
Data sourced from over 40 million exposures that pose high-impact risks to numerous critical business entities revealed that Active Directory typically accounts for 80% of all security exposures identified in organizations.
The
research from XM Cyber in collaboration with the Cyentia Institute found that identity and credential misconfigurations fuel a striking majority of security exposures across organizations. Among these exposures, a third directly jeopardize critical assets, serving as a prime target for adversaries seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
Active Directory Exposures Dominate the Attack Surface
Active Directory accounts for over half of entities identified across all environments, as per the report from XM
Cyber.
Thus, a significant portion of security exposures lies within a company's Active Directory, a vital component for user-network resource connectivity. However, this critical infrastructure also presents an attractive target for attackers as it interests them with additional elevated rights.
“An attacker who has compromised an Active Directory account could use it to elevate privileges, conceal
malicious activity in the network, execute malicious code and even gain access to the cloud environment,” XM Cyber explained.
“Many of these exposures stem from the inherent nature of dynamic configuration issues in Active Directory as well as the challenge of keeping it updated. This creates a blind spot that appears
secure on the surface but hides a nest of problems that many security tools can’t see,” the report said.
Misconfigurations and credential attacks emerge as the top contributors to these exposures, introducing gaps that traditional security tools often overlook, such as issues in member management and password resets. These issues “present a challenge for nearly every organization,” XM Cyber said.
Techniques like credential harvesting, dumping, relay and domain credentials feature prominently in the list of top techniques identified by attack path analysis for AWS, Azure and GCP, and Tools like Mimikatz make these techniques even easier to execute and thus make it extremely popular.
Poor practices also make credential-related
attack paths more easy and potent. XM Cyber said it identified highly privileged Active Directory credentials cached on multiple machines in 79% of organizations, and one in five of those have admin-level permissions on 100 or more devices.
Furthermore, poor endpoint hygiene afflicts the majority of environments, with over 25% of devices lacking EDR coverage or containing cached credentials, offering attackers ample entry points to establish footholds. These overlooked
vulnerabilities in identity and endpoint security form a fertile ground for hackers, demanding urgent attention from organizations.
Zur Ulianitzky, Vice President of Security Research at XM Cyber, emphasized the necessity of broadening exposure management beyond vulnerabilities to encompass all potential adversary pathways, including misconfigurations and user behavior. The research revealed that a mere 2% of exposures exist on critical 'choke points,' where adversaries
exploit vulnerabilities to access crucial assets.
CVEs are a Drop in the Ocean
Despite organizations' focus on managing traditional software vulnerabilities tracked by CVE identifiers, these efforts barely scratch the surface. XM Cyber's analysis uncovered approximately 15,000 exposures per organization, with CVE-based vulnerabilities constituting less than 1% of this extensive exposure landscape.
Even
concerning exposures affecting critical assets, CVEs represent only a minute fraction, highlighting significant blind spots in security programs fixated solely on vulnerability patching.
Exposed Critical Assets in the Cloud
Active Directory is the largest attack surface, according to XM Cyber, but the largest share of exposures to critical assets is in the cloud.
Cloud environments, amidst rapid adoption by organizations, are not immune to exposure
risks. Over half (56%) of exposures affecting critical assets are
traced back to cloud platforms, presenting a significant threat as attackers seamlessly traverse between on-premises and cloud environments.
This fluid movement poses a substantial
risk to cloud-based assets, allowing attackers to compromise critical resources with minimal effort.
Exposure Risks Across Sectors
Industry-specific analysis from the report reveals discrepancies in exposure
risks across sectors. Industries like Energy and Manufacturing exhibit a higher proportion of internet-exposed critical assets affected by exposures compared to
Financial Services organizations, despite the latter's larger digital footprint.
Healthcare providers, facing inherent challenges in minimizing risk, contend with a median number of exposures five times higher than the Energy and Utilities sector, emphasizing the need for tailored exposure management strategies.
Exposure Management is currently beyond addressing only vulnerabilities and CVEs. Organizations need to adopt a holistic and ongoing Exposure Management approach, incorporating attack path modeling to pinpoint and resolve infrastructure weak points.
Emphasis should be placed on tackling identity issues, Active Directory exposures and cloud cyber hygiene, while advocating for tailored solutions according to industry and scale.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.


















 Source: patents.google.com[/caption]
However,
Source: patents.google.com[/caption]
However, 

 Source: IC3[/caption]
Investment scams were the costliest elder fraud in 2023 and cost victims more than $1.2 billion in losses last year. Tech support scams, business email compromise scams, confidence and romance scams, government impersonation scams, and personal data breaches, all respectively cost victims hundreds of millions of dollars in 2023.
[caption id="attachment_69767" align="aligncenter" width="1400"]
Source: IC3[/caption]
Investment scams were the costliest elder fraud in 2023 and cost victims more than $1.2 billion in losses last year. Tech support scams, business email compromise scams, confidence and romance scams, government impersonation scams, and personal data breaches, all respectively cost victims hundreds of millions of dollars in 2023.
[caption id="attachment_69767" align="aligncenter" width="1400"] Source: IC3[/caption]
On the state level, Florida ranked second in the country for the number of complaints and reported losses.
Source: IC3[/caption]
On the state level, Florida ranked second in the country for the number of complaints and reported losses.

