the importance of cybersecurity awareness at industry conferences and events. Furthermore, he writes a blog where he regularly posts updates about his life in the industry.
[caption id="attachment_68532" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eric Geller is a freelance cybersecurity journalist recognised for his insightful coverage of digital security. With a comprehensive portfolio including esteemed publications like WIRED, Politico, and The Daily Dot, Geller offers in-depth analysis on cyber policy, encryption, and data breaches.
His investigative reporting touches the intricate intersections of cybersecurity and everyday life, from election security to critical infrastructure protection. Geller's expertise extends to interviews with top officials and breaking news on government initiatives. With a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science from Kenyon College, Geller's accolades include induction into the Pi Sigma Alpha national political science Honors society.
[caption id="attachment_68533" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: The Futurum Group[/caption]
Shira Rubinoff is a cybersecurity and blockchain advisor as well as being a popular keynote speaker and author. She is the President of SecureMySocial, a cybersecurity company that focuses on protecting organizations from social media risks such as data leakage, reputational damage, and insider threats. Her videos are many and impactful, consisting of interviews and conversations with other professionals.
She is known to be one of the top businesswomen in the field and currently runs a cybersecurity consulting firm and serves as the Chair of the Women in Cybersecurity Council (WCI), aiming to influence more women to join the field. Her follower count of 190.4k isn’t only due to her experience as a businesswoman, but also her constant interaction on social media as she posts talks, videos, podcasts, written work and more about many topics in cybersecurity.
[caption id="attachment_68535" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: WithSecure[/caption]
Miko Hyppönen has been in the world of cybersecurity since the late 1980s. Since then he has led researchers in identifying and eliminating emerging cyber threats, while providing insights and solutions to protect individuals, businesses, and governments from cybercrime.
Hyppönen has written for many famous newspapers like the New York Times and has also appeared on international TV and lectured at universities like Oxford and Cambridge. His 230.5k followers is due to his engaging and informative presentations, which help raise awareness about cybersecurity threats.
He also has a following for his blog posts and research papers detailing his expertise.
[caption id="attachment_68536" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: IMDb[/caption]
Kim Zetter is an award-winning investigative journalist renowned for her expertise in cybersecurity and national security. With a distinguished career spanning publications like WIRED, Politico, and The New York Times Magazine, Zetter is a respected authority on topics ranging from election security to cyber warfare.
Her book, "Countdown to Zero Day: Stuxnet and the Launch of the World's First Digital Weapon," offers a gripping narrative of covert cyber operations. As a sought-after speaker and social media personality with over 7K followers on LinkedIn, she shares insights at conferences worldwide. Zetter's relentless pursuit of truth has earned her acclaim and established her as a leading voice in the cybersecurity journalism.
[caption id="attachment_68537" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Keppler Speakers[/caption]
Brian Krebs is an investigative journalist who wrote for The Washington post from 1995 to 2009 for the security fix blog. He now runs his own blog, Krebs on Security. In it, he provides in-depth analysis and reports, along with promptly posted breaking news on cybercrime, hacking, data breaches, etc.
Krebs has received many awards for his investigative journalism, including the Pulitzer Prize finalist for his coverage of cybersecurity problems. Krebs’ 347.9k are due to the reputation his blog widely holds for being a first choice when looking for accurate, fast information, as well as the truth as he’s known to hold individuals and organisations accountable for in his work.
[caption id="attachment_68538" align="alignnone" width="541"]

Source: Cyderes[/caption]
Herjavec is the CEO of the Herjavec Group and the Global Cybersecurity Firm, Cyderes, which leads cybersecurity options and supports many security services including threat detection and response, identity and access management, and compliance solutions. Along with that, he features on BBC’s Shark Tank and also provides motivational business advice through his books and videos.
His following of 2.2 million may be due to his appearance on the show, but he continues to actively post insights and gives commentary on cybersecurity trends and ever-changing threats. Most of his followers are there to witness what he shares on business and entrepreneurship. Herjavec frequently shares cybersecurity related articles and updates.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.





 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The UserSec recruitment drive plan comes amidst ongoing tensions between Russia and NATO, with UserSec previously declaring a cyber campaign targeting NATO member states. Notably, the group has collaborated with other pro-Russian hacking groups, such as KillNet, to orchestrate coordinated attacks against NATO.
Talking about the recruitment plan, the threat actor stated they are “looking for promising specialists” to join their teams, including individuals who are interested in pen testing, social engineering, reverse engineers, and “people who know how to work with viruses”.
UserSec, a pro-Russian hacking group active since at least 2022, has gained notoriety for its Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and collaboration with other like-minded groups. In May 2023, UserSec made headlines by declaring a cyber campaign aimed at NATO member states, forming an alliance with KillNet to carry out coordinated attacks.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The UserSec recruitment drive plan comes amidst ongoing tensions between Russia and NATO, with UserSec previously declaring a cyber campaign targeting NATO member states. Notably, the group has collaborated with other pro-Russian hacking groups, such as KillNet, to orchestrate coordinated attacks against NATO.
Talking about the recruitment plan, the threat actor stated they are “looking for promising specialists” to join their teams, including individuals who are interested in pen testing, social engineering, reverse engineers, and “people who know how to work with viruses”.
UserSec, a pro-Russian hacking group active since at least 2022, has gained notoriety for its Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and collaboration with other like-minded groups. In May 2023, UserSec made headlines by declaring a cyber campaign aimed at NATO member states, forming an alliance with KillNet to carry out coordinated attacks.



 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The cyberattack on Heras comes amidst a spree of cyber attacks orchestrated by the LockBit ransomware group. Notably, the group targeted Allied Telesis, Inc., a leading American telecommunication equipment supplier. While the Heras data breach purportedly occurred on May 27, 2024, the authenticity of the claims and the leaked data remains unverified.
In a bold move earlier this year, the United States imposed sanctions on affiliates of the Russia-based LockBit ransomware group. This decisive action, led by the U.S. Department of Justice and the Federal Bureau of Investigation, signals a unified stance against cyber threats. LockBit, notorious for its Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, employs double extortion tactics to extort hefty ransoms from its victims.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The cyberattack on Heras comes amidst a spree of cyber attacks orchestrated by the LockBit ransomware group. Notably, the group targeted Allied Telesis, Inc., a leading American telecommunication equipment supplier. While the Heras data breach purportedly occurred on May 27, 2024, the authenticity of the claims and the leaked data remains unverified.
In a bold move earlier this year, the United States imposed sanctions on affiliates of the Russia-based LockBit ransomware group. This decisive action, led by the U.S. Department of Justice and the Federal Bureau of Investigation, signals a unified stance against cyber threats. LockBit, notorious for its Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, employs double extortion tactics to extort hefty ransoms from its victims.


 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The major concern for this BSNL data leak is the inclusion of sensitive customer information, which, if exploited, could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
The urgency of the situation is further emphasized by kiberphant0m's warning to potential buyers and Indian authorities, suggesting that the data could be sold to other parties if not addressed promptly.
“India if you want to secure your data and do not want it to be sold you must buy it first, contact me BEFORE someone purchases this data. It could be 3 hours to 24 hours, who knows”, says the hacker.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The major concern for this BSNL data leak is the inclusion of sensitive customer information, which, if exploited, could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
The urgency of the situation is further emphasized by kiberphant0m's warning to potential buyers and Indian authorities, suggesting that the data could be sold to other parties if not addressed promptly.
“India if you want to secure your data and do not want it to be sold you must buy it first, contact me BEFORE someone purchases this data. It could be 3 hours to 24 hours, who knows”, says the hacker.

 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The claims of this Shell data leak were shared on a popular hacking forum by the user Kingpin and shared glimpses into sample data allegedly related to the organization. The Cyber Express has reached out to the oil and gas company to learn more about this Shell data breach and the authenticity of the hackers over the claimed data.
However, at the time of writing this, no official statement or response has been received. This lack of confirmation leaves the claims regarding the Shell data breach unverified, although the potential implications are threatening for the customers and stakeholders associated with the organization.
Talking about the cyberattack on Shell, the hacker Kingpin states that the organization suffered a data breach in May 2024 and this data breach allegedly contained "Shopper Code, First Name, Last Name, Status, Shopper Email, Contact Mobile, Postcode, Nectar, Suburb, State, Site Address, Suburb 1, Country, Site Name, Last Login, Pay and Association Number".
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The claims of this Shell data leak were shared on a popular hacking forum by the user Kingpin and shared glimpses into sample data allegedly related to the organization. The Cyber Express has reached out to the oil and gas company to learn more about this Shell data breach and the authenticity of the hackers over the claimed data.
However, at the time of writing this, no official statement or response has been received. This lack of confirmation leaves the claims regarding the Shell data breach unverified, although the potential implications are threatening for the customers and stakeholders associated with the organization.
Talking about the cyberattack on Shell, the hacker Kingpin states that the organization suffered a data breach in May 2024 and this data breach allegedly contained "Shopper Code, First Name, Last Name, Status, Shopper Email, Contact Mobile, Postcode, Nectar, Suburb, State, Site Address, Suburb 1, Country, Site Name, Last Login, Pay and Association Number".

 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The cybercriminals have set a deadline of 5 days for the potential leak of the stolen data, adding urgency to the situation. The implications of such a breach extend beyond PSG BANATSKI DVOR, affecting not only the company but also its clients and stakeholders.
The Cyber Express has reached out to the Serbian gas service provider to learn more about the authenticity of this alleged PSG BANATSKI DVOR cyberattack. However, at the time of writing this, no official statement or response has been received, leaving the claims for this RansomHub cyberattack stand unconfirmed.
Moreover, the PSG BANATSKI DVOR website is currently nonfunctional and is displaying a "took too long to respond" error. This error, often associated with cyberattacks, suggests disruptions in the normal functioning of the website, possibly due to overwhelming server loads or exploitation of vulnerabilities in the site's infrastructure.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The cybercriminals have set a deadline of 5 days for the potential leak of the stolen data, adding urgency to the situation. The implications of such a breach extend beyond PSG BANATSKI DVOR, affecting not only the company but also its clients and stakeholders.
The Cyber Express has reached out to the Serbian gas service provider to learn more about the authenticity of this alleged PSG BANATSKI DVOR cyberattack. However, at the time of writing this, no official statement or response has been received, leaving the claims for this RansomHub cyberattack stand unconfirmed.
Moreover, the PSG BANATSKI DVOR website is currently nonfunctional and is displaying a "took too long to respond" error. This error, often associated with cyberattacks, suggests disruptions in the normal functioning of the website, possibly due to overwhelming server loads or exploitation of vulnerabilities in the site's infrastructure.

