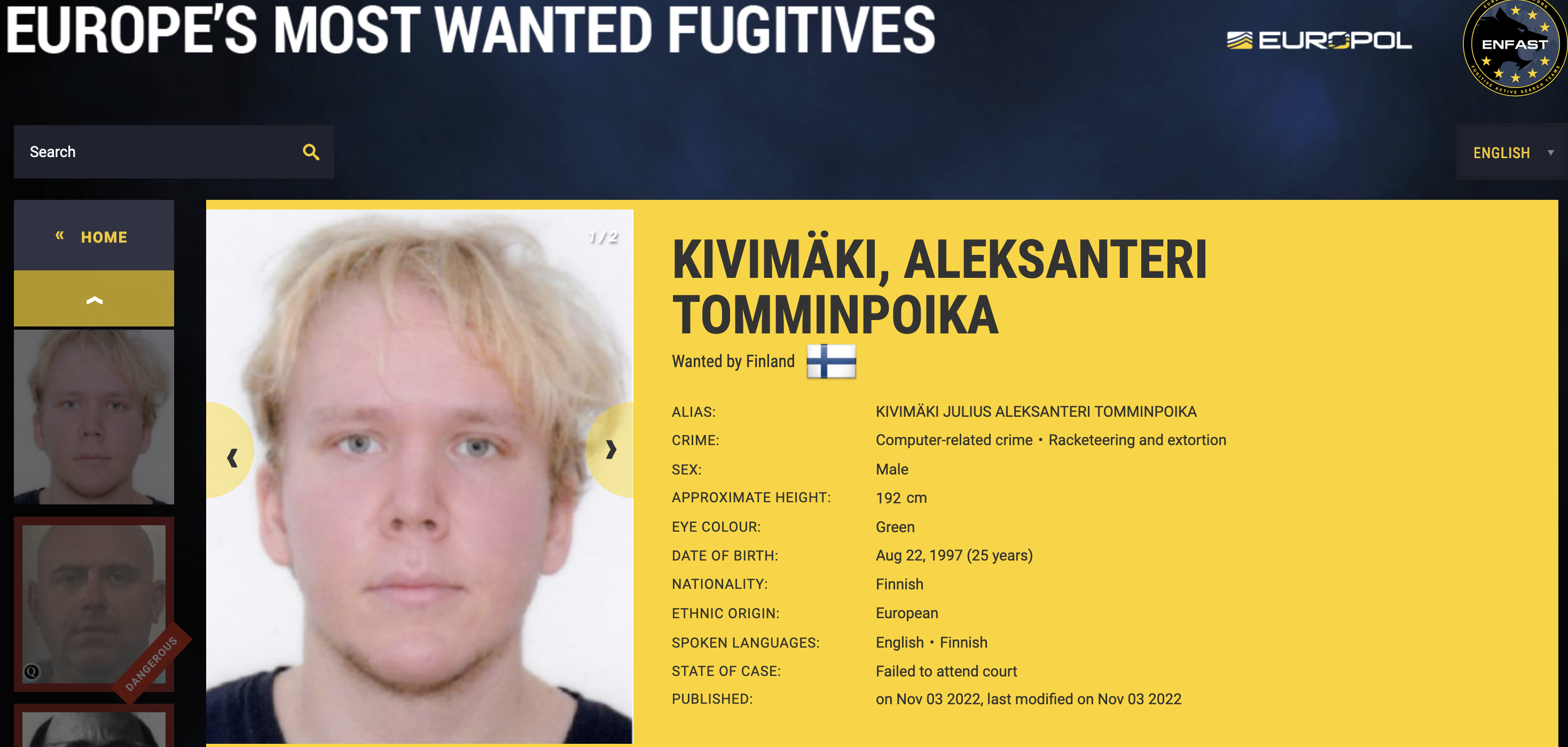
In a joint international law enforcement action dubbed “Operation Endgame,” the agencies and judicial authorities dismantled major botnet infrastructure, targeting notorious malware droppers like IcedID, SystemBC, Pikabot, Smokeloader, Bumblebee and TrickBot.
In a Thursday announcement Europol
said that between May 27 and 29, Operation Endgame led to four arrests and the takedown of over 100 servers worldwide.
“This is the largest ever operation against botnets, which play a major role in the deployment of ransomware,” Europol said.
Botnets are used for different types of cybercrime including
ransomware, identity theft, credit card scams, and several other financial crimes.
