The Cyber Express Weekly Roundup: Escalating Breaches, Regulatory Crackdowns, and Global Cybercrime Developments



const OPENAI_API_KEY = "sk-proj-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"; const OPENAI_API_KEY = "sk-svcacct-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX";The sk-proj- prefix typically denotes a project-scoped key tied to a specific environment and billing configuration. The sk-svcacct- prefix generally represents a service-account key intended for backend automation or system-level integration. Despite their differing scopes, both function as privileged authentication tokens granting direct access to AI inference services and billing resources. Embedding these keys in client-side JavaScript fully exposes them. Attackers do not need to breach infrastructure or exploit software vulnerabilities; they simply harvest what is publicly available.
 Cyble Vision indicates API key exposure leak (Source: Cyble Vision)[/caption]
Unlike traditional cloud infrastructure, AI API activity is often not integrated into centralized logging systems, SIEM platforms, or anomaly detection pipelines. As a result, abuse can persist undetected until billing spikes, quota exhaustion, or degraded service performance reveal the compromise.
Kaustubh Medhe, CPO at Cyble, warned: “Hard-coding LLM API keys risks turning innovation into liability, as attackers can drain AI budgets, poison workflows, and access sensitive prompts and outputs. Enterprises must manage secrets and monitor exposure across code and pipelines to prevent misconfigurations from becoming financial, privacy, or compliance issues.”
Cyble Vision indicates API key exposure leak (Source: Cyble Vision)[/caption]
Unlike traditional cloud infrastructure, AI API activity is often not integrated into centralized logging systems, SIEM platforms, or anomaly detection pipelines. As a result, abuse can persist undetected until billing spikes, quota exhaustion, or degraded service performance reveal the compromise.
Kaustubh Medhe, CPO at Cyble, warned: “Hard-coding LLM API keys risks turning innovation into liability, as attackers can drain AI budgets, poison workflows, and access sensitive prompts and outputs. Enterprises must manage secrets and monitor exposure across code and pipelines to prevent misconfigurations from becoming financial, privacy, or compliance issues.” As it is said, the ‘why’ and ‘how’ is much important than ‘should’. It’s exactly applicable in today’s cyberspace. Every day, organizations survive in an unpredictable cyber-risk climate. If your defense storehouse comprises just fragmented tools and manual processes, you are not playing it safe. If you are ‘not safe’, you are just seconds away […]
The post How AutoSecT VMDR Tool Simplifies Vulnerability Management appeared first on Kratikal Blogs.
The post How AutoSecT VMDR Tool Simplifies Vulnerability Management appeared first on Security Boulevard.


Darktrace researchers caught a sample of malware that was created by AI and LLMs to exploit the high-profiled React2Shell vulnerability, putting defenders on notice that the technology lets even lesser-skilled hackers create malicious code and build complex exploit frameworks.
The post Hackers Use LLM to Create React2Shell Malware, the Latest Example of AI-Generated Threat appeared first on Security Boulevard.
In this post we explore the data-driven shrinkage of the Time to Exploit (TTE) window from 745 days to just 44, and examine why N-day vulnerabilities have become the "turn-key" weapon of choice for modern threat actors.
The post N-Day Vulnerability Trends: The Shrinking Window of Exposure and the Rise of “Turn-Key” Exploitation appeared first on Flashpoint.
The post N-Day Vulnerability Trends: The Shrinking Window of Exposure and the Rise of “Turn-Key” Exploitation appeared first on Security Boulevard.


This article examines the widespread collection of personal data and the legal challenges individuals face from third-party subpoenas. It discusses key court rulings on government access to personal information and highlights the complexities of data privacy in the digital age.
The post How the Supreme Court’s “Third Party” Subpoena Doctrine Empowers Governments to Seize Sensitive Information Without Your Knowledge appeared first on Security Boulevard.








The BreachForums marketplace has suffered a leak, exposing the identities of nearly 324,000 cybercriminals. This incident highlights a critical shift in cyberattacks, creating opportunities for law enforcement while demonstrating the risks associated with breaches in the cybercriminal ecosystem.
The post BreachForums Breach Exposes Names of 324K Cybercriminals, Upends the Threat Intel Game appeared first on Security Boulevard.

Ukraine's cyber defenders warn Russian hackers weaponized a Microsoft zero-day within 24 hours of public disclosure, targeting government agencies with malicious documents delivering Covenant framework backdoors.
Russian state-sponsored hacking group APT28 used a critical Microsoft Office zero-day vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-21509, in less than a day after the vendor publicly disclosed the flaw, launching targeted attacks against Ukrainian government agencies and European Union institutions.
Ukraine's Computer Emergency Response Team detected exploitation attempts that began on January 27—just one day after Microsoft published details about CVE-2026-21509.
Microsoft had acknowledged active exploitation when it disclosed the flaw on January 26, but details pertaining to the threat actors were withheld and it is still unclear if it is the same or some other exploitation campaign that the vendor meant. However, the speed at which APT28 deployed customized attacks shows the narrow window defenders have to patch critical vulnerabilities.