 For those seeking guidance or further assistance, Murphy Law Firm can be reached directly via email at abm@murphylegalfirm.com or by phone at (405) 389-4989. Protecting the rights and interests of individuals affected by the TRC Staffing data breach is important, and Murphy Law Firm represents the victims with a legal process.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.
For those seeking guidance or further assistance, Murphy Law Firm can be reached directly via email at abm@murphylegalfirm.com or by phone at (405) 389-4989. Protecting the rights and interests of individuals affected by the TRC Staffing data breach is important, and Murphy Law Firm represents the victims with a legal process.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information. 

 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
Despite the gravity of the allegations, Allied Telesis has yet to confirm or refute the purported cyberattack. The Cyber Express reached out to the company for clarification, but as of this writing, no official statement has been issued. Consequently, the authenticity of the alleged breach remains unverified, leaving the situation shrouded in uncertainty.
Interestingly, the timing of these allegations coincides with significant organizational changes within Allied Telesis. On May 27, 2024, the company reportedly relocated its China branch to a new address. Moreover, the recent re-appointment of Jon Wilner as the Vice President of Customer Success highlights some of the big changes within the organization and possibly deciphering the “why” of the alleged data.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
Despite the gravity of the allegations, Allied Telesis has yet to confirm or refute the purported cyberattack. The Cyber Express reached out to the company for clarification, but as of this writing, no official statement has been issued. Consequently, the authenticity of the alleged breach remains unverified, leaving the situation shrouded in uncertainty.
Interestingly, the timing of these allegations coincides with significant organizational changes within Allied Telesis. On May 27, 2024, the company reportedly relocated its China branch to a new address. Moreover, the recent re-appointment of Jon Wilner as the Vice President of Customer Success highlights some of the big changes within the organization and possibly deciphering the “why” of the alleged data.

 Source: ONEKEY[/caption]
After collaborative efforts and validation processes, TP-Link shared a beta version of 1.1.7p1 on April 10 for further testing, culminating in the confirmation and release of the patch by ONEKEY on May 27, 2024.
The vulnerability exposed a critical flaw in the TP-Link Archer C5400X gaming router, rendering it susceptible to remote command execution. This exploit granted unauthorized users the ability to execute arbitrary commands on the device, posing security risks to users' data and network integrity.
“It seems the need to provide a wireless device configuration API at TP-Link had to be answered either fast or cheap, which ended up with them exposing a supposedly limited shell over the network that clients within the router could use as a way to configure wireless devices”, said OneKey in the advisory.
Source: ONEKEY[/caption]
After collaborative efforts and validation processes, TP-Link shared a beta version of 1.1.7p1 on April 10 for further testing, culminating in the confirmation and release of the patch by ONEKEY on May 27, 2024.
The vulnerability exposed a critical flaw in the TP-Link Archer C5400X gaming router, rendering it susceptible to remote command execution. This exploit granted unauthorized users the ability to execute arbitrary commands on the device, posing security risks to users' data and network integrity.
“It seems the need to provide a wireless device configuration API at TP-Link had to be answered either fast or cheap, which ended up with them exposing a supposedly limited shell over the network that clients within the router could use as a way to configure wireless devices”, said OneKey in the advisory.
 Source: TP-Link[/caption]
Central to this TP-Link Archer C5400X vulnerability is the rftest binary, launched during the device's initialization sequence. This binary, responsible for wireless interface self-assessment, inadvertently exposes a network service vulnerable to unauthenticated command injection. Attackers can leverage this vulnerability to remotely execute commands with elevated privileges, potentially compromising the device and its connected network.
To mitigate the risk posed by this vulnerability, users are strongly advised to upgrade their devices to version 1_1.1.7. TP-Link has implemented fixes to prevent command injection through shell meta-characters, thereby enhancing the security posture of affected devices. However, users must remain vigilant and proactive in ensuring their devices are up to date with the latest firmware releases to safeguard against emerging threats.
Source: TP-Link[/caption]
Central to this TP-Link Archer C5400X vulnerability is the rftest binary, launched during the device's initialization sequence. This binary, responsible for wireless interface self-assessment, inadvertently exposes a network service vulnerable to unauthenticated command injection. Attackers can leverage this vulnerability to remotely execute commands with elevated privileges, potentially compromising the device and its connected network.
To mitigate the risk posed by this vulnerability, users are strongly advised to upgrade their devices to version 1_1.1.7. TP-Link has implemented fixes to prevent command injection through shell meta-characters, thereby enhancing the security posture of affected devices. However, users must remain vigilant and proactive in ensuring their devices are up to date with the latest firmware releases to safeguard against emerging threats.

 Source: X[/caption]
Talking about the Bulgarian Ports Infrastructure Company cyberattack in its post, the Russian Cyber Army states that they are attacking the “State Enterprise “Port Infrastructure” (IF)”, which is the territorial authority of the Bulgarian ports, for public transport, providing traffic management and delivery information services.
The Russian Cyber Army's recent activities have garnered attention, including a peculiar interview conducted by WIRED with a purported spokesperson known as "Julia." The interview sheds light on the group's motivations, which ostensibly revolve around defending Russian interests in the face of perceived external pressure from the United States, the European Union, and Ukraine.
Source: X[/caption]
Talking about the Bulgarian Ports Infrastructure Company cyberattack in its post, the Russian Cyber Army states that they are attacking the “State Enterprise “Port Infrastructure” (IF)”, which is the territorial authority of the Bulgarian ports, for public transport, providing traffic management and delivery information services.
The Russian Cyber Army's recent activities have garnered attention, including a peculiar interview conducted by WIRED with a purported spokesperson known as "Julia." The interview sheds light on the group's motivations, which ostensibly revolve around defending Russian interests in the face of perceived external pressure from the United States, the European Union, and Ukraine.

 Source: Bitdefender[/caption]
The integration of Bitdefender’s Scamio with WhatsApp was a strategic response to the increasing use of artificial intelligence by malicious actors. Scammers were exploiting popular messaging apps and online services to steal money, credentials, and personal data. By integrating Scamio into WhatsApp, Bitdefender aimed to disrupt these criminal activities by offering a sophisticated tool capable of keeping pace with online scam tactics.
The enhanced accessibility provided by this feature aimed to provide an additional layer of security for Australians, who were disproportionately targeted by online fraudsters. Having Scamio available within WhatsApp streamlined the scam verification process for everyday users, reducing the time and effort required to identify potential scams.
Source: Bitdefender[/caption]
The integration of Bitdefender’s Scamio with WhatsApp was a strategic response to the increasing use of artificial intelligence by malicious actors. Scammers were exploiting popular messaging apps and online services to steal money, credentials, and personal data. By integrating Scamio into WhatsApp, Bitdefender aimed to disrupt these criminal activities by offering a sophisticated tool capable of keeping pace with online scam tactics.
The enhanced accessibility provided by this feature aimed to provide an additional layer of security for Australians, who were disproportionately targeted by online fraudsters. Having Scamio available within WhatsApp streamlined the scam verification process for everyday users, reducing the time and effort required to identify potential scams.


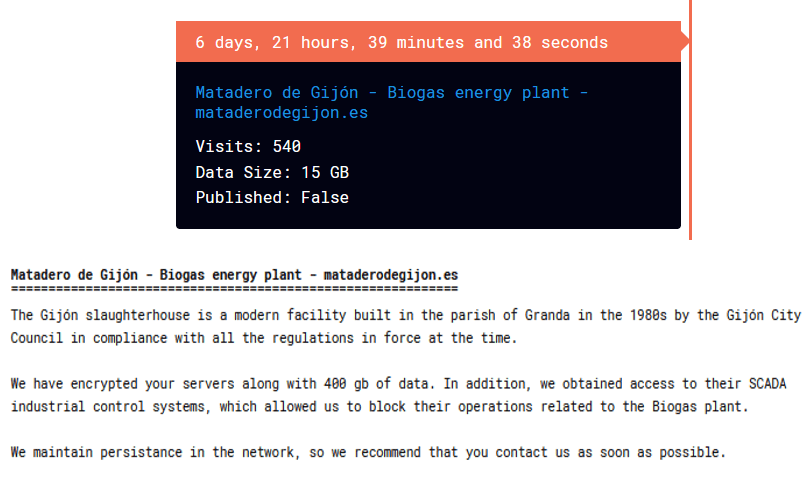 Ransomhub posts on their DLS.(Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The origins of Ransomhub trace back to February 2024 when it emerged as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) on cybercrime forums. Employing sophisticated encryption techniques and targeting organizations predominantly in the IT & ITES sector, particularly in the United States, Ransomhub quickly garnered notoriety within the underground cyber community.
[caption id="attachment_69994" align="alignnone" width="728"]
Ransomhub posts on their DLS.(Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The origins of Ransomhub trace back to February 2024 when it emerged as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) on cybercrime forums. Employing sophisticated encryption techniques and targeting organizations predominantly in the IT & ITES sector, particularly in the United States, Ransomhub quickly garnered notoriety within the underground cyber community.
[caption id="attachment_69994" align="alignnone" width="728"]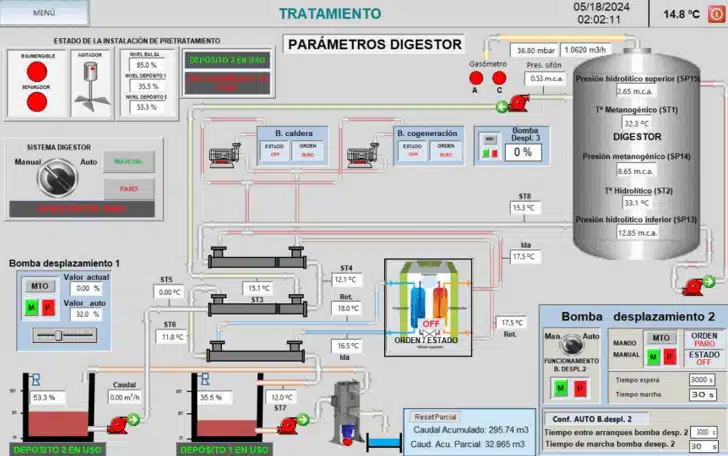 Alleged SCADA control of Gijón Bio-Energy Plant Digestor Tank (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The group's aggressive recruitment of affiliates, coupled with attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in SCADA systems, signify a strategic shift towards targeting Operational Technology (OT) environments. This shift aligns with broader trends in the ransomware landscape, wherein malicious actors seek to exploit weaknesses in interconnected systems for maximum impact.
CRIL's investigation into Ransomhub's activities reveals a concerning association with Initial Access Brokers (IABs) on Russian-language forums, indicating a sophisticated network for procuring compromised access to victims' networks. Such alliances highligh the need for heightened vigilance and proactive defense mechanisms to thwart potential breaches.
Alleged SCADA control of Gijón Bio-Energy Plant Digestor Tank (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The group's aggressive recruitment of affiliates, coupled with attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in SCADA systems, signify a strategic shift towards targeting Operational Technology (OT) environments. This shift aligns with broader trends in the ransomware landscape, wherein malicious actors seek to exploit weaknesses in interconnected systems for maximum impact.
CRIL's investigation into Ransomhub's activities reveals a concerning association with Initial Access Brokers (IABs) on Russian-language forums, indicating a sophisticated network for procuring compromised access to victims' networks. Such alliances highligh the need for heightened vigilance and proactive defense mechanisms to thwart potential breaches.





