60,000 Records Exposed in Cyberattack on Uzbekistan Government




 Image Source: X[/caption]
Image Source: X[/caption]






“Our priority response to this event is protecting the information entrusted to us and maintaining continuity of critical public health services. By taking a proactive approach and engaging specialized expertise, we are working diligently to restore systems and keep our community informed.”The organization serves Peterborough city and county, Northumberland and Haliburton counties, Kawartha Lakes, and the First Nations communities of Curve Lake and Alderville. The cyberattack prompted a review of all systems that could potentially be affected, ensuring that any vulnerabilities are mitigated.

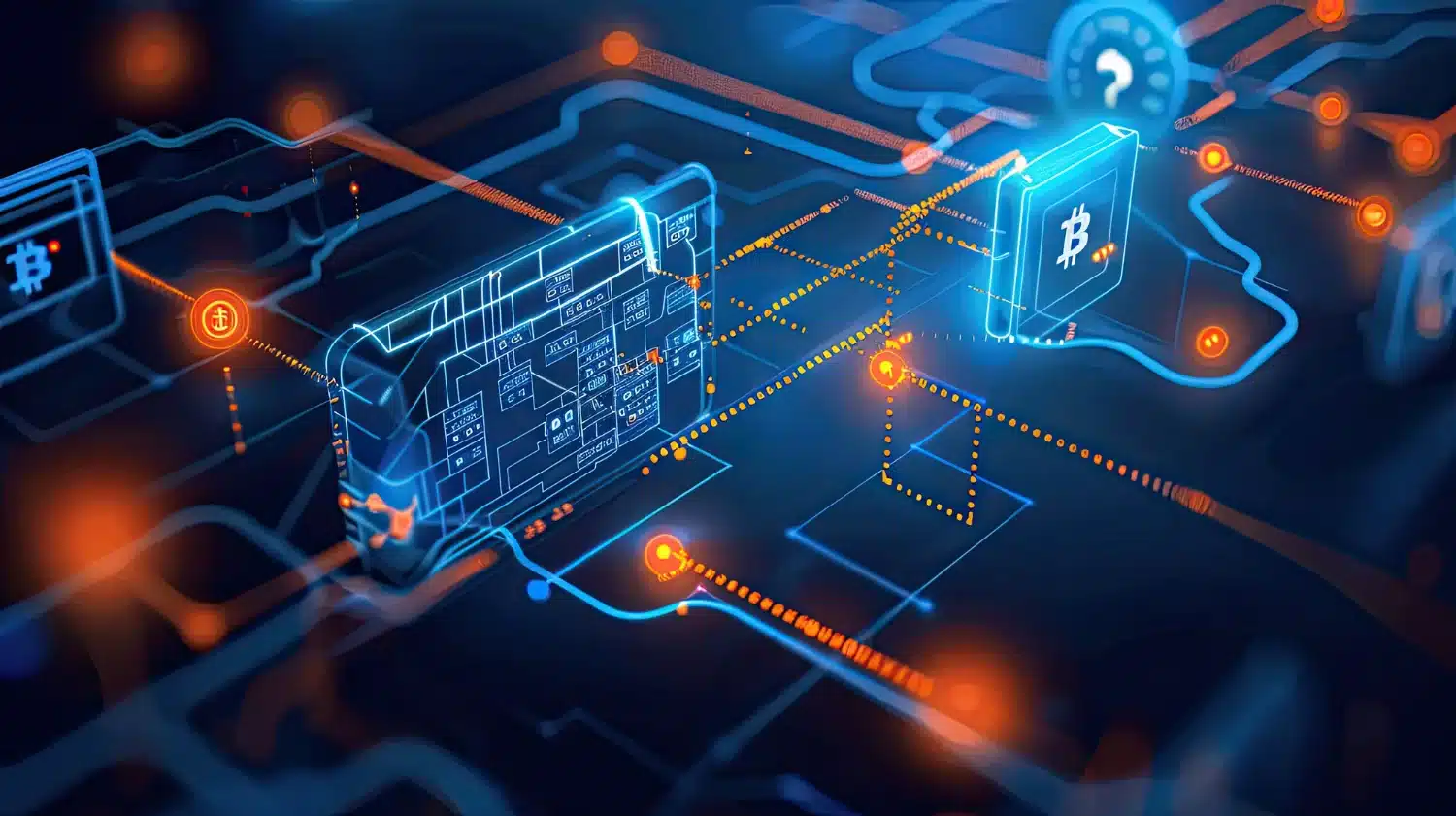
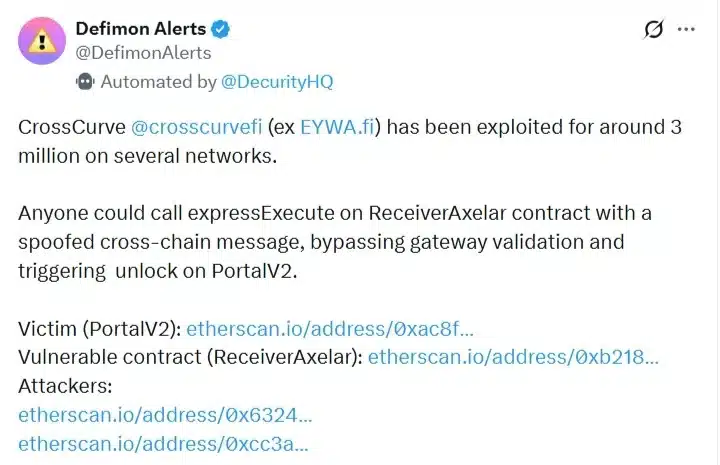 CrossCurve Exploit Details (Source: Defimon Alerts on X)[/caption]
By exploiting this flaw, attackers were able to bypass the intended gateway validation logic and trigger unauthorized token unlocks on the protocol’s PortalV2 contract. As a result, funds were drained without proper authorization. The exploit impacted the CrossCurve bridge across multiple networks, highlighting the risks associated with cross-chain messaging systems.
Data from Arkham Intelligence, shared by Defimon Alerts, shows that the PortalV2 contract’s balance dropped from roughly $3 million to nearly zero around January 31. Transaction data indicates that the exploit unfolded across several chains, rather than being confined to a single network.
CrossCurve Exploit Details (Source: Defimon Alerts on X)[/caption]
By exploiting this flaw, attackers were able to bypass the intended gateway validation logic and trigger unauthorized token unlocks on the protocol’s PortalV2 contract. As a result, funds were drained without proper authorization. The exploit impacted the CrossCurve bridge across multiple networks, highlighting the risks associated with cross-chain messaging systems.
Data from Arkham Intelligence, shared by Defimon Alerts, shows that the PortalV2 contract’s balance dropped from roughly $3 million to nearly zero around January 31. Transaction data indicates that the exploit unfolded across several chains, rather than being confined to a single network.

