Across America, survivors of domestic abuse and stalking are facing a unique location tracking crisis born out of policy failure, unclear corporate responsibility, and potentially risky behaviors around digital sharing that are now common in relationships.
No, we’re not talking about stalkerware. Or hidden Apple AirTags. We’re talking about cars.
Modern cars are the latest consumer “device” to undergo an internet-crazed overhaul, as manufacturers increasingly stuff their automobiles with the types of features you’d expect from a smartphone, not a mode of transportation.
There are cars with WiFi, cars with wireless charging, cars with cameras that not only help while you reverse out of a driveway, but which can detect whether you’re drowsy while on a long haul. Many cars now also come with connected apps that allow you to, through your smartphone, remotely start your vehicle, schedule maintenance, and check your tire pressure.
But one feature in particular, which has legitimate uses in responding to stolen and lost vehicles, is being abused: Location tracking.
It’s time car companies do something about it.
In December, The New York Times revealed the story of a married woman whose husband was abusing the location tracking capabilities of her Mercedes-Benz sedan to harass her. The woman tried every avenue she could to distance herself from her husband. After her husband became physically violent in an argument, she filed a domestic abuse report. Once she fled their home, she got a restraining order. She ignored his calls and texts.
But still her husband could follow her whereabouts by tracking her car—a level of access that Mercedes representatives reportedly could not turn off, as he was considered the rightful owner of the vehicle (according to The New York Times, the husband’s higher credit score convinced the married couple to have the car purchased in his name alone).
As reporter Kashmir Hill wrote of the impasse:
“Even though she was making the payments, had a restraining order against her husband and had been granted sole use of the car during divorce proceedings, Mercedes representatives told her that her husband was the customer so he would be able to keep his access. There was no button she could press to take away the app’s connection to the vehicle.”
This was far from an isolated incident.
In 2023, Reuters reported that a San Francisco woman sued her husband in 2020 for allegations of “assault and sexual battery.” But some months later, the woman’s allegations of domestic abuse grew into allegations of negligence—this time, against the carmaker Tesla.
Tesla, the woman claimed in legal filings, failed to turn off her husband’s access to the location tracking capabilities in their shared Model X SUV, despite the fact that she had obtained a restraining order against her husband, and that she was a named co-owner of the vehicle.
When The New York Times retrieved filings from the San Francisco lawsuit above, attorneys for Tesla argued that the automaker could not realistically play a role in this matter:
“Virtually every major automobile manufacturer offers a mobile app with similar functions for their customers,” the lawyers wrote. “It is illogical and impractical to expect Tesla to monitor every vehicle owner’s mobile app for misuse.”
Tesla was eventually removed from the lawsuit.
In the Reuters story, reporters also spoke with a separate woman who made similar allegations that her ex-husband had tracked her location by using the Tesla app associated with her vehicle. Because the separate woman was a “primary” account owner, she was able to remove the car’s access to the internet, Reuters reported.
A better path
Location tracking—and the abuse that can come with it—is a much-discussed topic for Malwarebytes Labs. But the type of location tracking abuse that is happening with shared cars is different because of the value that cars hold in situations of domestic abuse.
A car is an opportunity to physically leave an abusive partner. A car is a chance to start anew in a different, undisclosed location. In harrowing moments, cars have also served as temporary shelter for those without housing.
So when a survivor’s car is tracked by their abuser, it isn’t just a matter of their location and privacy being invaded, it is a matter of a refuge being robbed.
In speaking with the news outlet CalMatters, Yenni Rivera, who works on domestic violence cases, explained the stressful circumstances of exactly this dynamic.
“I hear the story over and over from survivors about being located by their vehicle and having it taken,” Rivera told CalMatters. “It just puts you in a worst case situation because it really triggers you thinking, ‘Should I go back and give in?’ and many do. And that’s why many end up being murdered in their own home. The law should make it easier to leave safely and protected.”
Though the state of California is considering legislative solutions to this problem, national lawmaking is slow.
Instead, we believe that the companies that have the power to do something act on that power. Much like how Malwarebytes and other cybersecurity vendors banded together to launch the Coalition Against Stalkerware, automakers should work together to help users.
Fortunately, an option may already exist.
When the Alliance for Automobile Innovation warned that consumer data collection requests could be weaponized by abusers who want to comb through the car location data of their partners and exes, the automaker General Motors already had a protection built in.
According to Reuters, the roadside assistance service OnStar, which is owned by General Motors, allows any car driver—be they a vehicle’s owner or not—to hide location data from other people who use the same vehicle. Rivian, a new electric carmaker, is reportedly working on a similar feature, said senior vice president of software development Wassym Bensaid in speaking with Reuters.
Though Reuters reported that Rivian had not heard of their company’s technology being leveraged in a situation of domestic abuse, Wassym believed that “users should have a right to control where that information goes.”
We agree.
We don’t just report on threats—we remove them
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Keep threats off your devices by downloading Malwarebytes today.