 [caption id="attachment_69815" align="alignnone" width="631"]
[caption id="attachment_69815" align="alignnone" width="631"] Source: First Nations Health Authority[/caption]
This cyber intrusion marks the latest in a string of cybersecurity incidents across British Columbia. While FNHA asserts no direct link between this attack and previous breaches, the province has been on high alert following similar incidents, including attempted ransomware attacks on B.C. libraries and a cybersecurity breach impacting the operations of a major retailer, London Drugs.
In response to the cyberattack, FNHA has mobilized a comprehensive response strategy. The authority has engaged third-party cybersecurity experts to contain and remediate the breach while conducting a thorough forensic investigation to gauge the extent of the incident. Moreover, FNHA has promptly notified law enforcement and the Office of the Information and Privacy Commissioner of British Columbia.
Acknowledging the severity of the situation, Premier David Eby highlighted earlier in the month the presence of "sophisticated cybersecurity incidents" targeting government networks. This sentiment highlights the urgent need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures across all sectors, particularly within critical infrastructure like healthcare.
Source: First Nations Health Authority[/caption]
This cyber intrusion marks the latest in a string of cybersecurity incidents across British Columbia. While FNHA asserts no direct link between this attack and previous breaches, the province has been on high alert following similar incidents, including attempted ransomware attacks on B.C. libraries and a cybersecurity breach impacting the operations of a major retailer, London Drugs.
In response to the cyberattack, FNHA has mobilized a comprehensive response strategy. The authority has engaged third-party cybersecurity experts to contain and remediate the breach while conducting a thorough forensic investigation to gauge the extent of the incident. Moreover, FNHA has promptly notified law enforcement and the Office of the Information and Privacy Commissioner of British Columbia.
Acknowledging the severity of the situation, Premier David Eby highlighted earlier in the month the presence of "sophisticated cybersecurity incidents" targeting government networks. This sentiment highlights the urgent need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures across all sectors, particularly within critical infrastructure like healthcare.






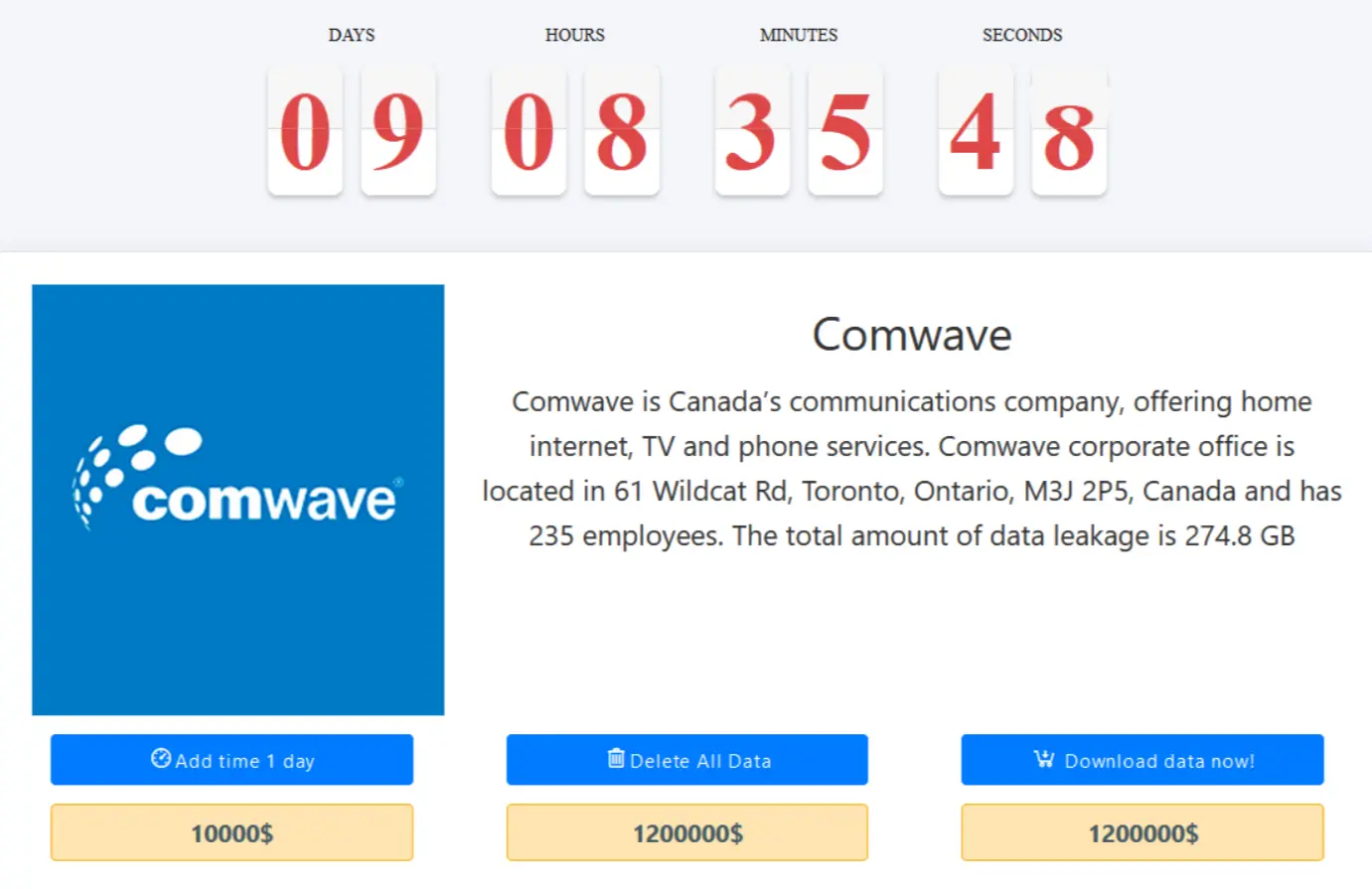 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
Among the information exfiltrated are scanned copies of various personal documents - likely belonging to its customers - such as driving licenses, birth certificates, identity cards, passports, invoices, screenshots of email correspondence, and an internal Excel database.
The Medusa ransomware group has issued a deadline, giving Comwave nine days to comply with their demands, failing which they threatened to publicly release the compromised data. The severity of the situation cannot be overstated, with implications reaching far beyond Comwave Networks Inc. itself.
As a leading player in Canada's telecommunications, the cyberattack on Comwave potentially impacts hundreds of thousands of users in 1,100 Canadian and 1,600 U.S. cities that use their services.
The Cyber Express has tried reaching out to the organization to learn more about this Comwave Networks cyberattack. However, due to communication issues, contact was not possible, leaving the claims for the Comwave Networks cyberattack unverified.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
Among the information exfiltrated are scanned copies of various personal documents - likely belonging to its customers - such as driving licenses, birth certificates, identity cards, passports, invoices, screenshots of email correspondence, and an internal Excel database.
The Medusa ransomware group has issued a deadline, giving Comwave nine days to comply with their demands, failing which they threatened to publicly release the compromised data. The severity of the situation cannot be overstated, with implications reaching far beyond Comwave Networks Inc. itself.
As a leading player in Canada's telecommunications, the cyberattack on Comwave potentially impacts hundreds of thousands of users in 1,100 Canadian and 1,600 U.S. cities that use their services.
The Cyber Express has tried reaching out to the organization to learn more about this Comwave Networks cyberattack. However, due to communication issues, contact was not possible, leaving the claims for the Comwave Networks cyberattack unverified.