CERT-UA discovered a malicious DOC file titled "Consultation_Topics_Ukraine(Final).doc" containing the CVE-2026-21509 exploit on January 29. Metadata revealed attackers created the document on January 27 at 07:43 UTC. The file masqueraded as materials related to Committee of Permanent Representatives to the European Union consultations on Ukraine's situation.
[caption id="attachment_109153" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Word file laced with malware (Source: CERT-UA)[/caption]
Word file laced with malware (Source: CERT-UA)[/caption]
On the same day, attackers impersonated Ukraine's Ukrhydrometeorological Center, distributing emails with an attached DOC file named "BULLETEN_H.doc" to more than 60 email addresses. Recipients primarily included Ukrainian central executive government agencies, representing a coordinated campaign against critical government infrastructure.
The attack chain begins when victims open malicious documents using Microsoft Office. The exploit establishes network connections to external resources using the WebDAV protocol—a file sharing protocol that extends HTTP to enable collaborative editing. The connection downloads a shortcut file containing program code designed to retrieve and execute additional malicious payloads.
[caption id="attachment_109150" align="aligncenter" width="600"]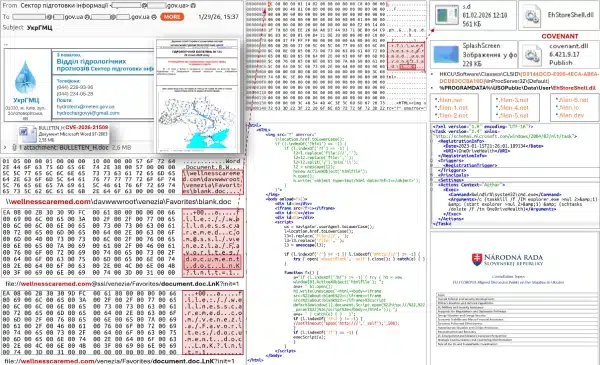 Exploit chain. (Source CERT-UA)[/caption]
Exploit chain. (Source CERT-UA)[/caption]
Successful execution creates a DLL file "EhStoreShell.dll" disguised as a legitimate "Enhanced Storage Shell Extension" library, along with an image file "SplashScreen.png" containing shellcode. Attackers implement COM hijacking by modifying Windows registry values for a specific CLSID identifier, a technique that allows malicious code to execute when legitimate Windows components load.
The malware creates a scheduled task named "OneDriveHealth" that executes periodically. When triggered, the task terminates and relaunches the Windows Explorer process. Because of the COM hijacking modification, Explorer automatically loads the malicious EhStoreShell.dll file, which then executes shellcode from the image file to deploy the Covenant framework on compromised systems.
Covenant is a post-exploitation framework similar to Cobalt Strike that provides attackers persistent command-and-control access. In this campaign, APT28 configured Covenant to use Filen.io, a legitimate cloud storage service, as command-and-control infrastructure. This technique, called living-off-the-land, makes malicious traffic appear legitimate and harder to detect.
CERT-UA discovered three additional malicious documents using similar exploits in late January 2026. Analysis of embedded URL structures and other technical indicators revealed these documents targeted organizations in EU countries. In one case, attackers registered a domain name on January 30, 2026—the same day they deployed it in attacks—demonstrating the operation's speed and agility.
"It is obvious that in the near future, including due to the inertia of the process or impossibility of users updating the Microsoft Office suite and/or using recommended protection mechanisms, the number of cyberattacks using the described vulnerability will begin to increase," CERT-UA warned in its advisory.
Microsoft released an emergency fix for CVE-2026-21509, but many organizations struggle to rapidly deploy patches across enterprise environments. The vulnerability affects multiple Microsoft Office products, creating a broad attack surface that threat actors will continue exploiting as long as unpatched systems remain accessible.
CERT-UA attributes the campaign to UAC-0001, the agency's designation for APT28, also known as Fancy Bear or Forest Blizzard. The group operates on behalf of Russia's GRU military intelligence agency and has conducted extensive operations targeting Ukraine since Russia's 2022 invasion. APT28 previously exploited Microsoft vulnerabilities within hours of disclosure, demonstrating consistent capability to rapidly weaponize newly discovered flaws.
CERT-UA recommends organizations immediately implement mitigation measures outlined in Microsoft's advisory, particularly Windows registry modifications that prevent exploitation. The agency specifically urges blocking or monitoring network connections to Filen cloud storage infrastructure, providing lists of domain names and IP addresses in its indicators of compromise section.

