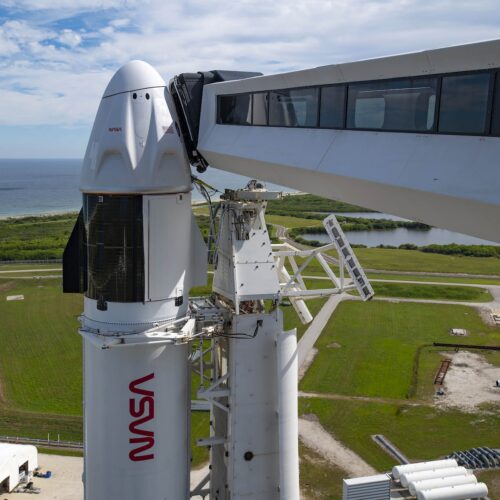
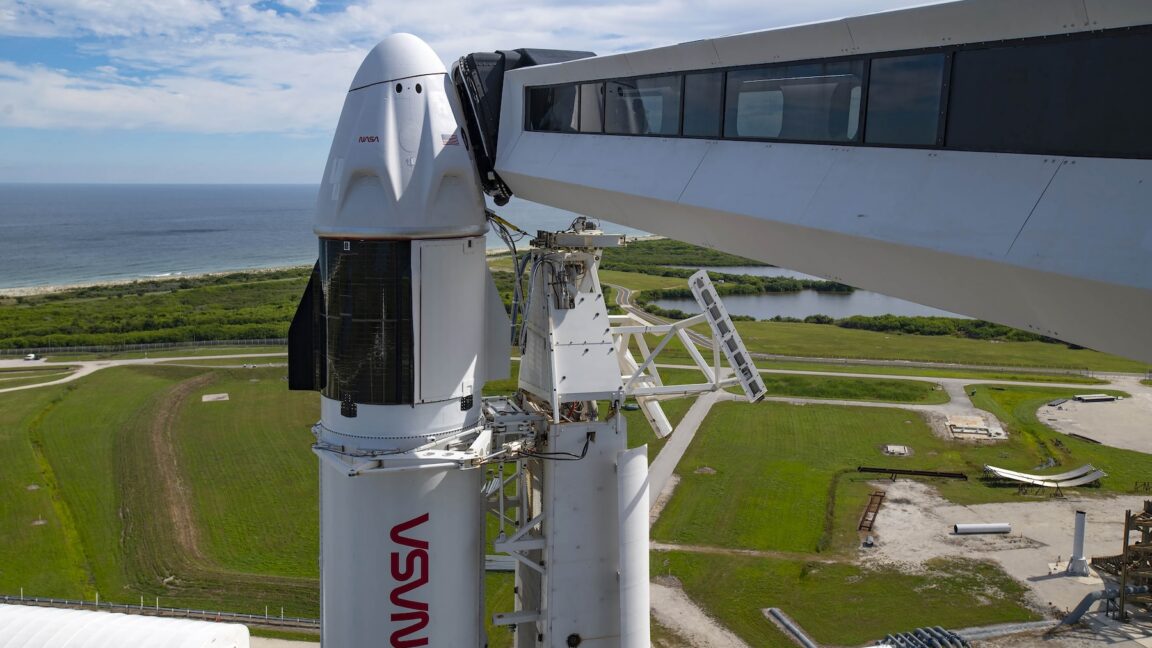
When Amazon badly needed a ride, Europe's Ariane 6 rocket delivered
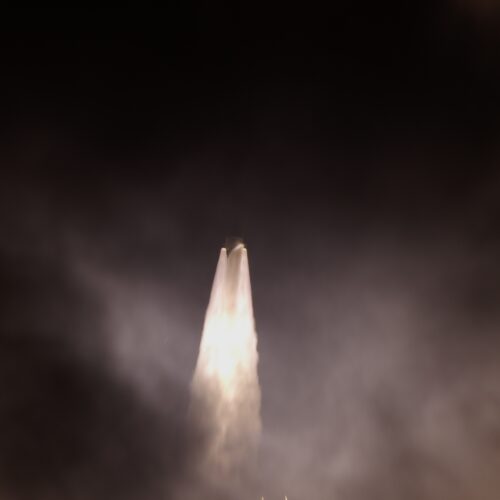
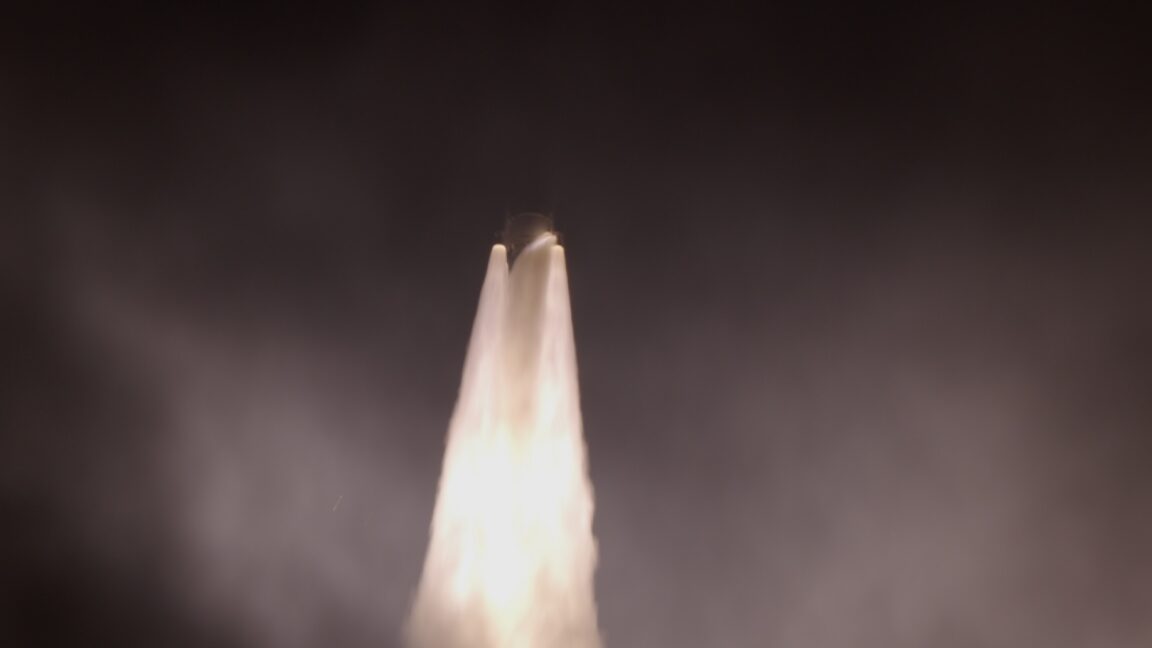
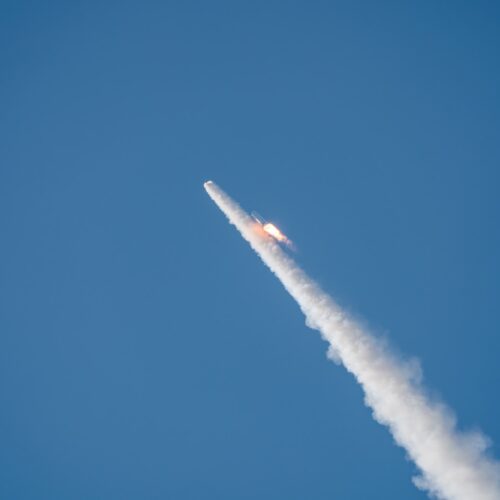
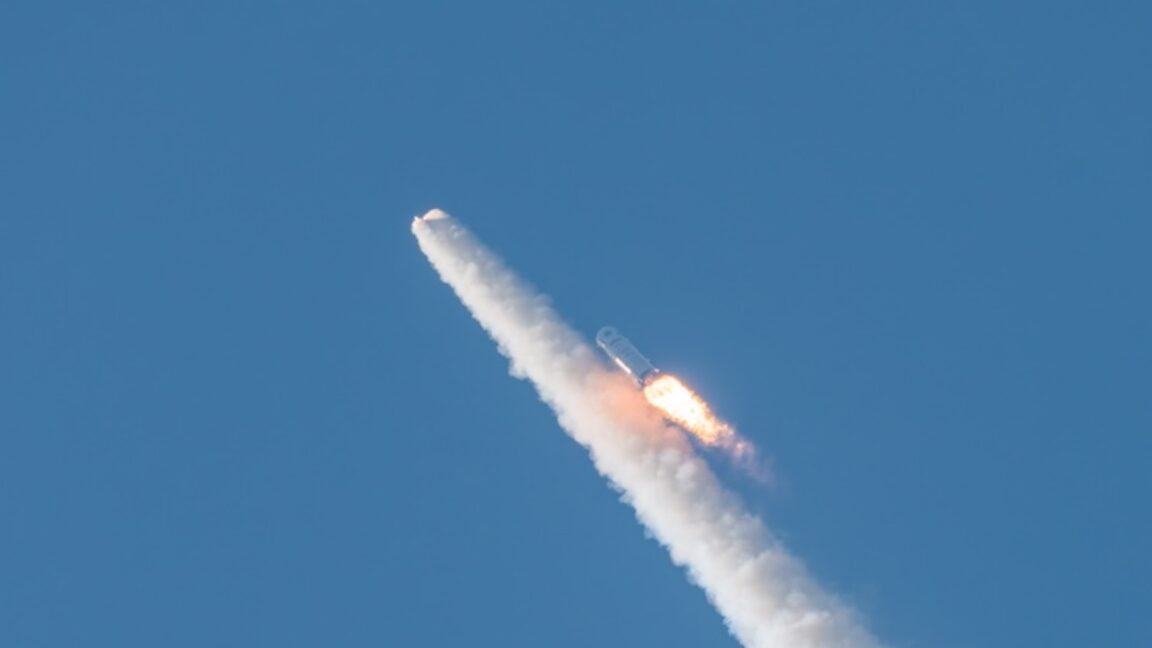
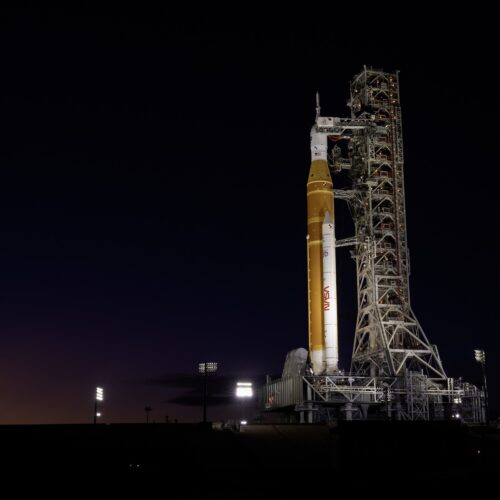