 Source: Cyble[/caption]
The attack unfolds with a malicious .LNK file concealed within a ZIP archive, potentially delivered via phishing emails. Upon execution, the .LNK file triggers a PowerShell script, initiating a sequence of operations. These operations include extracting content from the .LNK file and creating three distinct files in the %temp% location: a lure PDF, encrypted data, and a custom MSBuild project.
[caption id="attachment_69295" align="alignnone" width="1024"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
The attack unfolds with a malicious .LNK file concealed within a ZIP archive, potentially delivered via phishing emails. Upon execution, the .LNK file triggers a PowerShell script, initiating a sequence of operations. These operations include extracting content from the .LNK file and creating three distinct files in the %temp% location: a lure PDF, encrypted data, and a custom MSBuild project.
[caption id="attachment_69295" align="alignnone" width="1024"] Source: Cyble[/caption]
The disguised .LNK file triggers a PowerShell script, which then opens the lure PDF while silently executing the embedded MSBuild project.
[caption id="attachment_69299" align="alignnone" width="783"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
The disguised .LNK file triggers a PowerShell script, which then opens the lure PDF while silently executing the embedded MSBuild project.
[caption id="attachment_69299" align="alignnone" width="783"] Source: Cyble[/caption]
This project file, containing encrypted content, employs the Rijndael algorithm to decrypt data, subsequently executing a final backdoor payload.
[caption id="attachment_69296" align="alignnone" width="1119"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
This project file, containing encrypted content, employs the Rijndael algorithm to decrypt data, subsequently executing a final backdoor payload.
[caption id="attachment_69296" align="alignnone" width="1119"] Source: Cyble[/caption]
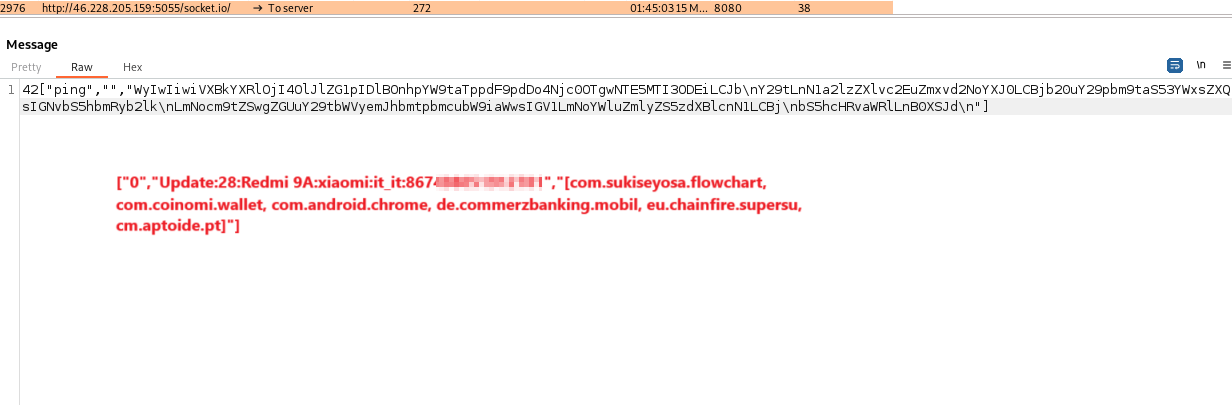
The decrypted MSBuild project file, when executed using MSBuild.exe, runs an inline task directly in memory. This task enables the backdoor to initiate various operations, including monitoring processes, executing commands, and communicating with a Command and Control (C&C) server for further instructions.
Source: Cyble[/caption]
The decrypted MSBuild project file, when executed using MSBuild.exe, runs an inline task directly in memory. This task enables the backdoor to initiate various operations, including monitoring processes, executing commands, and communicating with a Command and Control (C&C) server for further instructions.


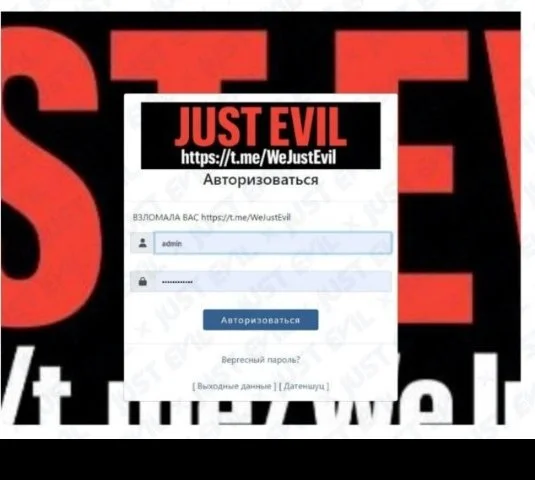 Source: X[/caption]
The Cyber Express reached out to the airport authorities for clarification on the alleged cyberattack on Hamburg Airport. However, at the time of writing this, no official statement of response has been received. This lack of response leaves the claims of a cyberattack on Hamburg Airport unverified at present.
While the airport's website appears to be functioning normally, with no visible signs of disruption, the possibility of a targeted cyberattack on the backend systems cannot be ruled out. If indeed an attack occurred, it may have been limited in scope or duration, as indicated by similar attacks in the past.
Adding to the intrigue surrounding these claims is the background of the individual behind Just Evil/Killmilk. Identified as Nikolai Serafimov, a 30-year-old Russian citizen, he is purportedly the leader of the infamous hacktivist group Killnet. Serafimov's past involvement in criminal activities, including narcotics-related offenses and a stint in a Russian prison, adds a layer of complexity to the situation.
Source: X[/caption]
The Cyber Express reached out to the airport authorities for clarification on the alleged cyberattack on Hamburg Airport. However, at the time of writing this, no official statement of response has been received. This lack of response leaves the claims of a cyberattack on Hamburg Airport unverified at present.
While the airport's website appears to be functioning normally, with no visible signs of disruption, the possibility of a targeted cyberattack on the backend systems cannot be ruled out. If indeed an attack occurred, it may have been limited in scope or duration, as indicated by similar attacks in the past.
Adding to the intrigue surrounding these claims is the background of the individual behind Just Evil/Killmilk. Identified as Nikolai Serafimov, a 30-year-old Russian citizen, he is purportedly the leader of the infamous hacktivist group Killnet. Serafimov's past involvement in criminal activities, including narcotics-related offenses and a stint in a Russian prison, adds a layer of complexity to the situation.

 Source: Cyble[/caption]
At its core, Antidot masquerades as a legitimate Google Play update application, luring unsuspecting users into its trap. Upon installation, it presents counterfeit Google Play update pages meticulously crafted in various languages, including German, French, Spanish, Russian, Portuguese, Romanian, and English. This strategic approach indicates a broad spectrum of targets, spanning multiple regions and demographics.
[caption id="attachment_68994" align="alignnone" width="1536"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
At its core, Antidot masquerades as a legitimate Google Play update application, luring unsuspecting users into its trap. Upon installation, it presents counterfeit Google Play update pages meticulously crafted in various languages, including German, French, Spanish, Russian, Portuguese, Romanian, and English. This strategic approach indicates a broad spectrum of targets, spanning multiple regions and demographics.
[caption id="attachment_68994" align="alignnone" width="1536"] Source: Cyble[/caption]
Behind its deceptive façade, Antidot operates with alarming sophistication. Leveraging overlay attacks as its primary modus operandi, the Trojan seamlessly overlays phishing pages onto legitimate applications, capturing sensitive credentials without the user's knowledge.
Additionally, Antidot integrates keylogging functionality, surreptitiously recording keystrokes to further enhance its data harvesting capabilities.
Source: Cyble[/caption]
Behind its deceptive façade, Antidot operates with alarming sophistication. Leveraging overlay attacks as its primary modus operandi, the Trojan seamlessly overlays phishing pages onto legitimate applications, capturing sensitive credentials without the user's knowledge.
Additionally, Antidot integrates keylogging functionality, surreptitiously recording keystrokes to further enhance its data harvesting capabilities.
 Source: Cyble[/caption]
Antidot maintains a stealthy line of communication with its Command and Control (C&C) server, facilitating real-time interaction for executing commands and transmitting stolen data. Through WebSocket communication, the malware establishes bidirectional connections, enabling seamless coordination between the infected devices and the malicious actors behind the scenes.
[caption id="attachment_68998" align="alignnone" width="1071"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
Antidot maintains a stealthy line of communication with its Command and Control (C&C) server, facilitating real-time interaction for executing commands and transmitting stolen data. Through WebSocket communication, the malware establishes bidirectional connections, enabling seamless coordination between the infected devices and the malicious actors behind the scenes.
[caption id="attachment_68998" align="alignnone" width="1071"] Source: Cyble[/caption]
One of Antidot's most insidious features is its implementation of VNC (Virtual Network Computing), enabling remote control of infected devices. By leveraging the MediaProjection feature, the Trojan captures and transmits display content to the C&C server, allowing attackers to remotely execute commands and manipulate device functions.
[caption id="attachment_69000" align="alignnone" width="1483"]
Source: Cyble[/caption]
One of Antidot's most insidious features is its implementation of VNC (Virtual Network Computing), enabling remote control of infected devices. By leveraging the MediaProjection feature, the Trojan captures and transmits display content to the C&C server, allowing attackers to remotely execute commands and manipulate device functions.
[caption id="attachment_69000" align="alignnone" width="1483"]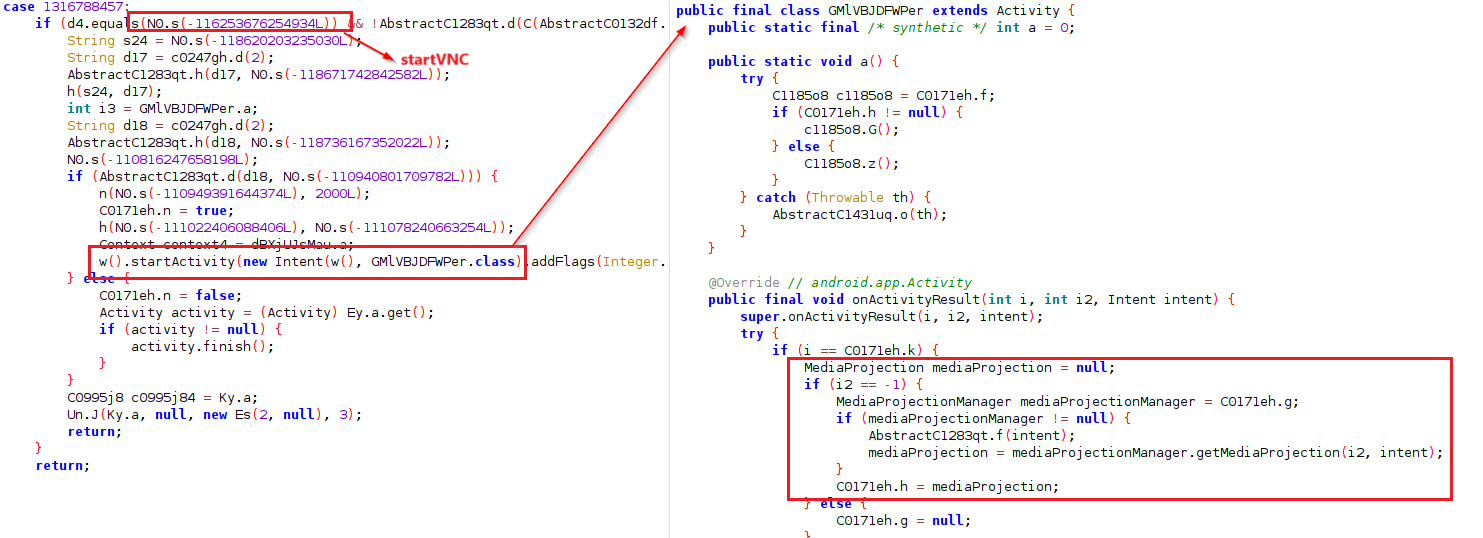 Source: Cyble[/caption]
To combat the growing threat posed by Antidot and similar Android banking trojans, cybersecurity experts from Cyble recommend adhering to essential best practices. These include downloading software from official app stores like Google Play or the iOS App Store.
Users can also utilize reputable antivirus and internet security software on all connected devices. Other precautionary methods include enforcing strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication whenever possible. Exercise caution when clicking on links received via SMS or email. Keep devices, operating systems, and applications up to date to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.
Source: Cyble[/caption]
To combat the growing threat posed by Antidot and similar Android banking trojans, cybersecurity experts from Cyble recommend adhering to essential best practices. These include downloading software from official app stores like Google Play or the iOS App Store.
Users can also utilize reputable antivirus and internet security software on all connected devices. Other precautionary methods include enforcing strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication whenever possible. Exercise caution when clicking on links received via SMS or email. Keep devices, operating systems, and applications up to date to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information. 