 Source: Hawk Eye App on Android[/caption]
Source: Hawk Eye App on Android[/caption]
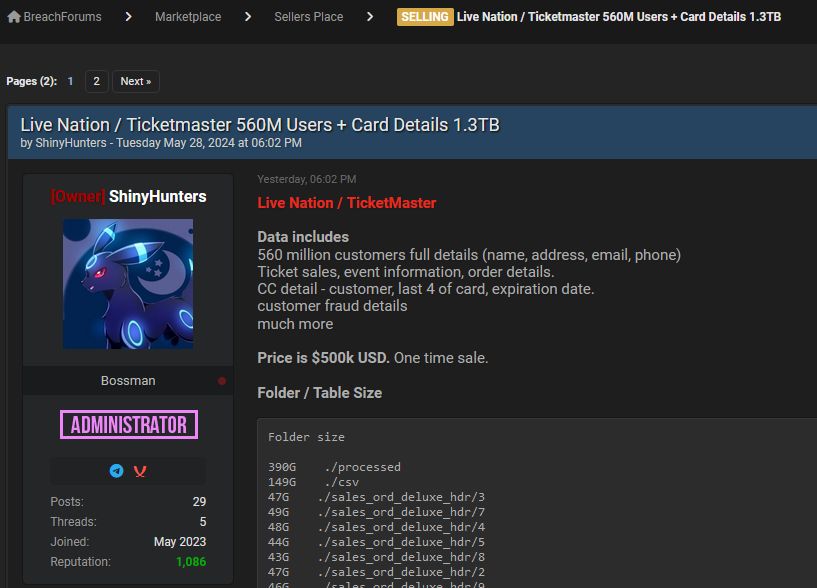
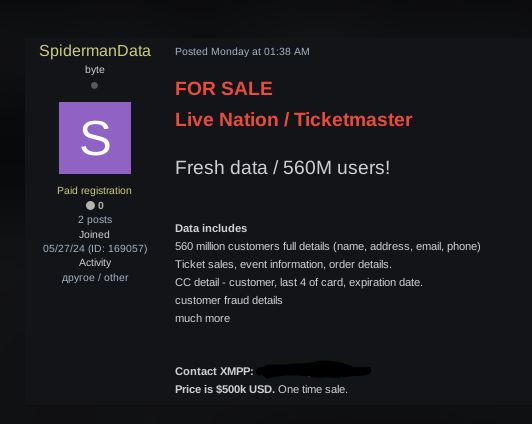
 What is noteworthy about the above examples is that all these users had filed complaints only in May 2024, which suggests that the data from the Hawk Eye App was hacked this month.
What is noteworthy about the above examples is that all these users had filed complaints only in May 2024, which suggests that the data from the Hawk Eye App was hacked this month.






 Source: LockBit leak site[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_69277" align="alignnone" width="323"]
Source: LockBit leak site[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_69277" align="alignnone" width="323"] Source: LockBit Telegram[/caption]
With a looming ransom deadline set for May 28, the university is racing against limited time to deal with the consequences of the digital assault.
Earlier on May 10th, the University of Siena acknowledged the
Source: LockBit Telegram[/caption]
With a looming ransom deadline set for May 28, the university is racing against limited time to deal with the consequences of the digital assault.
Earlier on May 10th, the University of Siena acknowledged the  Source: www.apply.unisi.it[/caption]
However, the
Source: www.apply.unisi.it[/caption]
However, the 











 Source: santander.com[/caption]
The bank apologized for the incident and acknowledged concerns arising from the data breach, taking action to directly notify the affected customers and employees. The security team also informed regulators and
Source: santander.com[/caption]
The bank apologized for the incident and acknowledged concerns arising from the data breach, taking action to directly notify the affected customers and employees. The security team also informed regulators and 




 Source:
Source: