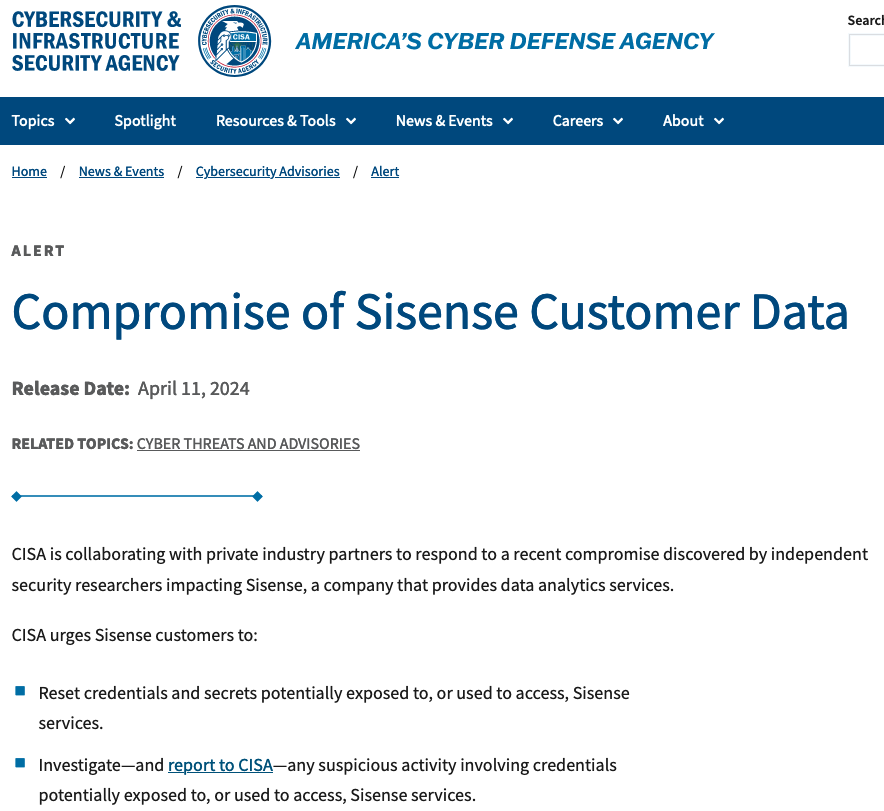
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) said today it is investigating a breach at business intelligence company Sisense, whose products are designed to allow companies to view the status of multiple third-party online services in a single dashboard. CISA urged all Sisense customers to reset any credentials and secrets that may have been shared with the company, which is the same advice Sisense gave to its customers Wednesday evening.
New York City based Sisense has more than a thousand customers across a range of industry verticals, including financial services, telecommunications, healthcare and higher education. On April 10, Sisense Chief Information Security Officer Sangram Dash told customers the company had been made aware of reports that “certain Sisense company information may have been made available on what we have been advised is a restricted access server (not generally available on the internet.)”
“We are taking this matter seriously and promptly commenced an investigation,” Dash continued. “We engaged industry-leading experts to assist us with the investigation. This matter has not resulted in an interruption to our business operations. Out of an abundance of caution, and while we continue to investigate, we urge you to promptly rotate any credentials that you use within your Sisense application.”
In its alert, CISA said it was working with private industry partners to respond to a recent compromise discovered by independent security researchers involving Sisense.
“CISA is taking an active role in collaborating with private industry partners to respond to this incident, especially as it relates to impacted critical infrastructure sector organizations,” the sparse alert reads. “We will provide updates as more information becomes available.”
Sisense declined to comment when asked about the veracity of information shared by two trusted sources with close knowledge of the breach investigation. Those sources said the breach appears to have started when the attackers somehow gained access to the company’s Gitlab code repository, and in that repository was a token or credential that gave the bad guys access to Sisense’s Amazon S3 buckets in the cloud.
Customers can use Gitlab either as a solution that is hosted in the cloud at Gitlab.com, or as a self-managed deployment. KrebsOnSecurity understands that Sisense was using the self-managed version of Gitlab.