A “scary” vulnerability in Broadcom Wi-Fi chipsets could lead to long-term instability and affect how an organization operates.
The post Flaw in Broadcom Wi-Fi Chipsets Illuminates Importance of Wireless Dependability and Business Continuity appeared first on Security Boulevard.
From an Anthropic blog post:
In a recent evaluation of AI models’ cyber capabilities, current Claude models can now succeed at multistage attacks on networks with dozens of hosts using only standard, open-source tools, instead of the custom tools needed by previous generations. This illustrates how barriers to the use of AI in relatively autonomous cyber workflows are rapidly coming down, and highlights the importance of security fundamentals like promptly patching known vulnerabilities.
[…]
A notable development during the testing of Claude Sonnet 4.5 is that the model can now succeed on a minority of the networks without the custom cyber toolkit needed by previous generations. In particular, Sonnet 4.5 can now exfiltrate all of the (simulated) personal information in a high-fidelity simulation of the Equifax data breach—one of the costliest cyber attacks in historyusing only a Bash shell on a widely-available Kali Linux host (standard, open-source tools for penetration testing; not a custom toolkit). Sonnet 4.5 accomplishes this by instantly recognizing a publicized CVE and writing code to exploit it without needing to look it up or iterate on it. Recalling that the original Equifax breach happened by exploiting a publicized CVE that had not yet been patched, the prospect of highly competent and fast AI agents leveraging this approach underscores the pressing need for security best practices like prompt updates and patches.
AI models are getting better at this faster than I expected. This will be a major power shift in cybersecurity.
From an Anthropic blog post:
In a recent evaluation of AI models’ cyber capabilities, current Claude models can now succeed at multistage attacks on networks with dozens of hosts using only standard, open-source tools, instead of the custom tools needed by previous generations. This illustrates how barriers to the use of AI in relatively autonomous cyber workflows are rapidly coming down, and highlights the importance of security fundamentals like promptly patching known vulnerabilities.
[…]
A notable development during the testing of Claude Sonnet 4.5 is that the model can now succeed on a minority of the networks without the custom cyber toolkit needed by previous generations. In particular, Sonnet 4.5 can now exfiltrate all of the (simulated) personal information in a high-fidelity simulation of the Equifax data breach—one of the costliest cyber attacks in historyusing only a Bash shell on a widely-available Kali Linux host (standard, open-source tools for penetration testing; not a custom toolkit). Sonnet 4.5 accomplishes this by instantly recognizing a publicized CVE and writing code to exploit it without needing to look it up or iterate on it. Recalling that the original Equifax breach happened by exploiting a publicized CVE that had not yet been patched, the prospect of highly competent and fast AI agents leveraging this approach underscores the pressing need for security best practices like prompt updates and patches...
The post AIs Are Getting Better at Finding and Exploiting Security Vulnerabilities appeared first on Security Boulevard.


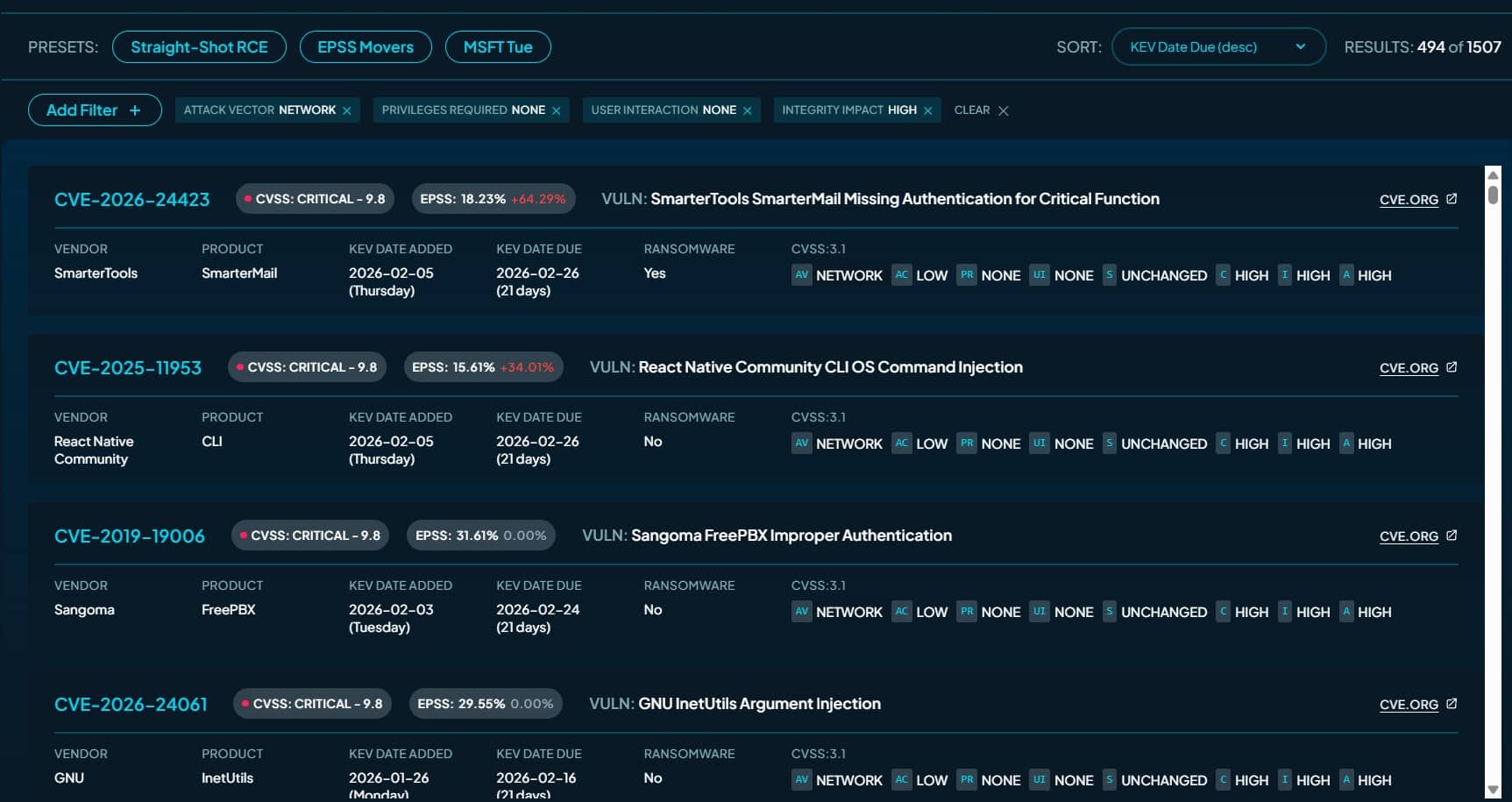
Ivanti released emergency patches for two critical zero-day vulnerabilities in Endpoint Manager Mobile after discovering attackers exploited the flaws to compromise customer systems. The company confirmed a limited number of organizations fell victim to attacks leveraging CVE-2026-1281, which CISA added to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog with a February 1 remediation deadline for federal agencies.
Both CVE-2026-1281 and CVE-2026-1340 are code injection flaws affecting EPMM's In-House Application Distribution and Android File Transfer Configuration features. Rated critical with CVSS scores of 9.8, the vulnerabilities allow unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable on-premises EPMM installations without any prior authentication.
"We are aware of a very limited number of customers whose solution has been exploited at the time of disclosure," Ivanti stated in its security advisory released Thursday. The company acknowledged it lacks sufficient information about the threat actors or comprehensive indicators of compromise due to the sophistication of the attacks.
The vulnerabilities affect only on-premises EPMM deployments and do not impact cloud-hosted Ivanti Neurons for Mobile Device Management, Ivanti Endpoint Manager, the Ivanti Sentry secure mobile gateway or any other Ivanti products. However, the company recommends organizations review Sentry logs alongside EPMM systems for potential lateral movement.

