MIT Grieves Shooting Death of Renowned Director of Plasma Science Center
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

©
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Mark Weiser has written a really interesting article about just how desirable new computing environments, like VR, “AI” agents, and so on, really are. On the topic of “AI” agents, he writes:
Take intelligent agents. The idea, as near as I can tell, is that the ideal computer should be like a human being, only more obedient. Anything so insidiously appealing should immediately give pause. Why should a computer be anything like a human being? Are airplanes like birds, typewriters like pens, alphabets like mouths, cars like horses? Are human interactions so free of trouble, misunderstandings, and ambiguity that they represent a desirable computer interface goal? Further, it takes a lot of time and attention to build and maintain a smoothly running team of people, even a pair of people. A computer that I must talk to, give commands to, or have a relationship with (much less be intimate with), is a computer that is too much the center of attention.
↫ Mark Weiser
That’s one hell of a laser-focused takedown of “AI” tools in modern computing. When it comes to voice input, he argues that it’s too intrusive, too attention-grabbing, and a good tool is supposed to be the exact opposite of that. Voice input, especially when there’s other people around, puts the interface at the center of everyone‘s attention, and that’s not what you should want. With regards to virtual reality, he notes that it replaces your entire perception with nothing but interface, all around you, making it as much the center of attention as it could be.
What’s most fascinating about this article and its focus on “AI” agents, virtual reality, and more, is that it was published in January 1994. All the same questions, worries, and problems in computing we deal with today, were just as much topics of debate over thirty years ago. It’s remarkable how you could copy and paste many of the paragraphs written by Weiser in 1994 into the modern day, and they’d be just applicable now as they were then. I bet many of you had no idea the quoted paragraph was over thirty years old.
Mark Weiser was a visionary computer scientist, and had a long career at Xerox PARC, eventually landing him the role of Chief Technology Officer at PARC in 1996. He coined the term “ubiquitous computing” in 1988, the idea that computers are everywhere, in the form of wearables, handhelds, and larger displays – very prescient for 1988. He argued that computers should be unobtrusive, get out of your way, help you get things done that aren’t managing and shepherding the computer itself, and most of all, that computers should make users feel calm.
Sadly, he passed away in 1999, at the age of 46, clearly way too early for someone with such astonishing forward-looking insight into computing. Looking at what computers have become today, and what kinds of interfaces the major technology companies are trying to shove down our throats, we clearly strayed far from Weiser’s vision. Modern computers and interfaces are the exact opposite of unobtrusive and calming, and often hinder the things you’re trying to get done more than they should.
I wonder what Weiser would think about computing in 2025.
The AI wars continue to heat up. Just weeks after OpenAI declared a "code red" in its race against Google, the latter released its latest lightweight model: Gemini 3 Flash. This particular Flash is the latest in Google's Gemini 3 family, which started with Gemini 3 Pro, and Gemini 3 Deep Think. But while this latest model is meant to be a lighter, less expensive variant of the existing Gemini 3 models, Gemini 3 Flash is actually quite powerful in its own right. In fact, it beats out both Gemini 3 Pro and OpenAI's GPT-5.2 models in some benchmarks.
Lightweight models are typically meant for more basic queries, for lower-budget requests, or to be run on lower-powered hardware. That means they're often faster than more powerful models that take longer to process, but can do more. According to Google, Gemini 3 Flash combines the best of both those worlds, producing a model with Gemini 3's "Pro-grade reasoning," with "Flash-level latency, efficiency, and cost." While that likely matters most to developers, general users should also notice the improvements, as Gemini 3 Flash is now the default for both Gemini (the chatbot) and AI Mode, Google's AI-powered search.