 Source: X[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_69158" align="aligncenter" width="922"]
Source: X[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_69158" align="aligncenter" width="922"] Source: X[/caption]
Source: X[/caption]
 Source: X[/caption]
One of the hacktivist groups, Silent Cyber Force, posted a message titled "Greetings Citizens Of The World," condemning the violence against foreign students and declaring their intention to take down Kyrgyzstan's governmental websites and large networks.
Their message explicitly mentioned targeting various international adversaries but stated that the current focus is on Kyrgyzstan due to the perceived inaction of its government in protecting foreign students.
[caption id="attachment_69155" align="aligncenter" width="788"]
Source: X[/caption]
One of the hacktivist groups, Silent Cyber Force, posted a message titled "Greetings Citizens Of The World," condemning the violence against foreign students and declaring their intention to take down Kyrgyzstan's governmental websites and large networks.
Their message explicitly mentioned targeting various international adversaries but stated that the current focus is on Kyrgyzstan due to the perceived inaction of its government in protecting foreign students.
[caption id="attachment_69155" align="aligncenter" width="788"]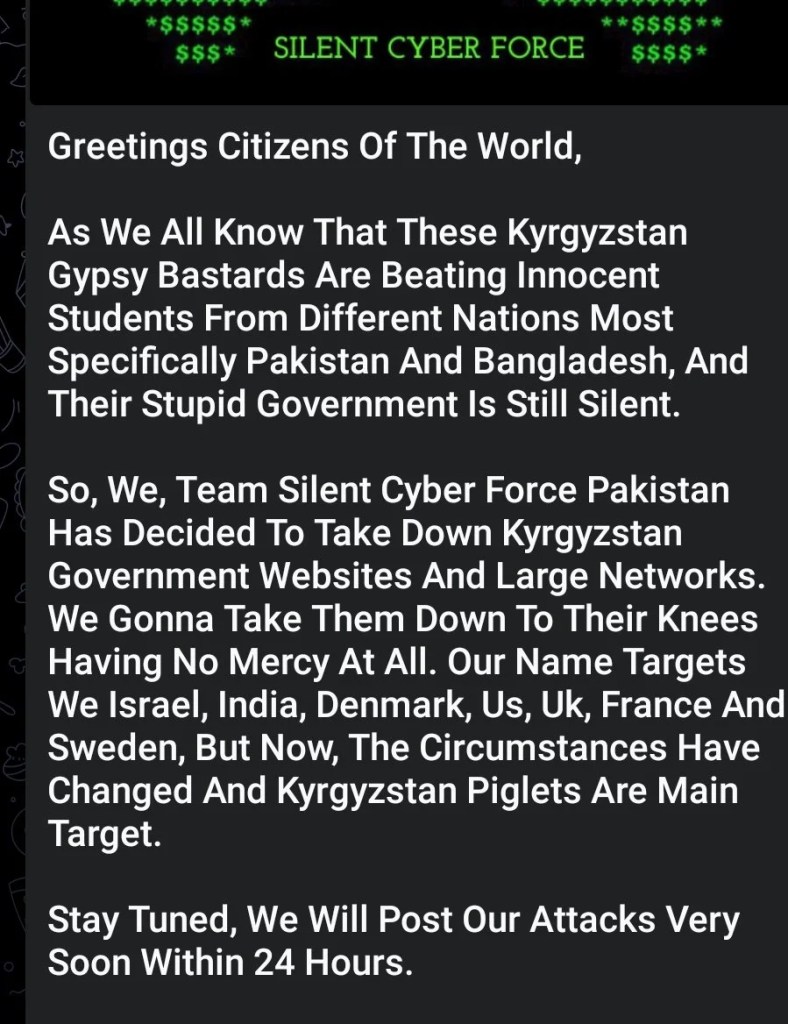 Source: X[/caption]
Despite these threats, the official websites of the targeted institutions appeared to be functioning normally when accessed. This raises questions about the hackers' actual capabilities or possible tactical delays in executing their threats. The full extent and impact of these cyberattacks on Kyrgyzstan will become clearer once official statements are released.
Source: X[/caption]
Despite these threats, the official websites of the targeted institutions appeared to be functioning normally when accessed. This raises questions about the hackers' actual capabilities or possible tactical delays in executing their threats. The full extent and impact of these cyberattacks on Kyrgyzstan will become clearer once official statements are released.




 Source: X[/caption]
Source: X[/caption]
 Source: X[/caption]
Source: X[/caption]