Successful exploitation grants attackers access to mobile device management infrastructure. Compromised EPMM appliances expose administrator and user credentials, including usernames and email addresses. Attackers gain visibility into managed mobile devices, accessing phone numbers, IP addresses, installed applications and device identifiers like IMEI and MAC addresses.
Organizations with location tracking enabled face additional exposure. Attackers accessing compromised systems can retrieve device location data including GPS coordinates and cellular tower information. More critically, attackers can leverage EPMM's API or web console to modify device configurations, including authentication settings.
Ivanti released RPM scripts providing temporary mitigation for affected EPMM versions. Organizations running versions 12.5.0.x, 12.6.0.x and 12.7.0.x should deploy RPM 12.x.0.x, while those operating versions 12.5.1.0 and 12.6.1.0 require RPM 12.x.1.x. The company emphasized that applying patches requires no downtime and causes no functional impact.
"If after applying the RPM script to your appliance, you upgrade to a new version you will need to reinstall the RPM," Ivanti warned. The permanent fix for this vulnerability will be included in the next product release: 12.8.0.0," scheduled for release later in Q1 2026.
Organizations suspecting compromise should not attempt to clean affected systems. Ivanti recommends either restoring EPMM from known-good backups taken before exploitation occurred or rebuilding the appliance and migrating data to replacement systems. After restoration, administrators must reset passwords for local EPMM accounts, LDAP and KDC service accounts, revoke and replace public certificates, and reset passwords for all internal and external service accounts configured with EPMM.
The company's analysis guidance shows particular risks around Sentry integration. While EPMM can be restricted to demilitarized zones with minimal corporate network access, Sentry specifically tunnels traffic from mobile devices to internal network assets. Organizations should review systems accessible through Sentry for potential reconnaissance or lateral movement.
CISA's addition of CVE-2026-1281 to the KEV catalog triggers Binding Operational Directive 22-01 requirements. Federal civilian agencies must apply vendor mitigations or discontinue using vulnerable systems by February 1, 2026. CISA strongly urges all organizations, not just federal agencies, to prioritize remediation as part of vulnerability management practices.
Notably, CISA added only CVE-2026-1281 to the KEV catalog despite Ivanti confirming exploitation of both vulnerabilities. The agency has not explained this discrepancy.
The disclosure continues Ivanti's troubled 2025, which saw widespread exploitation of multiple zero-day vulnerabilities across its product portfolio. Security researchers previously linked EPMM attacks to sophisticated threat actors, with some incidents attributed to China-nexus advanced persistent threat groups.
These management platforms represent high-value targets because compromising them effectively transforms the system into enterprise-wide command-and-control infrastructure.
Organizations should apply patches immediately and conduct thorough security assessments of potentially compromised systems to prevent further damage from these actively exploited vulnerabilities.