 Source: Chicago Fire FC[/caption]
To enroll in the Credit Monitoring services provided by Chicago Fire FC at no charge, individuals are instructed to visit https://bfs.cyberscout.com/activate and follow the provided instructions. It's essential to enroll within 90 days from the date of the notification letter to receive the monitoring services.
However, minors under 18 years of age may not be eligible for this service. During the enrollment process, individuals may need to verify personal information to confirm their identity for security purposes.
It's strongly advised to monitor accounts and credit reports regularly to detect any suspicious activity or errors. Under U.S. law, individuals are entitled to one free credit report annually from each of the three major credit reporting bureaus: TransUnion, Experian, and Equifax. These reports can be ordered at www.annualcreditreport.com or by calling 1-877-322-8228. Upon receiving the report, individuals should carefully review it for any discrepancies, unauthorized accounts, or inquiries.
Individuals also have the right to place a fraud alert on their credit file at no cost. This alert lasts for one year and requires businesses to verify the individual's identity before extending new credit. Victims of identity theft can request an extended fraud alert lasting seven years.
Alternatively, individuals can opt for a "credit freeze," which restricts access to their credit report without their explicit authorization. While this prevents unauthorized access, it may also delay or interfere with legitimate credit applications.
To request a fraud alert or credit freeze, individuals need to provide specific information to the three major credit reporting bureaus, including their full name, social security number, date of birth, address history, and proof of identity. Additionally, victims of identity theft should file a police report and notify law enforcement, their state Attorney General, and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.
Source: Chicago Fire FC[/caption]
To enroll in the Credit Monitoring services provided by Chicago Fire FC at no charge, individuals are instructed to visit https://bfs.cyberscout.com/activate and follow the provided instructions. It's essential to enroll within 90 days from the date of the notification letter to receive the monitoring services.
However, minors under 18 years of age may not be eligible for this service. During the enrollment process, individuals may need to verify personal information to confirm their identity for security purposes.
It's strongly advised to monitor accounts and credit reports regularly to detect any suspicious activity or errors. Under U.S. law, individuals are entitled to one free credit report annually from each of the three major credit reporting bureaus: TransUnion, Experian, and Equifax. These reports can be ordered at www.annualcreditreport.com or by calling 1-877-322-8228. Upon receiving the report, individuals should carefully review it for any discrepancies, unauthorized accounts, or inquiries.
Individuals also have the right to place a fraud alert on their credit file at no cost. This alert lasts for one year and requires businesses to verify the individual's identity before extending new credit. Victims of identity theft can request an extended fraud alert lasting seven years.
Alternatively, individuals can opt for a "credit freeze," which restricts access to their credit report without their explicit authorization. While this prevents unauthorized access, it may also delay or interfere with legitimate credit applications.
To request a fraud alert or credit freeze, individuals need to provide specific information to the three major credit reporting bureaus, including their full name, social security number, date of birth, address history, and proof of identity. Additionally, victims of identity theft should file a police report and notify law enforcement, their state Attorney General, and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information. 