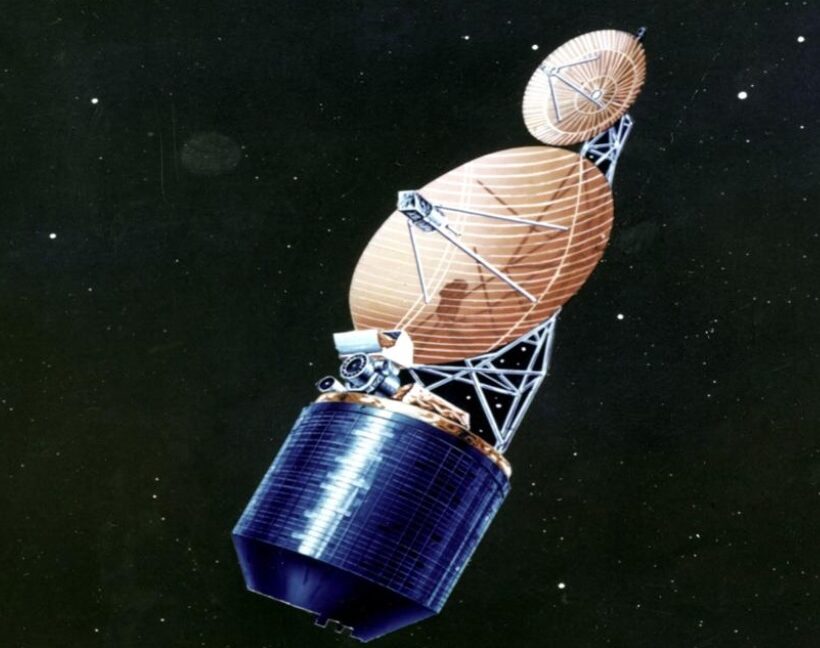
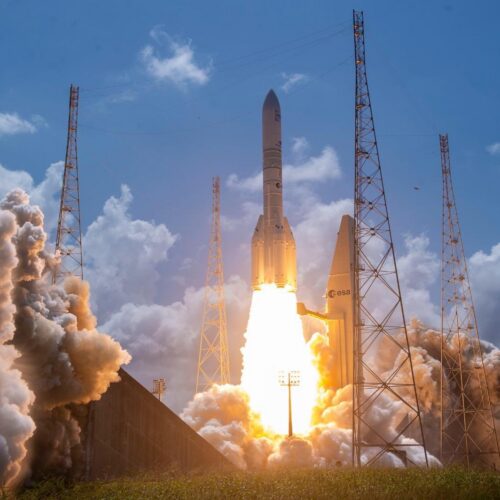
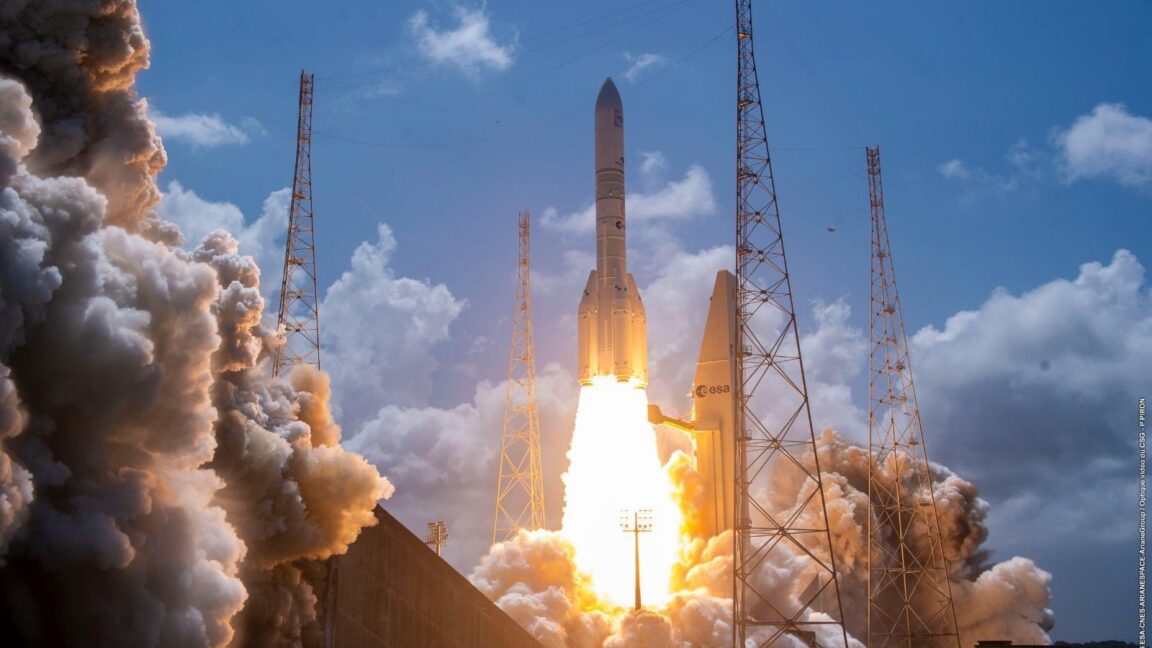
The heavy version of Europe's Ariane 6 rocket launched for the first time Thursday, hauling 32 spacecraft to low-Earth orbit for Amazon's satellite broadband constellation.
The Ariane 6 rocket lifted off from the Guiana Space Center on the northeastern coast of South America at 11:45 am EST (16:45 UTC), quickly soaring into a clear sky at the tropical spaceport on the power of a hydrogen-fueled main engine and four strap-on solid rocket boosters.
This Ariane 6 configuration, called Ariane 64, is the first to use the rocket's full complement of four boosters. Collectively, the rocket generated more than 3.4 million pounds of thrust (15,400 kilonewtons) of thrust as it steered northeast over the Atlantic Ocean. Less than two hours later, the rocket's upper stage released all 32 of Amazon's satellites into an on-target orbit at an altitude of 289 miles (465 kilometers).


© ESA-CNES-Arianespace-P. Piron