You can see these improvements in Google's reported benchmarking stats for Gemini 3 Flash. In Humanity's Last Exam, an academic reasoning benchmark that tests LLMs on 2,500 questions across over 100 subjects, Gemini 3 Flash scored 33.7% with no tools, and 43.5% with search and code execution. Compare that to Gemini 3 Pro's 37.5% and 45.8% scores, respectively, or OpenAI's GPT-5.2's scores of 34.5% and 45.5%. In MMMU-Pro, a benchmark that test a model's multimodal understanding and reasoning, Gemini 3 Flash got the top score (81.2%), compared to Gemini 3 Pro (81%) and GPT-5.2 (79.5). In fact, across the 21 benchmarking tests Google highlights in its announcement, Gemini 3 Flash has the top score in three: MMMU-Pro (tied with Gemini 3 Pro), Toolathlon, and MMMLU. Gemini 3 Pro still takes the number one spot on the most tests here (14), and GPT-5.2 topped eight tests, but Gemini 3 Flash is holding its own.
Google notes that Gemini 3 Flash also outperforms both Gemini 3 Pro and the entire 2.5 series in the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, which tests the model's coding agent capabilities. Gemini 3 Flash scored a 78%, while Gemini 3 Pro scored 76.2%, Gemini 2.5 Flash scored 60.4%, and Gemini 2.5 Pro scored 59.6%. (Note that GPT-5.2 scored the best of the models Google mentions in this announcement.) It's a close race, especially when you consider this is a lightweight model scoring alongside these company's flagship models.
That might present an interesting dilemma for developers who pay to use AI models in their programs. Gemini 3 Flash costs $0.50 per every million input tokens (what you ask the model to do), and $3.00 per every million output tokens (the result the models returns from your prompt). Compare that to Gemini 3 Pro, which costs $2.00 per every million input tokens, and $12.00 per every million output tokens, or GPT-5.2's $3.00 and $15.00 costs, respectively. For what it's worth, it's not as cheap as Gemini 2.5 Flash ($0.30 and $2.50), or Grok 4.1 Fast for that matter ($0.20 and $0.50), but it does outperform these models in Google's reported benchmarks. Google notes that Gemini 3 Flash uses 30% fewer tokens on average than 2.5 Pro, which will save on cost, while also being three times faster.
If you're someone who needs LLMs like Gemini 3 Flash to power your products, but you don't want to pay the higher costs associated with more powerful models, I could image this latest lightweight model looking appealing from a financial perspective.
Most of us using AI aren't doing so as developers who need to worry about API pricing. The majority of Gemini users are likely experiencing the model through Google's consumer products, like Search, Workspace, and the Gemini app.
Starting today, Gemini 3 Flash is the default model in the Gemini app. Google says it can handle many tasks "in just a few seconds." That might include asking Gemini for tips on improving your golf swing based on a video of yourself, or uploading a speech on a given historical topic and requesting any facts you might have missed. You could also ask the bot to code you a functioning app from a series of thoughts.
You'll also experience Gemini 3 Flash in Google Search's AI Mode. Google says the new model is better at "parsing the nuances of your question," and thinks through each part of your request. AI Mode tries to return a more complete search result by scanning hundreds of sites at once, and putting together a summary with sources for your answer. We'll have to see if Gemini 3 Flash improves on previous iterations of AI Mode.
I'm someone who still doesn't find much use for generative AI products in their day-to-day lives, and I'm not entirely sure Gemini 3 Flash is going to change that for me. However, the balance of performance gains with the cost to process that power is interesting, and I'm particularly intrigued to see how OpenAI responds.
Gemini 3 Flash is available to all users starting today. In addition to general users in Gemini and AI Mode, developers will find it in the Gemini API in Google AI Studio, Gemini CLI, and Google Antigravity, the company's new agentic development platform. Enterprise users can use it in Vertex AI and Gemini Enterprise.

We may earn a commission from links on this page.
America is a car-centric culture—more than 90% of U.S. households have at least one vehicle. There are a lot of different kinds of cars, from old classics being maintained with love, to snazzy new electric rides, or luxury cruisers filled with cutting-edge tech. Whichever kind you drive, getting the most out of your vehicle demands regular maintenance and sensible driving practices, but you can also goose just a bit more out of any vehicle with these universal car hacks.