Both sources said the attackers used the S3 access to copy and exfiltrate several terabytes worth of Sisense customer data, which apparently included millions of access tokens, email account passwords, and even SSL certificates.
The incident raises questions about whether Sisense was doing enough to protect sensitive data entrusted to it by customers, such as whether the massive volume of stolen customer data was ever encrypted while at rest in these Amazon cloud servers.
It is clear, however, that unknown attackers now have all of the credentials that Sisense customers used in their dashboards.
The breach also makes clear that Sisense is somewhat limited in the clean-up actions that it can take on behalf of customers, because access tokens are essentially text files on your computer that allow you to stay logged in for extended periods of time — sometimes indefinitely. And depending on which service we’re talking about, it may be possible for attackers to re-use those access tokens to authenticate as the victim without ever having to present valid credentials.
Beyond that, it is largely up to Sisense customers to decide if and when they change passwords to the various third-party services that they’ve previously entrusted to Sisense.
Earlier today, a public relations firm working with Sisense reached out to learn if KrebsOnSecurity planned to publish any further updates on their breach (KrebsOnSecurity posted a screenshot of the CISO’s customer email to both LinkedIn and Mastodon on Wednesday evening). The PR rep said Sisense wanted to make sure they had an opportunity to comment before the story ran.
But when confronted with the details shared by my sources, Sisense apparently changed its mind.
“After consulting with Sisense, they have told me that they don’t wish to respond,” the PR rep said in an emailed reply.
Update, 6:49 p.m., ET: Added clarification that Sisense is using a self-hosted version of Gitlab, not the cloud version managed by Gitlab.com.
Also, Sisense’s CISO Dash just sent an update to customers directly. The latest advice from the company is far more detailed, and involves resetting a potentially large number of access tokens across multiple technologies, including Microsoft Active Directory credentials, GIT credentials, web access tokens, and any single sign-on (SSO) secrets or tokens.
The full message from Dash to customers is below:
“Good Afternoon,
We are following up on our prior communication of April 10, 2024, regarding reports that certain Sisense company information may have been made available on a restricted access server. As noted, we are taking this matter seriously and our investigation remains ongoing.
Our customers must reset any keys, tokens, or other credentials in their environment used within the Sisense application.
Specifically, you should:
– Change Your Password: Change all Sisense-related passwords on http://my.sisense.com
– Non-SSO:
– Replace the Secret in the Base Configuration Security section with your GUID/UUID.
– Reset passwords for all users in the Sisense application.
– Logout all users by running GET /api/v1/authentication/logout_all under Admin user.
– Single Sign-On (SSO):
– If you use SSO JWT for the user’s authentication in Sisense, you will need to update sso.shared_secret in Sisense and then use the newly generated value on the side of the SSO handler.
– We strongly recommend rotating the x.509 certificate for your SSO SAML identity provider.
– If you utilize OpenID, it’s imperative to rotate the client secret as well.
– Following these adjustments, update the SSO settings in Sisense with the revised values.
– Logout all users by running GET /api/v1/authentication/logout_all under Admin user.
– Customer Database Credentials: Reset credentials in your database that were used in the Sisense application to ensure continuity of connection between the systems.
– Data Models: Change all usernames and passwords in the database connection string in the data models.
– User Params: If you are using the User Params feature, reset them.
– Active Directory/LDAP: Change the username and user password of users whose authorization is used for AD synchronization.
– HTTP Authentication for GIT: Rotate the credentials in every GIT project.
– B2D Customers: Use the following API PATCH api/v2/b2d-connection in the admin section to update the B2D connection.
– Infusion Apps: Rotate the associated keys.
– Web Access Token: Rotate all tokens.
– Custom Email Server: Rotate associated credentials.
– Custom Code: Reset any secrets that appear in custom code Notebooks.
If you need any assistance, please submit a customer support ticket at https://community.sisense.com/t5/support-portal/bd-p/SupportPortal and mark it as critical. We have a dedicated response team on standby to assist with your requests.
At Sisense, we give paramount importance to security and are committed to our customers’ success. Thank you for your partnership and commitment to our mutual security.
Regards,
Sangram Dash
Chief Information Security Officer”