 Payload Reconstruction & Fileless Execution (Source: CRIL)[/caption]
Once active, ShadowHS prioritizes reconnaissance, fingerprinting host security measures, evaluating prior compromises, and providing an operator-controlled interface. Its runtime behavior is deliberately restrained, allowing attackers to selectively invoke capabilities such as credential access, lateral movement, privilege escalation, cryptomining, and covert data exfiltration.
Payload Reconstruction & Fileless Execution (Source: CRIL)[/caption]
Once active, ShadowHS prioritizes reconnaissance, fingerprinting host security measures, evaluating prior compromises, and providing an operator-controlled interface. Its runtime behavior is deliberately restrained, allowing attackers to selectively invoke capabilities such as credential access, lateral movement, privilege escalation, cryptomining, and covert data exfiltration.
 Runtime Dependency Validation (Source: CRIL)[/caption]
“ShadowHS demonstrates a clear separation between restrained runtime activity and extensive dormant capabilities,” CRIL notes. “This is indicative of a deliberate operator-driven post-exploitation platform rather than automated malware.”
Runtime Dependency Validation (Source: CRIL)[/caption]
“ShadowHS demonstrates a clear separation between restrained runtime activity and extensive dormant capabilities,” CRIL notes. “This is indicative of a deliberate operator-driven post-exploitation platform rather than automated malware.”


Russian and Chinese espionage groups continue to exploit an N-day vulnerability (CVE-2025-8088) in WinRAR alongside financially motivated actors, all leveraging a path traversal vulnerability that drops malware into Windows Startup folders.
Google Threat Intelligence Group discovered widespread exploitation of a critical WinRAR vulnerability six months after the vendor patched it, with government-backed hackers from Russia and China deploying the flaw alongside financially motivated cybercriminals. The attacks demonstrate how effective exploits remain valuable long after patches become available, especially when organizations delay updates.
CVE-2025-8088, a high-severity path traversal vulnerability in WinRAR, allows attackers to write files to arbitrary system locations by crafting malicious RAR archives. RARLAB released WinRAR version 7.13 on July 30, 2025, to address the flaw. However, exploitation began at least 12 days earlier, on July 18, according to ESET research.
The vulnerability exploits Alternate Data Streams, a Windows feature that allows multiple data streams to be associated with a single file. Attackers conceal malicious files within ADS entries of decoy documents inside archives. While victims view what appears to be a legitimate PDF or document, hidden payload streams execute in the background.
The exploit uses specially crafted paths combining ADS features with directory traversal characters. A file might carry a composite name like "innocuous.pdf:malicious.lnk" paired with a path traversing to critical directories. When victims open the archive, the ADS content extracts to destinations specified by the traversal path, frequently targeting the Windows Startup folder for automatic execution at next login.
Multiple Russian threat groups consistently exploit the vulnerability in campaigns targeting Ukrainian military and government entities using highly tailored geopolitical lures. UNC4895, also known as RomCom, conducts dual financial and espionage operations through spearphishing emails with subject lines indicating targeting of specific Ukrainian military units. The attacks deliver NESTPACKER malware, externally known as Snipbot.
APT44, tracked under the designation FROZENBARENTS, drops decoy files with Ukrainian filenames alongside malicious LNK files attempting further downloads. TEMP.Armageddon, designated CARPATHIAN, uses RAR archives to place HTA files into Startup folders, with the HTA acting as a downloader for second-stage payloads. This activity continued through January 2026.
Turla, adopted CVE-2025-8088 to deliver the STOCKSTAY malware suite using lures themed around Ukrainian military activities and drone operations. A China-nexus actor exploits the vulnerability to deliver POISONIVY malware via BAT files dropped into Startup folders, which then download droppers.
The exploitation mirrors widespread abuse of CVE-2023-38831, a previous WinRAR bug that government-backed actors heavily exploited despite available patches. The pattern demonstrates that exploits for known vulnerabilities remain highly effective when organizations fail to patch promptly.
Financially motivated threat groups quickly adopted the vulnerability. One group targeting Indonesian entities uses lure documents to drop CMD files into Startup folders. These scripts download password-protected RAR archives from Dropbox containing backdoors that communicate with Telegram bot command-and-control servers.
Another group focuses on hospitality and travel sectors, particularly in Latin America, using phishing emails themed around hotel bookings to deliver commodity remote access trojans including XWorm and AsyncRAT. A separate group targeting Brazilian users via banking websites delivered malicious Chrome extensions that inject JavaScript into pages of two Brazilian banking sites to display phishing content and steal credentials.
An actor known as "zeroplayer" advertised a WinRAR exploit in July 2025, shortly before widespread exploitation began. zeroplayer's portfolio extends beyond WinRAR. In November 2025, the actor claimed a sandbox escape remote code execution zero-day exploit for Microsoft Office, advertising it for $300,000. In late September 2025, zeroplayer advertised a remote code execution zero-day for an unnamed popular corporate VPN provider.
Starting mid-October 2025, zeroplayer advertised a Windows local privilege escalation zero-day exploit for $100,000. In early September 2025, the actor advertised a zero-day for an unspecified drive allowing attackers to disable antivirus and endpoint detection and response software for $80,000.
zeroplayer's continued activity demonstrates the commoditization of the attack lifecycle. By providing ready-to-use capabilities, actors like zeroplayer reduce technical complexity and resource demands, allowing groups with diverse motivations—from ransomware deployment to state-sponsored intelligence gathering—to leverage sophisticated capabilities.
The rapid exploitation adoption occurred despite Google Safe Browsing and Gmail actively identifying and blocking files containing the exploit. When reliable proof of concept for critical flaws enters cybercriminal and espionage marketplaces, adoption becomes instantaneous. This blurs lines between sophisticated government-backed operations and financially motivated campaigns.
The vulnerability's commoditization reinforces that effective defense requires immediate application patching coupled with fundamental shifts toward detecting consistent, predictable post-exploitation tactics.
Google published comprehensive indicators of compromise in a VirusTotal collection for registered users to assist security teams in hunting and identifying related activity.