If you’ve been driving for a while, you know that flat tires only come at the worst possible times. Sunny days when you have plenty of time? Those tires are infallible. Whiteout conditions and you’re racing to a job interview? Guaranteed flat—and you will discover that your lug nuts have fused and become absolutely impossible to shift.
One way to prevent this is the judicious use of a little anti-seize lubricant, which is designed to prevent rust and other corrosion. Mechanics argue about this, to be fair—some professionals believe that using anti-seize on lug nuts changes the required torque, which can loosen them over time. But plenty of folks have used a small amount of anti-seize lubricant to make changing or rotating tires a lot easier without any adverse effects. The key is to use a very small amount—just enough to protect the threads.
The seals around your car’s doors help to insulate the interior. Over time, these seals can become stiff and begin to fall apart, which makes your vehicle unattractive and less comfortable to ride in. You can prevent this with a simple hack: Grab some silicon lubricant and apply thin layer onto the rubber gaskets around your doors, trunk, and windows. It’ll save you a bit of frustrating maintenance in the future—and can prevent doors from freezing closed in winter. (An oft-repeated version of this hack is to use petroleum jelly, which is OK in a pinch, but it can cause rubber to degrade over time, which silicone lubricants won't.)
Tire tread is essential for the safe and efficient operation of your car. Bald tires not only make it more likely you’ll hydroplane or otherwise lose control of the vehicle, they also make your car burn more fuel to overcome their rolling resistance, lowering your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
Tire tread is measured in 32nds of an inch—new tires typically have a tread depth of 10/32” or 11/32”, and you should replace your tires when the tread is eroded to about 4/32” or less. You can track this easily with a quarter—find the most worn-down spot on your tire, slide an upside-down quarter into the tread. If you can see the top of Washington’s head, you should replace the tire. You can also use a penny to see if you can still see the top of Lincoln’s head, but this measures 2/32” of tire tread, which means you should replace the tire immediately. The quarter test warns you to replace your tire before it’s a dangerous situation.
A cracked windshield is ugly, and even a tiny crack will probably spread, slowly but inexorably, until you have no choice but to replace the glass entirely. If you have a noticeable crack in your windshield, you should replace it—but if that’s not possible right away, there’s a short-term hack you can use: Nail polish.
This isn’t a permanent repair, but it will buy you some time by slowing down the crack’s spread. Clean the damaged area thoroughly, then coat the exterior and interior of the cracked area with clear nail polish. Let it dry, and go about your business. You'll still eventually need to replace the windshield (or have a more permanent repair job done to it), but this hack will let you plan for the work instead of having to deal with it as an emergency.
Have you ever lost your keys, phone, or anything else between the seats in your car? If so, you know it’s like Mission: Impossible to reclaim your property. Those spaces were just not designed for human beings to get into.
An easy hack to prevent the situation from happening in the first place is to close off those gaps (this also prevents crumbs and other dirt from filling those spaces). Pipe insulation is the perfect material for this: Cut a piece to length and jam it between the seats (or the seats and the console), and never lose anything ever again. In a pinch, the ever-useful pool noodle could be used as well. Alternatively, you can buy storage organizers designed to fit in those gaps, which solve the problem while giving you some extra space for stuff.
A dent in your car is annoying—and potentially expensive to fix. For minor cosmetic dents, you don’t need any special tools or professional help. All you need is a heat source and a common bathroom plunger.
For the heat source, you can boil some water, pour it over the dent, then use the plunger to pull the dent out. You can also use a heat gun or a hair dryer, though the water might help the plunger get a nice seal on the car body.
