Please Don’t Feed the Scattered Lapsus ShinyHunters
A prolific data ransom gang that calls itself Scattered Lapsus ShinyHunters (SLSH) has a distinctive playbook when it seeks to extort payment from victim firms: Harassing, threatening and even swatting executives and their families, all while notifying journalists and regulators about the extent of the intrusion. Some victims reportedly are paying — perhaps as much to contain the stolen data as to stop the escalating personal attacks. But a top SLSH expert warns that engaging at all beyond a “We’re not paying” response only encourages further harassment, noting that the group’s fractious and unreliable history means the only winning move is not to pay.

Image: Shutterstock.com, @Mungujakisa
Unlike traditional, highly regimented Russia-based ransomware affiliate groups, SLSH is an unruly and somewhat fluid English-language extortion gang that appears uninterested in building a reputation of consistent behavior whereby victims might have some measure of confidence that the criminals will keep their word if paid.
That’s according to Allison Nixon, director of research at the New York City based security consultancy Unit 221B. Nixon has been closely tracking the criminal group and individual members as they bounce between various Telegram channels used to extort and harass victims, and she said SLSH differs from traditional data ransom groups in other important ways that argue against trusting them to do anything they say they’ll do — such as destroying stolen data.
Like SLSH, many traditional Russian ransomware groups have employed high-pressure tactics to force payment in exchange for a decryption key and/or a promise to delete stolen data, such as publishing a dark web shaming blog with samples of stolen data next to a countdown clock, or notifying journalists and board members of the victim company. But Nixon said the extortion from SLSH quickly escalates way beyond that — to threats of physical violence against executives and their families, DDoS attacks on the victim’s website, and repeated email-flooding campaigns.
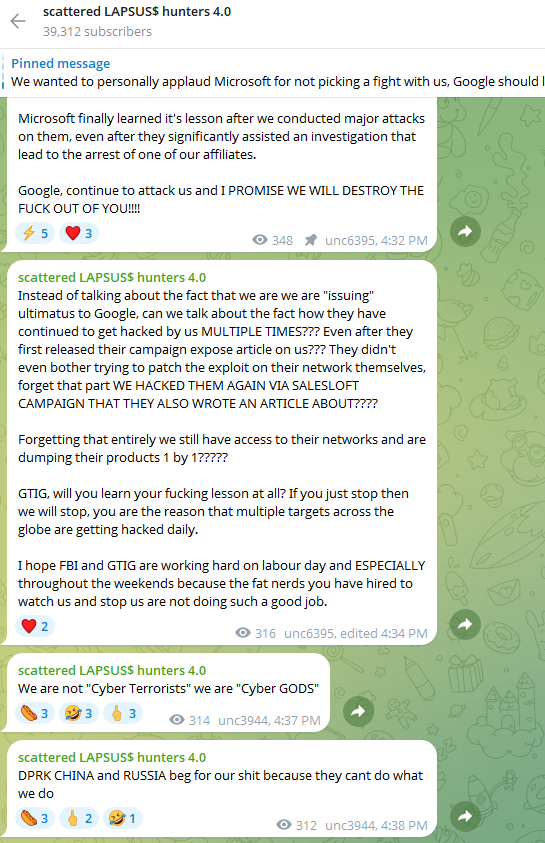
SLSH is known for breaking into companies by phishing employees over the phone, and using the purloined access to steal sensitive internal data. In a January 30 blog post, Google’s security forensics firm Mandiant said SLSH’s most recent extortion attacks stem from incidents spanning early to mid-January 2026, when SLSH members pretended to be IT staff and called employees at targeted victim organizations claiming that the company was updating MFA settings.
“The threat actor directed the employees to victim-branded credential harvesting sites to capture their SSO credentials and MFA codes, and then registered their own device for MFA,” the blog post explained.
Victims often first learn of the breach when their brand name is uttered on whatever ephemeral new public Telegram group chat SLSH is using to threaten, extort and harass their prey. According to Nixon, the coordinated harassment on the SLSH Telegram channels is part of a well-orchestrated strategy to overwhelm the victim organization by manufacturing humiliation that pushes them over the threshold to pay.
Nixon said multiple executives at targeted organizations have been subject to “swatting” attacks, wherein SLSH communicated a phony bomb threat or hostage situation at the target’s address in the hopes of eliciting a heavily armed police response at their home or place of work.
“A big part of what they’re doing to victims is the psychological aspect of it, like harassing executives’ kids and threatening the board of the company,” Nixon told KrebsOnSecurity. “And while these victims are getting extortion demands, they’re simultaneously getting outreach from media outlets saying, ‘Hey, do you have any comments on the bad things we’re going to write about you.”
In a blog post today, Unit 221B argues that no one should negotiate with SLSH because the group has demonstrated a willingness to extort victims based on promises that it has no intention to keep. Nixon points out that all of SLSH’s known members hail from The Com, shorthand for a constellation of cybercrime-focused Discord and Telegram communities which serve as a kind of distributed social network that facilitates instant collaboration.
Nixon said Com-based extortion groups tend to instigate feuds and drama between group members, leading to lying, betrayals, credibility destroying behavior, backstabbing, and sabotaging each other.
“With this type of ongoing dysfunction, often compounding by substance abuse, these threat actors often aren’t able to act with the core goal in mind of completing a successful, strategic ransom operation,” Nixon wrote. “They continually lose control with outbursts that put their strategy and operational security at risk, which severely limits their ability to build a professional, scalable, and sophisticated criminal organization network for continued successful ransoms – unlike other, more tenured and professional criminal organizations focused on ransomware alone.”
Intrusions from established ransomware groups typically center around encryption/decryption malware that mostly stays on the affected machine. In contrast, Nixon said, ransom from a Com group is often structured the same as violent sextortion schemes against minors, wherein members of The Com will steal damaging information, threaten to release it, and “promise” to delete it if the victim complies without any guarantee or technical proof point that they will keep their word. She writes:
A key component of SLSH’s efforts to convince victims to pay, Nixon said, involves manipulating the media into hyping the threat posed by this group. This approach also borrows a page from the playbook of sextortion attacks, she said, which encourages predators to keep targets continuously engaged and worrying about the consequences of non-compliance.
“On days where SLSH had no substantial criminal ‘win’ to announce, they focused on announcing death threats and harassment to keep law enforcement, journalists, and cybercrime industry professionals focused on this group,” she said.
Nixon knows a thing or two about being threatened by SLSH: For the past several months, the group’s Telegram channels have been replete with threats of physical violence against her, against Yours Truly, and against other security researchers. These threats, she said, are just another way the group seeks to generate media attention and achieve a veneer of credibility, but they are useful as indicators of compromise because SLSH members tend to name drop and malign security researchers even in their communications with victims.
“Watch for the following behaviors in their communications to you or their public statements,” Unit 221B’s advisory reads. “Repeated abusive mentions of Allison Nixon (or “A.N”), Unit 221B, or cybersecurity journalists—especially Brian Krebs—or any other cybersecurity employee, or cybersecurity company. Any threats to kill, or commit terrorism, or violence against internal employees, cybersecurity employees, investigators, and journalists.”
Unit 221B says that while the pressure campaign during an extortion attempt may be traumatizing to employees, executives, and their family members, entering into drawn-out negotiations with SLSH incentivizes the group to increase the level of harm and risk, which could include the physical safety of employees and their families.
“The breached data will never go back to the way it was, but we can assure you that the harassment will end,” Nixon said. “So, your decision to pay should be a separate issue from the harassment. We believe that when you separate these issues, you will objectively see that the best course of action to protect your interests, in both the short and long term, is to refuse payment.”