A 149M-credential breach shows why encryption alone isn’t enough. Infostealer malware bypasses cloud security by stealing passwords at the endpoint—where encryption offers no protection.
The post Another Credential Leak, Another Dollar appeared first on Security Boulevard.




Really interesting blog post from Anthropic:
In a recent evaluation of AI models’ cyber capabilities, current Claude models can now succeed at multistage attacks on networks with dozens of hosts using only standard, open-source tools, instead of the custom tools needed by previous generations. This illustrates how barriers to the use of AI in relatively autonomous cyber workflows are rapidly coming down, and highlights the importance of security fundamentals like promptly patching known vulnerabilities.
[…]
A notable development during the testing of Claude Sonnet 4.5 is that the model can now succeed on a minority of the networks without the custom cyber toolkit needed by previous generations. In particular, Sonnet 4.5 can now exfiltrate all of the (simulated) personal information in a high-fidelity simulation of the Equifax data breach—one of the costliest cyber attacks in history—using only a Bash shell on a widely-available Kali Linux host (standard, open-source tools for penetration testing; not a custom toolkit). Sonnet 4.5 accomplishes this by instantly recognizing a publicized CVE and writing code to exploit it without needing to look it up or iterate on it. Recalling that the original Equifax breach happened by exploiting a publicized CVE that had not yet been patched, the prospect of highly competent and fast AI agents leveraging this approach underscores the pressing need for security best practices like prompt updates and patches.
Read the whole thing. Automatic exploitation will be a major change in cybersecurity. And things are happening fast. There have been significant developments since I wrote this in October.



Network administrators worldwide are scrambling this morning following credible reports that the critical Fortinet Single Sign-On (SSO) vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-59718, is being actively exploited on systems previously thought to be patched.
The vulnerability, originally disclosed in December 2025, allows unauthenticated attackers to bypass authentication on FortiGate firewalls by forging SAML assertions. At the time, Fortinet released FortiOS version 7.4.9 as the definitive fix for the 7.4 release branch. However, emerging data from the cybersecurity community suggests this update may have failed to close the door on attackers.
Over the last 48 hours, a wave of reports has surfaced on community hubs like Reddit, where verified administrators have shared logs indicating successful breaches on devices running the supposedly secure FortiOS 7.4.9.
The attack pattern is distinct and alarming. Victims report observing unauthorized logins via the FortiCloud SSO mechanism—even when they do not actively use the feature for their own administration. Once access is gained, the attackers typically create a local administrator account, often named "helpdesk" or similar generic terms, to establish persistence independent of the SSO flaw.
"We have been on 7.4.9 since December 30th," wrote one frustrated administrator who shared redacted logs of the incident. "Our SIEM caught a local admin account being created. The attack vector looks exactly like the original CVE-2025-59718 exploit, but against the patched firmware.
The persistence of this flaw in version 7.4.9 has led to speculation that the initial patch was incomplete or that attackers have found a bypass to the mitigation logic. Some users report that Fortinet support has acknowledged the issue privately, hinting that the vulnerability might persist even into upcoming builds like 7.4.10, though this remains unconfirmed by official public advisories.
The exploit relies on the "Allow administrative login using FortiCloud SSO" setting, which is often enabled by default when a device is registered to FortiCloud.
Security experts are now advising a "trust no patch" approach for this specific vector. The only guaranteed mitigation currently circulating in professional circles is to manually disable the vulnerable feature via the Command Line Interface (CLI), regardless of the firmware version installed.
Administrators are urged to run the following command immediately on all FortiGate units:
config system global
set admin-forticloud-sso-login disable
end
Organizations running FortiOS 7.4.x—including version 7.4.9—should immediately audit their system event logs for the following activity:
Unexpected SSO Logins: Filter logs for successful logins where the method is forticloud-sso, especially from unrecognized public IP addresses.
New User Creation: Check for the recent creation of administrator accounts with names like helpdesk, support, or fortinet-admin.
Configuration Exports: Look for logs indicating a full system configuration download shortly after an SSO login.
As trust in the official patch cycle wavers, the community is once again serving as the first line of defense, sharing Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and workarounds faster than vendors can issue bulletins. For now, disable the SSO feature, or risk compromise.