 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alexandre Blanc is a renowned Cybersecurity dvisor, ISO/IEC 27001 and 27701 Lead Implementer, and a recognised security expert. With a track record of holding successful cybersecurity events, Blanc serves as an Independent Strategic and Security Advisor, providing invaluable counsel to various organisations. His expertise spans incident response management, digital transformations, and dark web investigations.
Recognised as a LinkedIn Top Voice in Technology and named among the top security experts with over 75k followers on LinkedIn, Blanc's insights are highly sought-after in the cybersecurity community. Through publications, speaking engagements, and advisory roles, he continues uplift the IT and security industry.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alexandre Blanc is a renowned Cybersecurity dvisor, ISO/IEC 27001 and 27701 Lead Implementer, and a recognised security expert. With a track record of holding successful cybersecurity events, Blanc serves as an Independent Strategic and Security Advisor, providing invaluable counsel to various organisations. His expertise spans incident response management, digital transformations, and dark web investigations.
Recognised as a LinkedIn Top Voice in Technology and named among the top security experts with over 75k followers on LinkedIn, Blanc's insights are highly sought-after in the cybersecurity community. Through publications, speaking engagements, and advisory roles, he continues uplift the IT and security industry.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alissa Abdullah, PhD, is a distinguished senior information technology and cybersecurity executive with a rich background spanning Fortune 100 companies, the White House, and the government intelligence community. Currently serving as Deputy Chief Security Officer for Mastercard, she brings over 20 years of experience in IT strategy, fiscal management, and leading large government programmes.
Abdullah's strategic leadership extends beyond her corporate role; she serves as a board member for organisations like Girls in Tech, Inc. and Smartsheet, while also lecturing at the University of California, Berkeley. With a PhD in Information Technology Management, and over 17k followers on LinkedIn, she is a recognised authority in cybersecurity and IT leadership.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Alissa Abdullah, PhD, is a distinguished senior information technology and cybersecurity executive with a rich background spanning Fortune 100 companies, the White House, and the government intelligence community. Currently serving as Deputy Chief Security Officer for Mastercard, she brings over 20 years of experience in IT strategy, fiscal management, and leading large government programmes.
Abdullah's strategic leadership extends beyond her corporate role; she serves as a board member for organisations like Girls in Tech, Inc. and Smartsheet, while also lecturing at the University of California, Berkeley. With a PhD in Information Technology Management, and over 17k followers on LinkedIn, she is a recognised authority in cybersecurity and IT leadership.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Jane Frankland is a prominent figure in cybersecurity with a career spanning over two decades of experience in the field. As a cybersecurity influencer and LinkedIn Top Voice, she has established herself as an award-winning leader, coach, board advisor, author, and speaker.
Frankland's expertise lies in bridging the gap between business strategy and technical cybersecurity needs, enabling smoother and more effective engagements. With a portfolio career, she works with major brands as an influencer, leadership coach, and board advisor. Additionally, Frankland is deeply involved in initiatives promoting diversity and inclusion in cybersecurity, aligning her work with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Jane Frankland is a prominent figure in cybersecurity with a career spanning over two decades of experience in the field. As a cybersecurity influencer and LinkedIn Top Voice, she has established herself as an award-winning leader, coach, board advisor, author, and speaker.
Frankland's expertise lies in bridging the gap between business strategy and technical cybersecurity needs, enabling smoother and more effective engagements. With a portfolio career, she works with major brands as an influencer, leadership coach, and board advisor. Additionally, Frankland is deeply involved in initiatives promoting diversity and inclusion in cybersecurity, aligning her work with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Mark Lynd is a globally recognised cybersecurity strategist, and keynote speaker in cybersecurity and AI. With over 25 years of experience, including four stints as a CIO & CISO for global companies, he excels in technology, cybersecurity, and AI.
Currently, he serves as the Head of Executive Advisory & Corporate Strategy at Netsync, a global technology reseller, where he concentrates on cybersecurity, AI, data center, IoT, and digital transformation. Lynd's accolades include being ranked globally for security and AI thought leadership, and he's authored acclaimed books and eBooks.
He holds a Bachelor of Science from the University of Tulsa and is a proud military veteran.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Mark Lynd is a globally recognised cybersecurity strategist, and keynote speaker in cybersecurity and AI. With over 25 years of experience, including four stints as a CIO & CISO for global companies, he excels in technology, cybersecurity, and AI.
Currently, he serves as the Head of Executive Advisory & Corporate Strategy at Netsync, a global technology reseller, where he concentrates on cybersecurity, AI, data center, IoT, and digital transformation. Lynd's accolades include being ranked globally for security and AI thought leadership, and he's authored acclaimed books and eBooks.
He holds a Bachelor of Science from the University of Tulsa and is a proud military veteran.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Naomi Buckwalter is an accomplished Information Security Leader, Nonprofit Director, Keynote Speaker, and LinkedIn Learning Instructor. With extensive experience in directing information security programmes, she has notably served as Director of Product Security at Contrast Security and Director of Information Security & IT at Beam Dental. Buckwalter's expertise encompasses compliance, risk management, and security operations.
She is also the Founder & Executive Director of the Cybersecurity Gatebreakers Foundation, aiming to revolutionise cybersecurity hiring practices. With a background in computer science and over 99K followers on LinkedIn, she is recognised for her contributions as a cybersecurity thought leader and advocate for diversity in tech.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Naomi Buckwalter is an accomplished Information Security Leader, Nonprofit Director, Keynote Speaker, and LinkedIn Learning Instructor. With extensive experience in directing information security programmes, she has notably served as Director of Product Security at Contrast Security and Director of Information Security & IT at Beam Dental. Buckwalter's expertise encompasses compliance, risk management, and security operations.
She is also the Founder & Executive Director of the Cybersecurity Gatebreakers Foundation, aiming to revolutionise cybersecurity hiring practices. With a background in computer science and over 99K followers on LinkedIn, she is recognised for her contributions as a cybersecurity thought leader and advocate for diversity in tech.
 Source: Australian Cyber Conference 2024[/caption]
Raj Samani is currently a Chief Scientist at Rapid7 and has experience in this industry spanning 20 years. He has worked with law enforcement and is also advisor to the European Cybercrime Centre. Samani is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences, a published author, and continues to make appearances in podcasts where he discusses his expertise surrounding threat intelligence, cyber defence strategies, and emerging threats.
With his following of over 15.2k followers on LinkedIn and 14.4k on Twitter, Samani is influential to his followers due to the cybersecurity related articles, updates and insights he shares, often engaging not only cybersecurity enthusiasts but also professionals.
Source: Australian Cyber Conference 2024[/caption]
Raj Samani is currently a Chief Scientist at Rapid7 and has experience in this industry spanning 20 years. He has worked with law enforcement and is also advisor to the European Cybercrime Centre. Samani is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences, a published author, and continues to make appearances in podcasts where he discusses his expertise surrounding threat intelligence, cyber defence strategies, and emerging threats.
With his following of over 15.2k followers on LinkedIn and 14.4k on Twitter, Samani is influential to his followers due to the cybersecurity related articles, updates and insights he shares, often engaging not only cybersecurity enthusiasts but also professionals.
 Source: BankInfoSecurity[/caption]
Tyler Cohen Wood is a prominent and respected figure in the cybersecurity field. Currently the co-founder of Dark Cryptonite, a Special Comms method of cybersecurity, Woods has over 20 years of experience in the intelligence community. Woods previously served as Senior Intelligence Officer at the Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA) and Cyber Branch Chief at the DIA's Science and Technology Directorate.
Woods is also a keynote speaker and provides insight into global cyber threats and national security due to her knowledge on digital privacy and national security. Woods has a following of over 27k on LinkedIn, attention she’s garnered due to her ability to share insightful commentary on cybersecurity issues which explains complex technical concepts easily for all types of audiences.
Source: BankInfoSecurity[/caption]
Tyler Cohen Wood is a prominent and respected figure in the cybersecurity field. Currently the co-founder of Dark Cryptonite, a Special Comms method of cybersecurity, Woods has over 20 years of experience in the intelligence community. Woods previously served as Senior Intelligence Officer at the Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA) and Cyber Branch Chief at the DIA's Science and Technology Directorate.
Woods is also a keynote speaker and provides insight into global cyber threats and national security due to her knowledge on digital privacy and national security. Woods has a following of over 27k on LinkedIn, attention she’s garnered due to her ability to share insightful commentary on cybersecurity issues which explains complex technical concepts easily for all types of audiences.
 Source: Experience McIntire[/caption]
Theresa Payton was the first ever female Chief Information Officer for the White House from 2006-2008, serving under George W. Bush, and is now the CEO of her company Fortalice Solutions which she founded in 2008.
Payton is best known for consulting as that is the purpose of her company, providing services like risk assessments, incident response, and digital forensics to government agencies and different industries and businesses about cybersecurity strategy and best IT practices.
Payton has over 25k followers on LinkedIn and this is due to her continuous and avid blogging exposing cybercrimes and tackling cybersecurity on her companies page.
Source: Experience McIntire[/caption]
Theresa Payton was the first ever female Chief Information Officer for the White House from 2006-2008, serving under George W. Bush, and is now the CEO of her company Fortalice Solutions which she founded in 2008.
Payton is best known for consulting as that is the purpose of her company, providing services like risk assessments, incident response, and digital forensics to government agencies and different industries and businesses about cybersecurity strategy and best IT practices.
Payton has over 25k followers on LinkedIn and this is due to her continuous and avid blogging exposing cybercrimes and tackling cybersecurity on her companies page.
 Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Bill Brenner is an experienced professional in the cybersecurity field and has ventured into many areas including journalist, editor, and community manager. His work has focused on cybersecurity education and awareness.
Brenner is currently the Vice President of Custom and Research Content Strategy at CyberRisk Alliance. Brenners 15.7k followers on Twitter come from his influence surrounding articles posted on CS Media and Techtarget which are informative and relevant to cybersecurity professionals.
Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Bill Brenner is an experienced professional in the cybersecurity field and has ventured into many areas including journalist, editor, and community manager. His work has focused on cybersecurity education and awareness.
Brenner is currently the Vice President of Custom and Research Content Strategy at CyberRisk Alliance. Brenners 15.7k followers on Twitter come from his influence surrounding articles posted on CS Media and Techtarget which are informative and relevant to cybersecurity professionals.
 Source: BH Consulting[/caption]
Brian Honan is the CEO of BH Consulting and has over 30 years of experience in cybersecurity. He was formerly a special advisor on cyber security to Europol’s Cyber Crime Centre, along with being an advisor to the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security.
Honan’s work in consultancy is not just aimed at government agencies but also multinational corporations, and small businesses. Honan advocates highly for education in the field and is a founding member of the Irish Reporting and Information Security Service (IRISS-CERT).
His following of 36.2k on Twitter can be attested to the articles and blogs he’s written and posted along with presentations at industry conferences worldwide.
Source: BH Consulting[/caption]
Brian Honan is the CEO of BH Consulting and has over 30 years of experience in cybersecurity. He was formerly a special advisor on cyber security to Europol’s Cyber Crime Centre, along with being an advisor to the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security.
Honan’s work in consultancy is not just aimed at government agencies but also multinational corporations, and small businesses. Honan advocates highly for education in the field and is a founding member of the Irish Reporting and Information Security Service (IRISS-CERT).
His following of 36.2k on Twitter can be attested to the articles and blogs he’s written and posted along with presentations at industry conferences worldwide.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Magda Chelly is the first Tunisian woman to be on the advisory board of Blackhat. She has over 10 years of experience in security architecture, risk management, and incident response. Chelly is also a published author and is also known to be a keynote speaker who can deliver her talks in five different languages.
She is currently the Managing Director at Responsible Cyber where she helps organisations implement effective cybersecurity strategies, while also being the founder of Women of Security (WoSEC) Singapore which aims to encourage women to join the field of cybersecurity.
Chelly has over 57k followers on LinkedIn due to her posts on cybersecurity, but also her diversity initiatives which make her an advocate in the field.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Magda Chelly is the first Tunisian woman to be on the advisory board of Blackhat. She has over 10 years of experience in security architecture, risk management, and incident response. Chelly is also a published author and is also known to be a keynote speaker who can deliver her talks in five different languages.
She is currently the Managing Director at Responsible Cyber where she helps organisations implement effective cybersecurity strategies, while also being the founder of Women of Security (WoSEC) Singapore which aims to encourage women to join the field of cybersecurity.
Chelly has over 57k followers on LinkedIn due to her posts on cybersecurity, but also her diversity initiatives which make her an advocate in the field.
 Source: Facebook[/caption]
Marcus J Carey is a former Navy Cryptologist who is now in cybersecurity innovation. He has worked many roles including penetration tester, security researcher, and security engineer, all of which helped to gain new and revolutionary insights into offensive and defensive cybersecurity techniques.
Carey is famous for the books he has written surrounding hackers and cybersecurity and is an established CEO of Threatcare, a cybersecurity company focused on providing proactive threat detection and risk assessment solutions.
His 52.4k Twitter followers stem from the expertise he shares on social media and his importance in educating future professionals in the field. He is also sought after for speaking in industry conferences.
Source: Facebook[/caption]
Marcus J Carey is a former Navy Cryptologist who is now in cybersecurity innovation. He has worked many roles including penetration tester, security researcher, and security engineer, all of which helped to gain new and revolutionary insights into offensive and defensive cybersecurity techniques.
Carey is famous for the books he has written surrounding hackers and cybersecurity and is an established CEO of Threatcare, a cybersecurity company focused on providing proactive threat detection and risk assessment solutions.
His 52.4k Twitter followers stem from the expertise he shares on social media and his importance in educating future professionals in the field. He is also sought after for speaking in industry conferences.
 Source: Penguin Random House[/caption]
Andy Greenberg is currently a senior writer at Wired magazine, and has written many articles investigating high-profile cyber incidents, hacking groups, and emerging cybersecurity threats.
Greenberg's reports often focus on the details of cyberattacks and looks at the broader implications for people, the government, and the industry as a whole.
His 70.4k followers on Twitter are influenced by his updates and in-depth articles exploring the world of cybersecurity, not only informing the general public but also professionals about the hazards.
Source: Penguin Random House[/caption]
Andy Greenberg is currently a senior writer at Wired magazine, and has written many articles investigating high-profile cyber incidents, hacking groups, and emerging cybersecurity threats.
Greenberg's reports often focus on the details of cyberattacks and looks at the broader implications for people, the government, and the industry as a whole.
His 70.4k followers on Twitter are influenced by his updates and in-depth articles exploring the world of cybersecurity, not only informing the general public but also professionals about the hazards.
 Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Paul Asadoorian is a professional in the cybersecurity field for over 20 years, but his following comes from his blogs and podcasts. He’s best known as the founder and host of Security Weekly where Asadoorian brings together experts and practitioners from the cybersecurity field to discuss latest news and research in the field such as network security, application security, incident response, etc.
Additionally, he is also the founder and CEO of Offensive Countermeasures, a company that helps cybersecurity professionals enhance their skills and stay ahead of evolving threats. His 77.3k followers on Twitter are mostly due to his large social media presence as a podcaster and his posts surrounding resources , opinions, and promotion of Security Weekly.
Source: SC Magazine[/caption]
Paul Asadoorian is a professional in the cybersecurity field for over 20 years, but his following comes from his blogs and podcasts. He’s best known as the founder and host of Security Weekly where Asadoorian brings together experts and practitioners from the cybersecurity field to discuss latest news and research in the field such as network security, application security, incident response, etc.
Additionally, he is also the founder and CEO of Offensive Countermeasures, a company that helps cybersecurity professionals enhance their skills and stay ahead of evolving threats. His 77.3k followers on Twitter are mostly due to his large social media presence as a podcaster and his posts surrounding resources , opinions, and promotion of Security Weekly.
 Source:[/caption]
Nicole Perlroth is a Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist who covers cybersecurity and digital espionage for The New York Times. She is regarded for her intensive reporting on cyber threats, hacking incidents, and the intersection of technology and national security.
Perlroth has also written a book on the cyberweapons arms race. With 91.5k followers on Twitter, Perlroth shares her own articles, as well as insights and updates related to cybersecurity and technology which creates engagement for her from both cybersecurity professionals and general readers interested in security.
Source:[/caption]
Nicole Perlroth is a Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist who covers cybersecurity and digital espionage for The New York Times. She is regarded for her intensive reporting on cyber threats, hacking incidents, and the intersection of technology and national security.
Perlroth has also written a book on the cyberweapons arms race. With 91.5k followers on Twitter, Perlroth shares her own articles, as well as insights and updates related to cybersecurity and technology which creates engagement for her from both cybersecurity professionals and general readers interested in security.
 Source: Smashing Security[/caption]
Graham Cluley is an author and blogger who has written books on cybersecurity and continues to be avid in sharing news and stories on cybersecurity through the written word and speech. Currently, Graham Cluley is an independent cybersecurity analyst, writer, and public speaker.
He also runs a podcast where he discusses internet threats and safety in an entertaining, engaging and informative way. Cluley’s 112.9k Twitter followers are updated with his podcast, tweets and YouTube videos which explain cybersecurity topics and how to tackle them in a way patented to the general users of the internet.