 The Polish report notes that the DynoWiper malware used in the latest attacks “contains certain similarities to wiper-type tools3 associated with the activity cluster publicly known as ‘Sandworm’ and ‘SeashellBlizzard,’” but the report adds, “Despite identifying commonalities in behavioral characteristics and overall architecture, the level of similarity is too low to attribute DynoWiper to previously used wiper families.”
The attackers’ activities began between March and May 2025, months before the December 29 attack.
The Polish report notes that the DynoWiper malware used in the latest attacks “contains certain similarities to wiper-type tools3 associated with the activity cluster publicly known as ‘Sandworm’ and ‘SeashellBlizzard,’” but the report adds, “Despite identifying commonalities in behavioral characteristics and overall architecture, the level of similarity is too low to attribute DynoWiper to previously used wiper families.”
The attackers’ activities began between March and May 2025, months before the December 29 attack.






 Krzysztof Gawkowski Speaks on the Poland cyberattack (Source: RMF)[/caption]
While stressing over the seriousness of the Poland cyberattack, Gawkowski also sought to reassure the public. “There is no need to panic,” he said, adding that state institutions were well prepared to respond and had acted effectively to prevent the worst-case scenario.
Additional details were provided earlier by Energy Minister Miłosz Motyka, who said that hackers attempted to breach multiple electricity-producing facilities across the country. The targets included one combined heat and power plant as well as numerous individual renewable energy sources. Motyka described the incident as unprecedented in its coordination.
“We have not experienced an attack like this before,” he said. “For the first time, various locations were targeted simultaneously.” According to the minister, the attack was successfully countered before it could cause lasting damage.
Krzysztof Gawkowski Speaks on the Poland cyberattack (Source: RMF)[/caption]
While stressing over the seriousness of the Poland cyberattack, Gawkowski also sought to reassure the public. “There is no need to panic,” he said, adding that state institutions were well prepared to respond and had acted effectively to prevent the worst-case scenario.
Additional details were provided earlier by Energy Minister Miłosz Motyka, who said that hackers attempted to breach multiple electricity-producing facilities across the country. The targets included one combined heat and power plant as well as numerous individual renewable energy sources. Motyka described the incident as unprecedented in its coordination.
“We have not experienced an attack like this before,” he said. “For the first time, various locations were targeted simultaneously.” According to the minister, the attack was successfully countered before it could cause lasting damage.

 Kyowon Group alerts users to a cyberattack on its systems (Source: Kyowon Group)[/caption]
A Kyowon Group representative confirmed the breach, stating, “We have confirmed indications of a breach,” while emphasizing that investigations were still underway. The representative added, “We are still investigating whether any personal information has been leaked.” The company also announced that it planned to release an official statement the following morning once more details were confirmed.
Kyowon Group alerts users to a cyberattack on its systems (Source: Kyowon Group)[/caption]
A Kyowon Group representative confirmed the breach, stating, “We have confirmed indications of a breach,” while emphasizing that investigations were still underway. The representative added, “We are still investigating whether any personal information has been leaked.” The company also announced that it planned to release an official statement the following morning once more details were confirmed.



We don’t have many details:
President Donald Trump suggested Saturday that the U.S. used cyberattacks or other technical capabilities to cut power off in Caracas during strikes on the Venezuelan capital that led to the capture of Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro.
If true, it would mark one of the most public uses of U.S. cyber power against another nation in recent memory. These operations are typically highly classified, and the U.S. is considered one of the most advanced nations in cyberspace operations globally.


News:
The Danish Defence Intelligence Service (DDIS) announced on Thursday that Moscow was behind a cyber-attack on a Danish water utility in 2024 and a series of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on Danish websites in the lead-up to the municipal and regional council elections in November.
The first, it said, was carried out by the pro-Russian group known as Z-Pentest and the second by NoName057(16), which has links to the Russian state.
Slashdot thread.


 Source: Twitter[/caption]
While digital access was disrupted, card payments at in-store terminals, ATM withdrawals, and SMS-authenticated online payments remained functional, reducing the impact on day-to-day financial transactions.
Source: Twitter[/caption]
While digital access was disrupted, card payments at in-store terminals, ATM withdrawals, and SMS-authenticated online payments remained functional, reducing the impact on day-to-day financial transactions.