Nothing’s more fun than fighting your way through frigid cold to your car, only to discover that the wiper blades have frozen to your windshield. Sure, your car will eventually heat up enough to free the wipers, but if you’d prefer not to have to wait for that miracle to happen, keep an old pair of tube socks in the glove compartment. On cold nights when frozen wipers are a good probability, cover your wiper blades with the socks. This will protect them from damage as well as prevent them from freezing onto your windshield.
This is one of those amazing tricks that people have difficulty believing, but it actually works: To save money on gas, always make right turns unless a left turn is absolutely necessary—yes, even if that makes your trip longer.
UPS put this policy into its vehicle routing software, instructing their drivers to avoid left turns as much as algorithmically possible, and it claims to use about 10 million fewer gallons of gas every year as a result. In fact, our greatest repository of scientific knowledge, Mythbusters, once did a segment proving that they used about 3% less fuel by avoiding as many left turns as possible while driving a fake delivery truck.
Note, this doesn’t mean never making a left turn. It means prioritizing right turns when planning your route, even if it makes your trip longer. Whether the extra time involved is worth saving a little gas money is a whole other decision.
Another annoyance on cold winter mornings? Frozen car locks and doors. While most newer cars have keyless entry these days, you can still find yourself dealing with a frozen door, and if your battery has died due to the cold, you might need to use a physical key to gain entry to the car. When that happens, a simple hack is to whip out the hand sanitizer you probably have in your coat pocket. Squirt some into the lock (or coat your physical key before you insert it) or around the edge of the door. After a few seconds, the alcohol in the sanitizer will have melted the ice and you’ll be able to easily open everything up.
No one has used a car’s glovebox to store gloves in a long time. What most of us do is jam things in there on the theory that we might need them someday, then forget what’s in there and go a decade or two without actually opening it.
Instead, hack that space with an organizer. You can find some molded plastic organizers designed to fit specific models (like this one for a Toyota Tacoma, or this one for Tesla Model 3s), or you can find wallet-style organizers that will keep your documentation and other items neatly stored, making the glove box actually useful for a change.

Physicists at the University of Amsterdam came up with a really cool bit of Christmas decor: a miniature 3D-printed Christmas tree, a mere 8 centimeters tall, made of ice, without any refrigeration equipment or other freezing technology, and at minimal cost. The secret is evaporative cooling, according to a preprint posted to the physics arXiv.
Evaporative cooling is a well-known phenomenon; mammals use it to regulate body temperature. You can see it in your morning cup of hot coffee: the hotter atoms rise to the top of the magnetic trap and “jump out” as steam. It also plays a role (along with shock wave dynamics and various other factors) in the formation of “wine tears.” It’s a key step in creating Bose-Einstein condensates.
And evaporative cooling is also the main culprit behind the infamous “stall” that so frequently plagues aspiring BBQ pit masters eager to make a successful pork butt. The meat sweats as it cooks, releasing the moisture within, and that moisture evaporates and cools the meat, effectively canceling out the heat from the BBQ. That’s why a growing number of competitive pit masters wrap their meat in tinfoil after the first few hours (usually when the internal temperature hits 170° F).
