Alleged Boss of ‘Scattered Spider’ Hacking Group Arrested
A 22-year-old man from the United Kingdom arrested this week in Spain is allegedly the ringleader of Scattered Spider, a cybercrime group suspected of hacking into Twilio, LastPass, DoorDash, Mailchimp, and nearly 130 other organizations over the past two years.
The Spanish daily Murcia Today reports the suspect was wanted by the FBI and arrested in Palma de Mallorca as he tried to board a flight to Italy.

A still frame from a video released by the Spanish national police shows Tylerb in custody at the airport.
“He stands accused of hacking into corporate accounts and stealing critical information, which allegedly enabled the group to access multi-million-dollar funds,” Murcia Today wrote. “According to Palma police, at one point he controlled Bitcoins worth $27 million.”
The cybercrime-focused Twitter/X account vx-underground said the U.K. man arrested was a SIM-swapper who went by the alias “Tyler.” In a SIM-swapping attack, crooks transfer the target’s phone number to a device they control and intercept any text messages or phone calls sent to the victim — including one-time passcodes for authentication, or password reset links sent via SMS.
“He is a known SIM-swapper and is allegedly involved with the infamous Scattered Spider group,” vx-underground wrote on June 15, referring to a prolific gang implicated in costly data ransom attacks at MGM and Caesars casinos in Las Vegas last year.
Sources familiar with the investigation told KrebsOnSecurity the accused is a 22-year-old from Dundee, Scotland named Tyler Buchanan, also allegedly known as “tylerb” on Telegram chat channels centered around SIM-swapping.
In January 2024, U.S. authorities arrested another alleged Scattered Spider member — 19-year-old Noah Michael Urban of Palm Coast, Fla. — and charged him with stealing at least $800,000 from five victims between August 2022 and March 2023. Urban allegedly went by the nicknames “Sosa” and “King Bob,” and is believed to be part of the same crew that hacked Twilio and a slew of other companies in 2022.
Investigators say Scattered Spider members are part of a more diffuse cybercriminal community online known as “The Com,” wherein hackers from different cliques boast loudly about high-profile cyber thefts that almost invariably begin with social engineering — tricking people over the phone, email or SMS into giving away credentials that allow remote access to corporate internal networks.
One of the more popular SIM-swapping channels on Telegram maintains a frequently updated leaderboard of the most accomplished SIM-swappers, indexed by their supposed conquests in stealing cryptocurrency. That leaderboard currently lists Sosa as #24 (out of 100), and Tylerb at #65.
0KTAPUS
In August 2022, KrebsOnSecurity wrote about peering inside the data harvested in a months-long cybercrime campaign by Scattered Spider involving countless SMS-based phishing attacks against employees at major corporations. The security firm Group-IB called the gang by a different name — 0ktapus, a nod to how the criminal group phished employees for credentials.
The missives asked users to click a link and log in at a phishing page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page. Those who submitted credentials were then prompted to provide the one-time password needed for multi-factor authentication.
These phishing attacks used newly-registered domains that often included the name of the targeted company, and sent text messages urging employees to click on links to these domains to view information about a pending change in their work schedule. The phishing sites also featured a hidden Telegram instant message bot to forward any submitted credentials in real-time, allowing the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
One of Scattered Spider’s first big victims in its 2022 SMS phishing spree was Twilio, a company that provides services for making and receiving text messages and phone calls. The group then pivoted, using their access to Twilio to attack at least 163 of its customers.
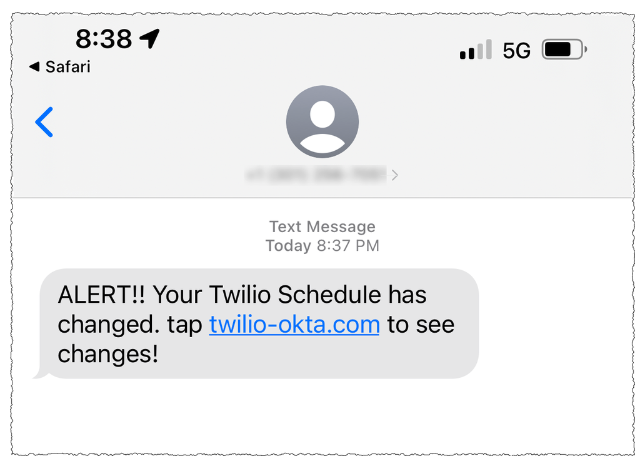
A Scattered Spider phishing lure sent to Twilio employees.
Among those was the encrypted messaging app Signal, which said the breach could have let attackers re-register the phone number on another device for about 1,900 users.
Also in August 2022, several employees at email delivery firm Mailchimp provided their remote access credentials to this phishing group. According to Mailchimp, the attackers used their access to Mailchimp employee accounts to steal data from 214 customers involved in cryptocurrency and finance.
On August 25, 2022, the password manager service LastPass disclosed a breach in which attackers stole some source code and proprietary LastPass technical information, and weeks later LastPass said an investigation revealed no customer data or password vaults were accessed.
However, on November 30, 2022 LastPass disclosed a far more serious breach that the company said leveraged data stolen in the August breach. LastPass said criminal hackers had stolen encrypted copies of some password vaults, as well as other personal information.
In February 2023, LastPass disclosed that the intrusion involved a highly complex, targeted attack against an engineer who was one of only four LastPass employees with access to the corporate vault. In that incident, the attackers exploited a security vulnerability in a Plex media server that the employee was running on his home network, and succeeded in installing malicious software that stole passwords and other authentication credentials. The vulnerability exploited by the intruders was patched back in 2020, but the employee never updated his Plex software.
Plex announced its own data breach one day before LastPass disclosed its initial August intrusion. On August 24, 2022, Plex’s security team urged users to reset their passwords, saying an intruder had accessed customer emails, usernames and encrypted passwords.
TURF WARS
Sosa and Tylerb were both subjected to physical attacks from rival SIM-swapping gangs. These communities have been known to settle scores by turning to so-called “violence-as-a-service” offerings on cybercrime channels, wherein people can be hired to perform a variety geographically-specific “in real life” jobs, such as bricking windows, slashing car tires, or even home invasions.
In 2022, a video surfaced on a popular cybercrime channel purporting to show attackers hurling a brick through a window at an address that matches the spacious and upscale home of Urban’s parents in Sanford, Fl.
January’s story on Sosa noted that a junior member of his crew named “Foreshadow” was kidnapped, beaten and held for ransom in September 2022. Foreshadow’s captors held guns to his bloodied head while forcing him to record a video message pleading with his crew to fork over a $200,000 ransom in exchange for his life (Foreshadow escaped further harm in that incident).
According to several SIM-swapping channels on Telegram where Tylerb was known to frequent, rival SIM-swappers hired thugs to invade his home in February 2023. Those accounts state that the intruders assaulted Tylerb’s mother in the home invasion, and that they threatened to burn him with a blowtorch if he didn’t give up the keys to his cryptocurrency wallets. Tylerb was reputed to have fled the United Kingdom after that assault.
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from Mr. Buchanan, and will update this story in the event he responds.