 CL0P is a top five ransomware group over its six-year history (Cyble)[/caption]
CL0P is a top five ransomware group over its six-year history (Cyble)[/caption] 

Denmark cyberattack allegations have escalated into a diplomatic confrontation with Russia, after Danish authorities accused Moscow of orchestrating two cyber incidents targeting critical infrastructure and democratic processes. On Thursday, Denmark announced it would summon the Russian ambassador following findings by the Danish Defence Intelligence Service (DDIS) linking Russia to a destructive cyberattack on a Danish water utility in 2024 and a series of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on Danish websites ahead of elections last month.
Danish officials described the Denmark cyberattack incidents as part of Russia’s broader hybrid warfare campaign against European countries supporting Ukraine, marking a rare public attribution of state-linked cyber operations.
[caption id="attachment_107928" align="alignnone" width="709"]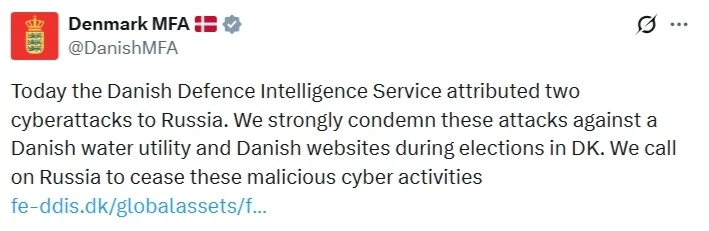 Denmark accuses Russia of cyberattacks (Source: Denmark MFA)[/caption]
In an official statement, Danish authorities said, “Russia is responsible for destructive and disruptive cyberattacks against Denmark.” The DDIS assessed that the Z-Pentest group, which executed the 2024 water utility attack, has links to the Russian state. Similarly, the agency determined that NoName057(16), the group responsible for the election-related DDoS attacks, also maintains ties to Russian state interests.
Denmark accuses Russia of cyberattacks (Source: Denmark MFA)[/caption]
In an official statement, Danish authorities said, “Russia is responsible for destructive and disruptive cyberattacks against Denmark.” The DDIS assessed that the Z-Pentest group, which executed the 2024 water utility attack, has links to the Russian state. Similarly, the agency determined that NoName057(16), the group responsible for the election-related DDoS attacks, also maintains ties to Russian state interests.



 Source: French Interior Ministry[/caption]
Source: French Interior Ministry[/caption]
















 Source: X[/caption]
WCC issued a similar update, explaining that its computer networks were temporarily shut down as a precaution. The council apologised to residents for the inconvenience but emphasised that immediate action was necessary to prevent further impact. “We are taking swift and effective action to bring all our systems back online as soon as possible,” the council stated on its website. Emergency contact numbers were provided for urgent issues.
Source: X[/caption]
WCC issued a similar update, explaining that its computer networks were temporarily shut down as a precaution. The council apologised to residents for the inconvenience but emphasised that immediate action was necessary to prevent further impact. “We are taking swift and effective action to bring all our systems back online as soon as possible,” the council stated on its website. Emergency contact numbers were provided for urgent issues.

From Anthropic:
In mid-September 2025, we detected suspicious activity that later investigation determined to be a highly sophisticated espionage campaign. The attackers used AI’s “agentic” capabilities to an unprecedented degree—using AI not just as an advisor, but to execute the cyberattacks themselves.
The threat actor—whom we assess with high confidence was a Chinese state-sponsored group—manipulated our Claude Code tool into attempting infiltration into roughly thirty global targets and succeeded in a small number of cases. The operation targeted large tech companies, financial institutions, chemical manufacturing companies, and government agencies. We believe this is the first documented case of a large-scale cyberattack executed without substantial human intervention.
[…]
The attack relied on several features of AI models that did not exist, or were in much more nascent form, just a year ago:
- Intelligence. Models’ general levels of capability have increased to the point that they can follow complex instructions and understand context in ways that make very sophisticated tasks possible. Not only that, but several of their well-developed specific skills—in particular, software coding—lend themselves to being used in cyberattacks.
- Agency. Models can act as agents—that is, they can run in loops where they take autonomous actions, chain together tasks, and make decisions with only minimal, occasional human input.
- Tools. Models have access to a wide array of software tools (often via the open standard Model Context Protocol). They can now search the web, retrieve data, and perform many other actions that were previously the sole domain of human operators. In the case of cyberattacks, the tools might include password crackers, network scanners, and other security-related software.