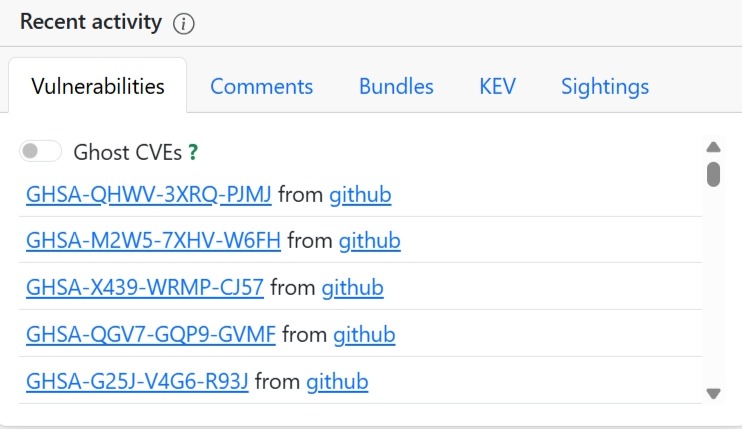 EU vulnerability database dashboard (Source: GCVE)[/caption]
The dashboard tracks more than identifiers. Weekly observations, comments, bundles, known exploited vulnerabilities (KEV), sightings, and even “ghost CVEs” are surfaced to show how issues evolve after disclosure. A rolling, month-long evolution view highlights how frequently vulnerabilities are seen, confirmed, exploited, or accompanied by proof-of-concept code.
Concrete examples illustrate the breadth of historical and current coverage. Widely known issues like CVE-2021-44228 (Log4Shell), CVE-2019-19781, CVE-2018-13379, and CVE-2017-17215 appear alongside recent entries such as CVE-2025-14847, CVE-2025-55182, CVE-2025-68613, and CVE-2025-59374. Older vulnerabilities, CVE-2015-2051 or CVE-2017-18368, sit next to newly published 2026 identifiers, reinforcing that the EU vulnerability database is designed for continuity, not just novelty.
EU vulnerability database dashboard (Source: GCVE)[/caption]
The dashboard tracks more than identifiers. Weekly observations, comments, bundles, known exploited vulnerabilities (KEV), sightings, and even “ghost CVEs” are surfaced to show how issues evolve after disclosure. A rolling, month-long evolution view highlights how frequently vulnerabilities are seen, confirmed, exploited, or accompanied by proof-of-concept code.
Concrete examples illustrate the breadth of historical and current coverage. Widely known issues like CVE-2021-44228 (Log4Shell), CVE-2019-19781, CVE-2018-13379, and CVE-2017-17215 appear alongside recent entries such as CVE-2025-14847, CVE-2025-55182, CVE-2025-68613, and CVE-2025-59374. Older vulnerabilities, CVE-2015-2051 or CVE-2017-18368, sit next to newly published 2026 identifiers, reinforcing that the EU vulnerability database is designed for continuity, not just novelty.