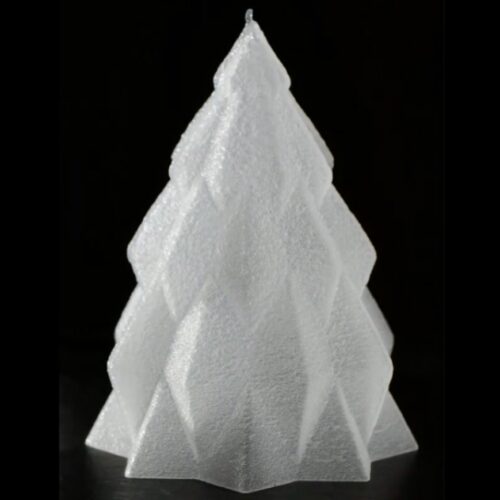
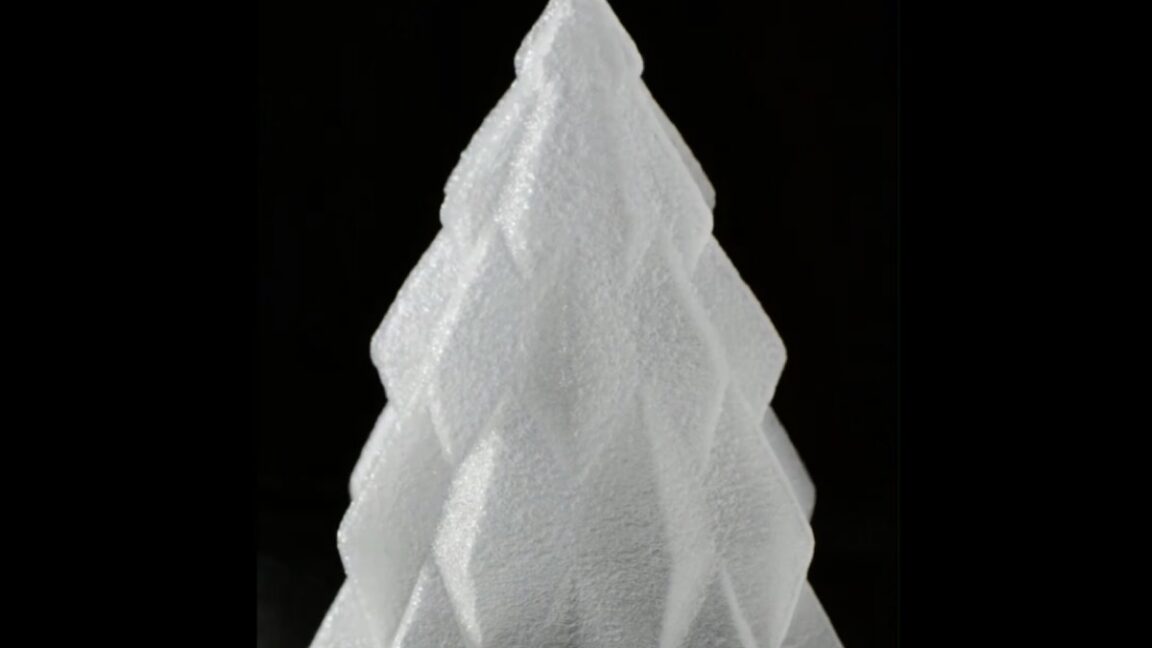


© University of Amsterdam
For most of photography’s roughly 200-year history, altering a photo convincingly required either a darkroom, some Photoshop expertise, or, at minimum, a steady hand with scissors and glue. On Tuesday, OpenAI released a tool that reduces the process to typing a sentence.
It’s not the first company to do so. While OpenAI had a conversational image-editing model in the works since GPT-4o in 2024, Google beat OpenAI to market in March with a public prototype, then refined it to a popular model called Nano Banana image model (and Nano Banana Pro). The enthusiastic response to Google’s image-editing model in the AI community got OpenAI’s attention.
OpenAI’s new GPT Image 1.5 is an AI image synthesis model that reportedly generates images up to four times faster than its predecessor and costs about 20 percent less through the API. The model rolled out to all ChatGPT users on Tuesday and represents another step toward making photorealistic image manipulation a casual process that requires no particular visual skills.


© OpenAI / ChatGPT
Larry Bushart, a man who was jailed for 37 days for reposting a Trump meme, has now sued the cops who allegedly schemed to keep him imprisoned for as long as possible simply because they disagreed with his point of view.
Bushart is a former cop who lost his post-retirement job after a seemingly vengeful sheriff jailed him for trolling a Charlie Kirk vigil post in a Facebook group. Upset that Kirk’s death commanded more attention than other victims of gun violence, Bushart posted a string of memes, among which was an image of Trump with an actual quote saying “We have to get over it” about a 2024 school shooting.