“The dismantled botnets consisted of millions of infected computer systems,” a joint
press statement from the Operation Endgame team said.
Led by France, Germany, and the Netherlands, and supported by Eurojust, the operation involved countries including Denmark, the United Kingdom, the United States, Armenia, Bulgaria, Lithuania, Portugal, Romania, Switzerland, and Ukraine.
Operation Endgame resulted in:
- 4 arrests - 1 in Armenia and 3 in Ukraine.
- 16 location searches - 1 in Armenia, 1 in the Netherlands, 3 in Portugal, and 11 in Ukraine.
- Over 100 servers dismantled or disrupted in countries such as Bulgaria, Canada, Germany, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Romania, Switzerland, the UK, the US, and Ukraine.
- Over 2,000 domains seized and brought under law enforcement control.
- 8 summons were also served against other suspects.
Targeting the Cybercrime Infrastructure
Operation Endgame focused on high-value targets, their criminal infrastructure behind various
malware and the freezing of illicit proceeds.
“The malware, whose infrastructure was taken down during the action days, facilitated attacks with ransomware and other malicious software,” according to Europol.
One primary suspect, the Europol said, earned at least €69 million in cryptocurrency by renting out sites for ransomware deployment. Authorities are closely monitoring these transactions and have secured permissions to seize the assets. The infrastructure and financial seizures had a global impact on the dropper ecosystem, the authorities believe.
Key Dropper Malware Dismantled in Operation Endgame
-
SystemBC: Facilitated anonymous communication between infected systems and command-and-control servers.
-
Bumblebee: Delivered via phishing campaigns or compromised websites, enabling further payload execution.
-
Smokeloader: Used primarily to download and install additional malicious software.
-
IcedID (BokBot): Evolved from a banking trojan to a multi-purpose tool for various cybercrimes.
-
Pikabot: Enabled ransomware deployment, remote takeovers, and
data theft through initial system access.
“All of them are now being used to deploy ransomware and are seen as the main threat in the infection chain,” Europol said.
[caption id="attachment_72953" align="aligncenter" width="1920"]

Operation Endgame seizure notice (Credit: Europol)[/caption]
The Role of Dropper Malware in Cyberattacks
Droppers are essential tools in cyberattacks, acting as the initial vector to bypass security and install harmful software such as ransomware and spyware. They facilitate further malicious activities by enabling the deployment of additional malware on compromised systems.
How Droppers Operate
- Infiltration: Enter systems through email attachments, compromised websites, or bundled with legitimate software.
- Execution: Install additional malware on the victim's computer without the user's knowledge.
- Evasion: Avoid detection by security software through methods like code obfuscation and running in memory.
- Payload Delivery: Deploy additional malware, potentially becoming inactive or removing itself to evade detection.
The success of the operation was bolstered by private partners such as Bitdefender, Sekoia, Shadowserver, Proofpoint, and Fox-IT, among others. Their support was crucial in disrupting the criminal networks and infrastructure, the authorities said.
Wait for Operation Endgame Season 2
Operation Endgame signifies a major victory, but this is not really the end of it. Taking cue from the Marvel cinematic movie ‘Avengers – Endgame,’ the law enforcement is set to to release a part two of this operation in a few hours from now as they said their efforts continue.
“This is Season 1 of operation Endgame. Stay tuned. It sure will be exciting. Maybe not for everyone though. Some results can be found here, others will come to you in different and unexpected ways,” the authorities said.
“Feel free to get in touch, you might need us. Surely, we could both benefit from an openhearted dialogue. You would not be the first one, nor will you be the last. Think about (y)our next move.”
Future actions will be announced on the
Operation Endgame website, possibly targeting suspects and users, and ensuring accountability.
The news of this massive botnet takedown operation comes a day after the announcement of the dismantling of “
likely the world’s largest botnet ever” – the 911 S5 botnet. The botnet’s alleged administrator Yunhe Wang, was arrested last week and a subsequent seizure of infrastructure and assets was announced by the FBI.
The recent law enforcement actions represent a historic milestone in combating
cybercrime, dealing a significant blow to the dropper malware ecosystem that supports ransomware and other malicious activities. The operation's success underscores the importance of international cooperation and the need for robust
cybersecurity measures to tackle evolving threats.


 Operation Endgame seizure notice (Credit: Europol)[/caption]
Operation Endgame seizure notice (Credit: Europol)[/caption]