This isn’t good:
We discovered a critical vulnerability (CVE-2026-21858, CVSS 10.0) in n8n that enables attackers to take over locally deployed instances, impacting an estimated 100,000 servers globally. No official workarounds are available for this vulnerability. Users should upgrade to version 1.121.0 or later to remediate the vulnerability.
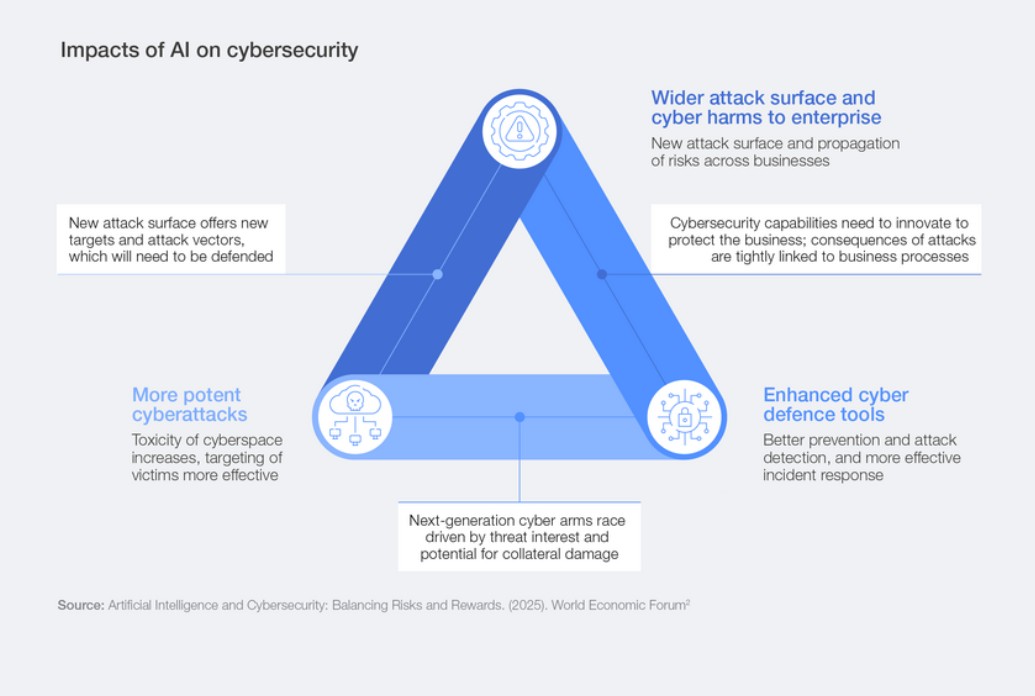
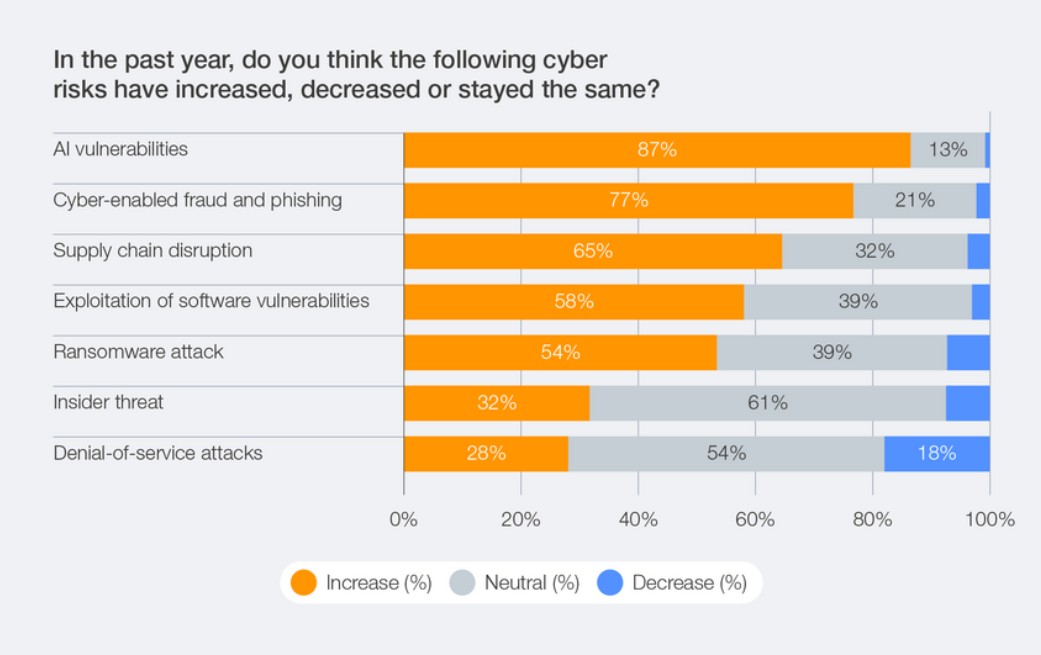 Growing cybersecurity risks (World Economic Forum)[/caption]
The top generative AI (GenAI) concerns include data leaks exposing personal data, advancement of adversarial capabilities (phishing, malware development and deepfakes, for example), the technical security of the AI systems themselves, and increasingly complex security governance (chart below).
[caption id="attachment_108655" align="aligncenter" width="1038"]
Growing cybersecurity risks (World Economic Forum)[/caption]
The top generative AI (GenAI) concerns include data leaks exposing personal data, advancement of adversarial capabilities (phishing, malware development and deepfakes, for example), the technical security of the AI systems themselves, and increasingly complex security governance (chart below).
[caption id="attachment_108655" align="aligncenter" width="1038"]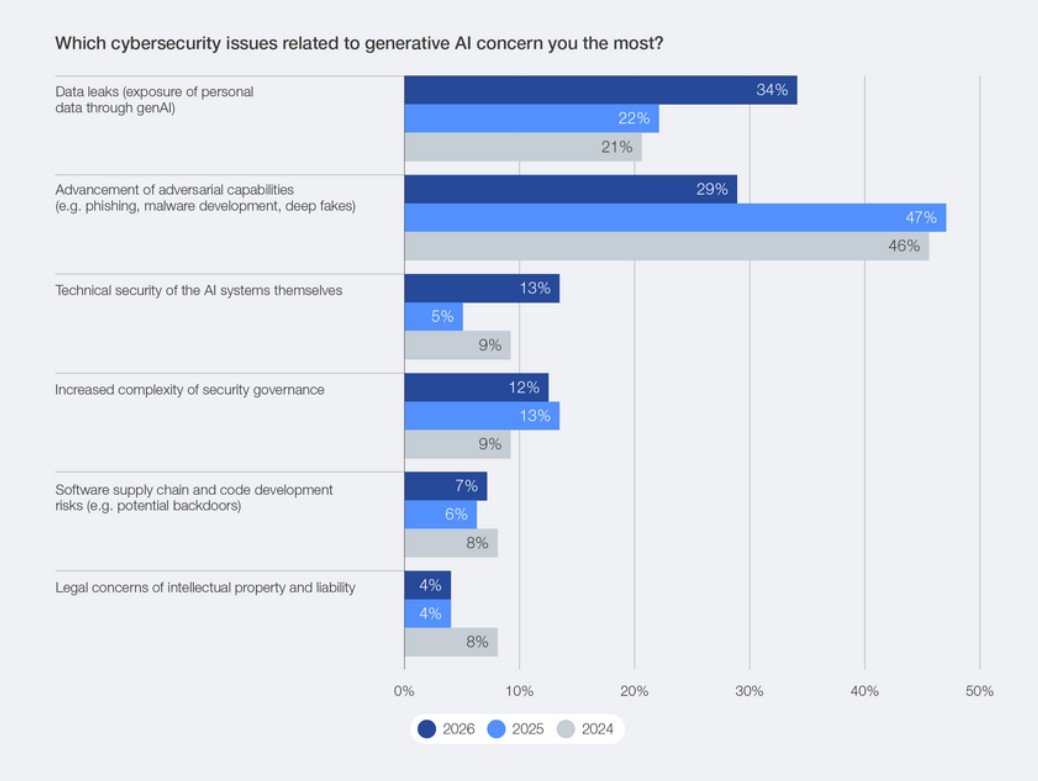 GenAI security concerns[/caption]
GenAI security concerns[/caption]