Perry County sheriff Nick Weems has since acknowledged that he “knew” that the meme referenced a prior school shooting. However, the entire time that Bushart was detained, Weems maintained that Bushart’s post incited “mass hysteria” from parents concerned that he was threatening violence at a local high school. Painting Bushart as indifferent to the supposed hysteria, Weems justified his arrest, as well as the $2 million bond ensuring Bushart couldn’t afford bail and remained behind bars.


© via FIRE
Federal Communications Commission Chairman Brendan Carr today faced blistering criticism in a Senate hearing for his September threats to revoke ABC station licenses over comments made by Jimmy Kimmel. While Democrats provided nearly all the criticism, Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) said that Congress should act to restrict the FCC’s power to intimidate news broadcasters.
As an immediate result of today’s hearing, the FCC removed a statement from its website that said it is an independent agency. Carr, who has embraced President Trump’s declaration that independent agencies may no longer operate independently from the White House, apparently didn’t realize that the website still called the FCC an independent agency.
“Yes or no, is the FCC an independent agency?” Sen. Ben Ray Luján (D-N.M.) asked. Carr answered that the FCC is not independent, prompting Luján to point to a statement on the FCC website calling the FCC “an independent US government agency overseen by Congress.”


© Getty Images | Heather Diehl
One of the big stories of last year’s Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas was the debut of Donut Lab’s diminutive but powerful electric motors. When I spoke with Donut earlier this year, the company told me that it was looking at applications ranging from drones to large automotive motors, but also things like wind turbines and even washing machines. Now, almost a year later, we have our first look at an electric vehicle that uses the technology, thanks to a new collaboration between Donut Lab and WATT Electric Vehicle Company.
WATT had previously developed the Passenger and Commercial EV Skateboard (PACES), a lightweight aluminum platform for low-volume EVs. Now, it’s integrating Donut’s motors, first with one for each rear wheel, although there will eventually be an all-wheel-drive variant, too.
The small EV chassis is rather intriguing—with the motors in the rear wheel hubs, the layout is even more space-efficient than a more conventional EV, which still needs to find a few cubic feet to package its drive unit(s). The two companies see plenty of potential for the platform, which they say could give rise to “multiple vehicle configurations from beach buggies to high-performance sports cars to commercial delivery vehicles.”
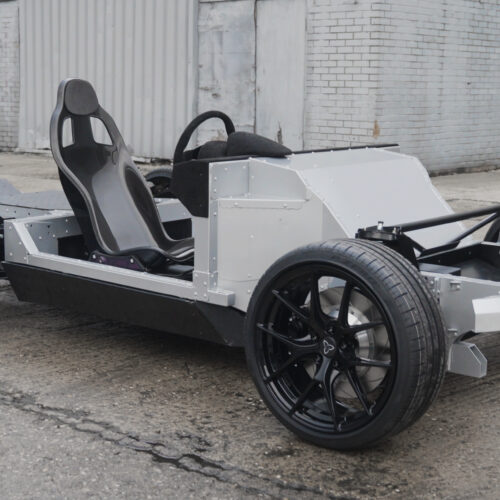


© Donut Lab
The US threatened to restrict some of the largest service providers in the European Union as retaliation for EU tech regulations and investigations are increasingly drawing Donald Trump’s ire.
On Tuesday, the Office of the US Trade Representative (USTR) issued a warning on X, naming Spotify, Accenture, Amadeus, Mistral, Publicis, and DHL among nine firms suddenly yanked into the middle of the US-EU tech fight.
“The European Union and certain EU Member States have persisted in a continuing course of discriminatory and harassing lawsuits, taxes, fines, and directives against US service providers,” USTR’s post said.