Source: Smashing Security[/caption]
Graham Cluley is an author and blogger who has written books on cybersecurity and continues to be avid in sharing news and stories on cybersecurity through the written word and speech. Currently, Graham Cluley is an independent cybersecurity analyst, writer, and public speaker.
He also runs a podcast where he discusses internet threats and safety in an entertaining, engaging and informative way. Cluley’s 112.9k Twitter followers are updated with his podcast, tweets and YouTube videos which explain cybersecurity topics and how to tackle them in a way patented to the general users of the internet.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Rachel Tobac is an ethical hacker who helps companies keep safe through her work as CEO of SocialProof Security, which she co-founded. The company focuses on educating employees to recognize and deal with cyberattacks. She has a background in behavioural psychology and uses it to improve cybersecurity awareness and defences in the general public.
Tobac also works with the non-profit Women in Security and Privacy (WISP) where she helps women advance in the security field and often speaks for underrepresented groups to pursue a career in cybersecurity. Tobac’s 106k strong following on Twitter is due to her activism and due to the tips and updates she shares related to the industry, with some posts being popular for starting debates amongst professionals.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Rachel Tobac is an ethical hacker who helps companies keep safe through her work as CEO of SocialProof Security, which she co-founded. The company focuses on educating employees to recognize and deal with cyberattacks. She has a background in behavioural psychology and uses it to improve cybersecurity awareness and defences in the general public.
Tobac also works with the non-profit Women in Security and Privacy (WISP) where she helps women advance in the security field and often speaks for underrepresented groups to pursue a career in cybersecurity. Tobac’s 106k strong following on Twitter is due to her activism and due to the tips and updates she shares related to the industry, with some posts being popular for starting debates amongst professionals.
 Source: SANS Cyber Security Certifications & Research[/caption]
Katie Moussouris is the Founder of Luta Security which encompasses her aims surrounding vulnerability disclosure and safer and responsible research in security. She is a leading figure in both the aspects and has 20 years of experience on the field. Some of Moussouris’s leading work is the Microsoft's bug bounty programme, which she developed and was one of the first-of-its-kind in the industry.
She also advocates for vulnerability disclosure, which merits more transparency between security researchers and organisations. Moussouris’s 115.5k followers come from her revolutionary developments. She is a frequent speaker at cybersecurity conferences and events. She often posts and talks about her advocacy for ethical hacking and responsible security practices along with her expertise on vulnerability disclosure and bug bounty programmes.
Source: SANS Cyber Security Certifications & Research[/caption]
Katie Moussouris is the Founder of Luta Security which encompasses her aims surrounding vulnerability disclosure and safer and responsible research in security. She is a leading figure in both the aspects and has 20 years of experience on the field. Some of Moussouris’s leading work is the Microsoft's bug bounty programme, which she developed and was one of the first-of-its-kind in the industry.
She also advocates for vulnerability disclosure, which merits more transparency between security researchers and organisations. Moussouris’s 115.5k followers come from her revolutionary developments. She is a frequent speaker at cybersecurity conferences and events. She often posts and talks about her advocacy for ethical hacking and responsible security practices along with her expertise on vulnerability disclosure and bug bounty programmes.
 Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Brooks is the president of his consulting company where he advises clients on cybersecurity strategy, risk assessment, and business development. Along with that, he is a featured author in many technology and cybersecurity blogs.
Brooks has previously worked in advisory roles with corporations and also at government agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security and the Defence Intelligence Agency.
Brooks’ 116k LinkedIn followers are due to his regular contributions to industry research and news, media articles. Along with that, he is a popular keynote speaker who shares his expertise on a wide range of cybersecurity topics.
Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Brooks is the president of his consulting company where he advises clients on cybersecurity strategy, risk assessment, and business development. Along with that, he is a featured author in many technology and cybersecurity blogs.
Brooks has previously worked in advisory roles with corporations and also at government agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security and the Defence Intelligence Agency.
Brooks’ 116k LinkedIn followers are due to his regular contributions to industry research and news, media articles. Along with that, he is a popular keynote speaker who shares his expertise on a wide range of cybersecurity topics.
 Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Miessler is the founder and CEO of Unsupervised Learning where he writes informative articles and tackles relevant issues surrounding cybersecurity and what the world after AI means for human beings.
Miesslers following of 139.4k on Twitter comes from professionals in the field and novice enthusiasts engaging with his content and discussions due to his experience in the field. He also avidly shares articles, podcasts, bringing his audience up to speed with cybersecurity.
Source: The Official Cybersecurity Summit[/caption]
Miessler is the founder and CEO of Unsupervised Learning where he writes informative articles and tackles relevant issues surrounding cybersecurity and what the world after AI means for human beings.
Miesslers following of 139.4k on Twitter comes from professionals in the field and novice enthusiasts engaging with his content and discussions due to his experience in the field. He also avidly shares articles, podcasts, bringing his audience up to speed with cybersecurity.
 Source: iTWire[/caption]
Kevin Beaumont is an experienced professional who has worked in various cybersecurity roles, including security engineer and consultant. He also specialises in threat detection and incident response. Kevin is now the Head of Cybersecurity Operations at Arcadia Ltd. along with being a cybersecurity researcher who runs his own platform where he discusses cybersecurity.
Beaumont appeals to newer, younger cybersecurity enthusiasts with around 150.9k followers on Twitter due to his engagement with trolling on the internet. Additionally, he writes articles for Medium where he informs about cybercrime issues such as Microsoft Windows vulnerability.
Source: iTWire[/caption]
Kevin Beaumont is an experienced professional who has worked in various cybersecurity roles, including security engineer and consultant. He also specialises in threat detection and incident response. Kevin is now the Head of Cybersecurity Operations at Arcadia Ltd. along with being a cybersecurity researcher who runs his own platform where he discusses cybersecurity.
Beaumont appeals to newer, younger cybersecurity enthusiasts with around 150.9k followers on Twitter due to his engagement with trolling on the internet. Additionally, he writes articles for Medium where he informs about cybercrime issues such as Microsoft Windows vulnerability.
 Source: hacks4pancakes[/caption]
Lesley Carhart is currently a threat analyst and principal responder at Dragos, a company which works to protect industrial control systems from cyber threats, and has experience as a security analyst, incident responder and threat hunter.
Her work in both the public and private sectors allowed her to gain valuable insights into cybersecurity issues across different industries. Her following of 168k comes from her works such as blogger and speaker who offers career advice in the field of cybersecurity. She also speaks about topics such as industrial control, ransomware attacks and more.
Source: hacks4pancakes[/caption]
Lesley Carhart is currently a threat analyst and principal responder at Dragos, a company which works to protect industrial control systems from cyber threats, and has experience as a security analyst, incident responder and threat hunter.
Her work in both the public and private sectors allowed her to gain valuable insights into cybersecurity issues across different industries. Her following of 168k comes from her works such as blogger and speaker who offers career advice in the field of cybersecurity. She also speaks about topics such as industrial control, ransomware attacks and more.
 Source: Wikipedia[/caption]
Schneier is a specialist in computer security and privacy along with being a cryptographer. Schneier is regarded as one of the most influential people in his field of cryptography and has written numerous books on cybersecurity, some of which are considered seminal works in the field.
He has also written articles about security and privacy for magazines such as Wired. Schneier’s following of 147.1k comes from being acknowledged as impactful in his field but also due to his blog where he addresses the prevalence of hacking and other cyber dangers intersecting with our everyday lives.
Source: Wikipedia[/caption]
Schneier is a specialist in computer security and privacy along with being a cryptographer. Schneier is regarded as one of the most influential people in his field of cryptography and has written numerous books on cybersecurity, some of which are considered seminal works in the field.
He has also written articles about security and privacy for magazines such as Wired. Schneier’s following of 147.1k comes from being acknowledged as impactful in his field but also due to his blog where he addresses the prevalence of hacking and other cyber dangers intersecting with our everyday lives.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eugene Kaspersky is an individual most impactful in the cybersecurity, best known as the CEO of Kaspersky Lab, a company he co-founded in 1997 which identified government-sponsored cyberwarfare. Kaspersky’s following of 187.5k comes from how Kaspersky Lab has grown into a global cybersecurity powerhouse, offering a wide range of products and services, along with his advocacy for cybersecurity education.
Kaspersky is also a keynote speaker on emerging threats, and the importance of cybersecurity awareness at industry conferences and events. Furthermore, he writes a blog where he regularly posts updates about his life in the industry.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eugene Kaspersky is an individual most impactful in the cybersecurity, best known as the CEO of Kaspersky Lab, a company he co-founded in 1997 which identified government-sponsored cyberwarfare. Kaspersky’s following of 187.5k comes from how Kaspersky Lab has grown into a global cybersecurity powerhouse, offering a wide range of products and services, along with his advocacy for cybersecurity education.
Kaspersky is also a keynote speaker on emerging threats, and the importance of cybersecurity awareness at industry conferences and events. Furthermore, he writes a blog where he regularly posts updates about his life in the industry.
 Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eric Geller is a freelance cybersecurity journalist recognised for his insightful coverage of digital security. With a comprehensive portfolio including esteemed publications like WIRED, Politico, and The Daily Dot, Geller offers in-depth analysis on cyber policy, encryption, and data breaches.
His investigative reporting touches the intricate intersections of cybersecurity and everyday life, from election security to critical infrastructure protection. Geller's expertise extends to interviews with top officials and breaking news on government initiatives. With a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science from Kenyon College, Geller's accolades include induction into the Pi Sigma Alpha national political science Honors society.
Source: LinkedIn[/caption]
Eric Geller is a freelance cybersecurity journalist recognised for his insightful coverage of digital security. With a comprehensive portfolio including esteemed publications like WIRED, Politico, and The Daily Dot, Geller offers in-depth analysis on cyber policy, encryption, and data breaches.
His investigative reporting touches the intricate intersections of cybersecurity and everyday life, from election security to critical infrastructure protection. Geller's expertise extends to interviews with top officials and breaking news on government initiatives. With a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science from Kenyon College, Geller's accolades include induction into the Pi Sigma Alpha national political science Honors society.
 Source: The Futurum Group[/caption]
Shira Rubinoff is a cybersecurity and blockchain advisor as well as being a popular keynote speaker and author. She is the President of SecureMySocial, a cybersecurity company that focuses on protecting organizations from social media risks such as data leakage, reputational damage, and insider threats. Her videos are many and impactful, consisting of interviews and conversations with other professionals.
She is known to be one of the top businesswomen in the field and currently runs a cybersecurity consulting firm and serves as the Chair of the Women in Cybersecurity Council (WCI), aiming to influence more women to join the field. Her follower count of 190.4k isn’t only due to her experience as a businesswoman, but also her constant interaction on social media as she posts talks, videos, podcasts, written work and more about many topics in cybersecurity.
Source: The Futurum Group[/caption]
Shira Rubinoff is a cybersecurity and blockchain advisor as well as being a popular keynote speaker and author. She is the President of SecureMySocial, a cybersecurity company that focuses on protecting organizations from social media risks such as data leakage, reputational damage, and insider threats. Her videos are many and impactful, consisting of interviews and conversations with other professionals.
She is known to be one of the top businesswomen in the field and currently runs a cybersecurity consulting firm and serves as the Chair of the Women in Cybersecurity Council (WCI), aiming to influence more women to join the field. Her follower count of 190.4k isn’t only due to her experience as a businesswoman, but also her constant interaction on social media as she posts talks, videos, podcasts, written work and more about many topics in cybersecurity.
 Source: WithSecure[/caption]
Miko Hyppönen has been in the world of cybersecurity since the late 1980s. Since then he has led researchers in identifying and eliminating emerging cyber threats, while providing insights and solutions to protect individuals, businesses, and governments from cybercrime.
Hyppönen has written for many famous newspapers like the New York Times and has also appeared on international TV and lectured at universities like Oxford and Cambridge. His 230.5k followers is due to his engaging and informative presentations, which help raise awareness about cybersecurity threats.
He also has a following for his blog posts and research papers detailing his expertise.
Source: WithSecure[/caption]
Miko Hyppönen has been in the world of cybersecurity since the late 1980s. Since then he has led researchers in identifying and eliminating emerging cyber threats, while providing insights and solutions to protect individuals, businesses, and governments from cybercrime.
Hyppönen has written for many famous newspapers like the New York Times and has also appeared on international TV and lectured at universities like Oxford and Cambridge. His 230.5k followers is due to his engaging and informative presentations, which help raise awareness about cybersecurity threats.
He also has a following for his blog posts and research papers detailing his expertise.
 Source: IMDb[/caption]
Kim Zetter is an award-winning investigative journalist renowned for her expertise in cybersecurity and national security. With a distinguished career spanning publications like WIRED, Politico, and The New York Times Magazine, Zetter is a respected authority on topics ranging from election security to cyber warfare.
Her book, "Countdown to Zero Day: Stuxnet and the Launch of the World's First Digital Weapon," offers a gripping narrative of covert cyber operations. As a sought-after speaker and social media personality with over 7K followers on LinkedIn, she shares insights at conferences worldwide. Zetter's relentless pursuit of truth has earned her acclaim and established her as a leading voice in the cybersecurity journalism.
Source: IMDb[/caption]
Kim Zetter is an award-winning investigative journalist renowned for her expertise in cybersecurity and national security. With a distinguished career spanning publications like WIRED, Politico, and The New York Times Magazine, Zetter is a respected authority on topics ranging from election security to cyber warfare.
Her book, "Countdown to Zero Day: Stuxnet and the Launch of the World's First Digital Weapon," offers a gripping narrative of covert cyber operations. As a sought-after speaker and social media personality with over 7K followers on LinkedIn, she shares insights at conferences worldwide. Zetter's relentless pursuit of truth has earned her acclaim and established her as a leading voice in the cybersecurity journalism.
 Source: Keppler Speakers[/caption]
Brian Krebs is an investigative journalist who wrote for The Washington post from 1995 to 2009 for the security fix blog. He now runs his own blog, Krebs on Security. In it, he provides in-depth analysis and reports, along with promptly posted breaking news on cybercrime, hacking, data breaches, etc.
Krebs has received many awards for his investigative journalism, including the Pulitzer Prize finalist for his coverage of cybersecurity problems. Krebs’ 347.9k are due to the reputation his blog widely holds for being a first choice when looking for accurate, fast information, as well as the truth as he’s known to hold individuals and organisations accountable for in his work.
Source: Keppler Speakers[/caption]
Brian Krebs is an investigative journalist who wrote for The Washington post from 1995 to 2009 for the security fix blog. He now runs his own blog, Krebs on Security. In it, he provides in-depth analysis and reports, along with promptly posted breaking news on cybercrime, hacking, data breaches, etc.
Krebs has received many awards for his investigative journalism, including the Pulitzer Prize finalist for his coverage of cybersecurity problems. Krebs’ 347.9k are due to the reputation his blog widely holds for being a first choice when looking for accurate, fast information, as well as the truth as he’s known to hold individuals and organisations accountable for in his work.
 Source: Cyderes[/caption]
Herjavec is the CEO of the Herjavec Group and the Global Cybersecurity Firm, Cyderes, which leads cybersecurity options and supports many security services including threat detection and response, identity and access management, and compliance solutions. Along with that, he features on BBC’s Shark Tank and also provides motivational business advice through his books and videos.
His following of 2.2 million may be due to his appearance on the show, but he continues to actively post insights and gives commentary on cybersecurity trends and ever-changing threats. Most of his followers are there to witness what he shares on business and entrepreneurship. Herjavec frequently shares cybersecurity related articles and updates.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.
Source: Cyderes[/caption]
Herjavec is the CEO of the Herjavec Group and the Global Cybersecurity Firm, Cyderes, which leads cybersecurity options and supports many security services including threat detection and response, identity and access management, and compliance solutions. Along with that, he features on BBC’s Shark Tank and also provides motivational business advice through his books and videos.
His following of 2.2 million may be due to his appearance on the show, but he continues to actively post insights and gives commentary on cybersecurity trends and ever-changing threats. Most of his followers are there to witness what he shares on business and entrepreneurship. Herjavec frequently shares cybersecurity related articles and updates.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information. 
 Source: X[/caption]
Interestingly, both victims' websites remain operational, showing no immediate signs of the cyberattacks. This discrepancy adds another layer of mystery to the unfolding situation.
Moreover, along with the cyberattack post, the DragonForce ransomware group stated that it had access to 15.34 GB of data associated with Malone & Co. The hacker group has shared a deadline of 16 days before the data gets published.
[caption id="attachment_68490" align="alignnone" width="353"]
Source: X[/caption]
Interestingly, both victims' websites remain operational, showing no immediate signs of the cyberattacks. This discrepancy adds another layer of mystery to the unfolding situation.
Moreover, along with the cyberattack post, the DragonForce ransomware group stated that it had access to 15.34 GB of data associated with Malone & Co. The hacker group has shared a deadline of 16 days before the data gets published.
[caption id="attachment_68490" align="alignnone" width="353"] Source: X[/caption]
As for the second alleged victim, Watt Carmicheal, the hacker group claims access to 27.3 GB of data, and no ransom deadline was shared. The threat actor, DragonForce, has used the same modus operandi to target similar victims in the past.
Source: X[/caption]
As for the second alleged victim, Watt Carmicheal, the hacker group claims access to 27.3 GB of data, and no ransom deadline was shared. The threat actor, DragonForce, has used the same modus operandi to target similar victims in the past.



 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
As proof of their claims, the threat actor shared sample records showcasing live GPS vehicle information sorted by country and offered the compromised database for sale at a staggering price of USD 5,000.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
As proof of their claims, the threat actor shared sample records showcasing live GPS vehicle information sorted by country and offered the compromised database for sale at a staggering price of USD 5,000.


 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The discrepancies didn't end there. The Cyber Express further analyzed the claims and found inconsistencies within the data itself. Specifically, discrepancies between names and associated phone numbers raised red flags. Given qpwomsx's brief tenure on the platform and apparent credibility issues, discerning the authenticity of the Meesho data breach becomes a daunting task.
However, examining the stolen data paints a perplexing situation as the majority of the email addresses are valid and deliverable. Along with the emails, the data appears to be a compilation of personal information belonging to individuals, predominantly based in India.
Alongside names, email addresses, and phone numbers, additional details such as location and workplace affiliations were also included. However, the presence of "null" values suggests potential gaps or inaccuracies within the dataset.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The discrepancies didn't end there. The Cyber Express further analyzed the claims and found inconsistencies within the data itself. Specifically, discrepancies between names and associated phone numbers raised red flags. Given qpwomsx's brief tenure on the platform and apparent credibility issues, discerning the authenticity of the Meesho data breach becomes a daunting task.
However, examining the stolen data paints a perplexing situation as the majority of the email addresses are valid and deliverable. Along with the emails, the data appears to be a compilation of personal information belonging to individuals, predominantly based in India.
Alongside names, email addresses, and phone numbers, additional details such as location and workplace affiliations were also included. However, the presence of "null" values suggests potential gaps or inaccuracies within the dataset.