© Moor Studio | DigitalVision Vectors
Jeremy Carrasco makes videos under the handle @showtoolsai on TikTok, advocating for AI video literacy and pointing out tells you can look for to see if the videos on your feed are AI generated.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
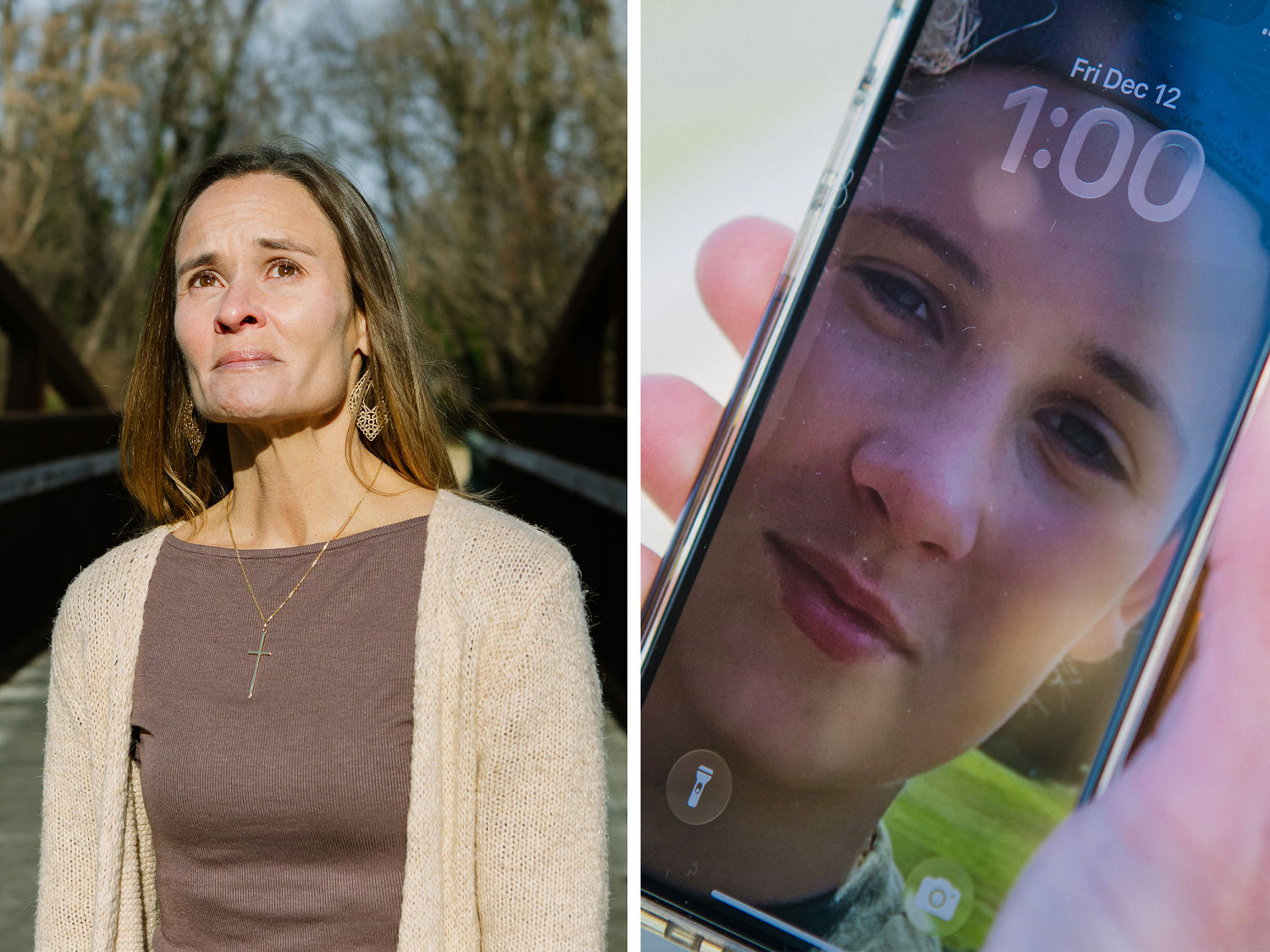



© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News

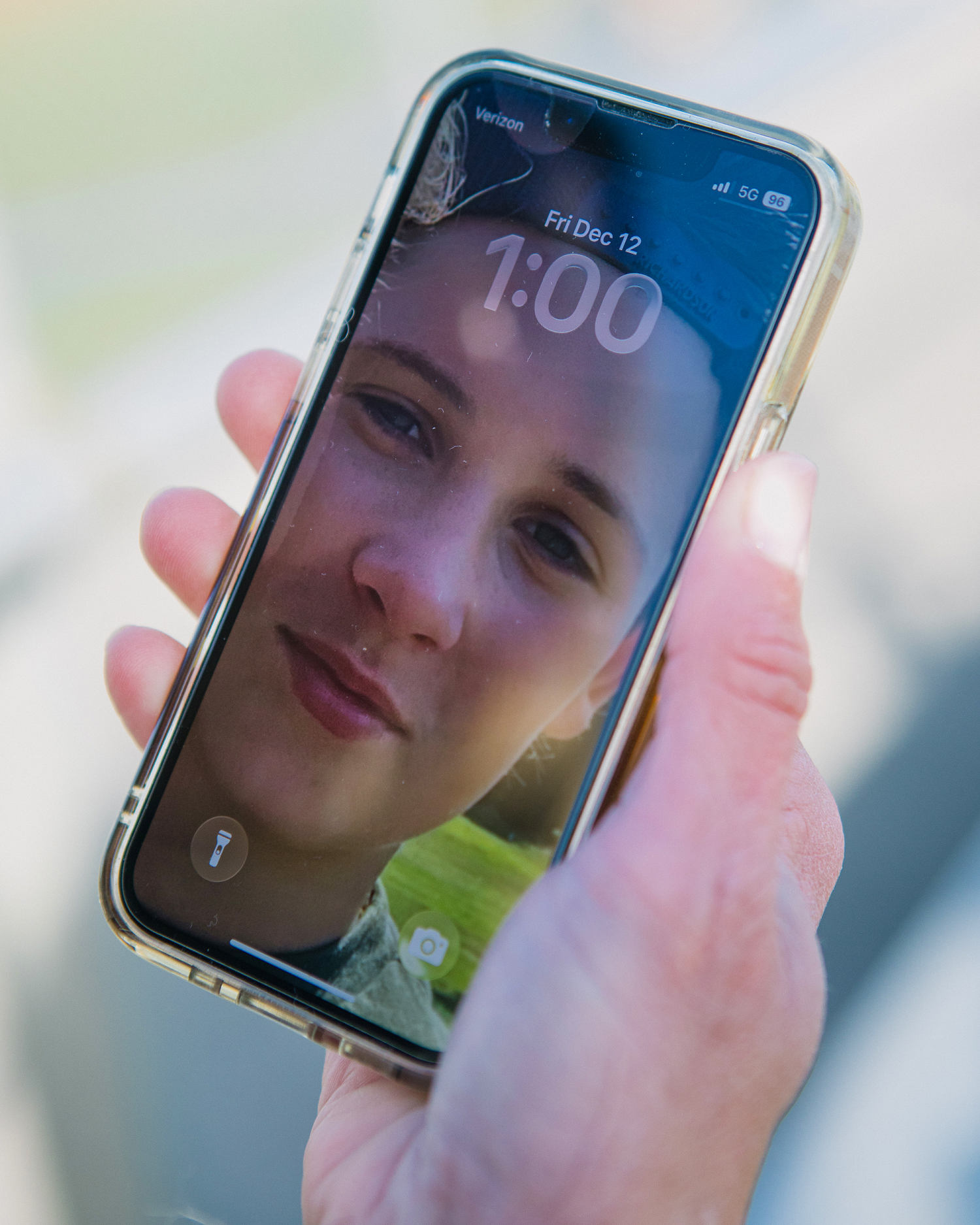
© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News
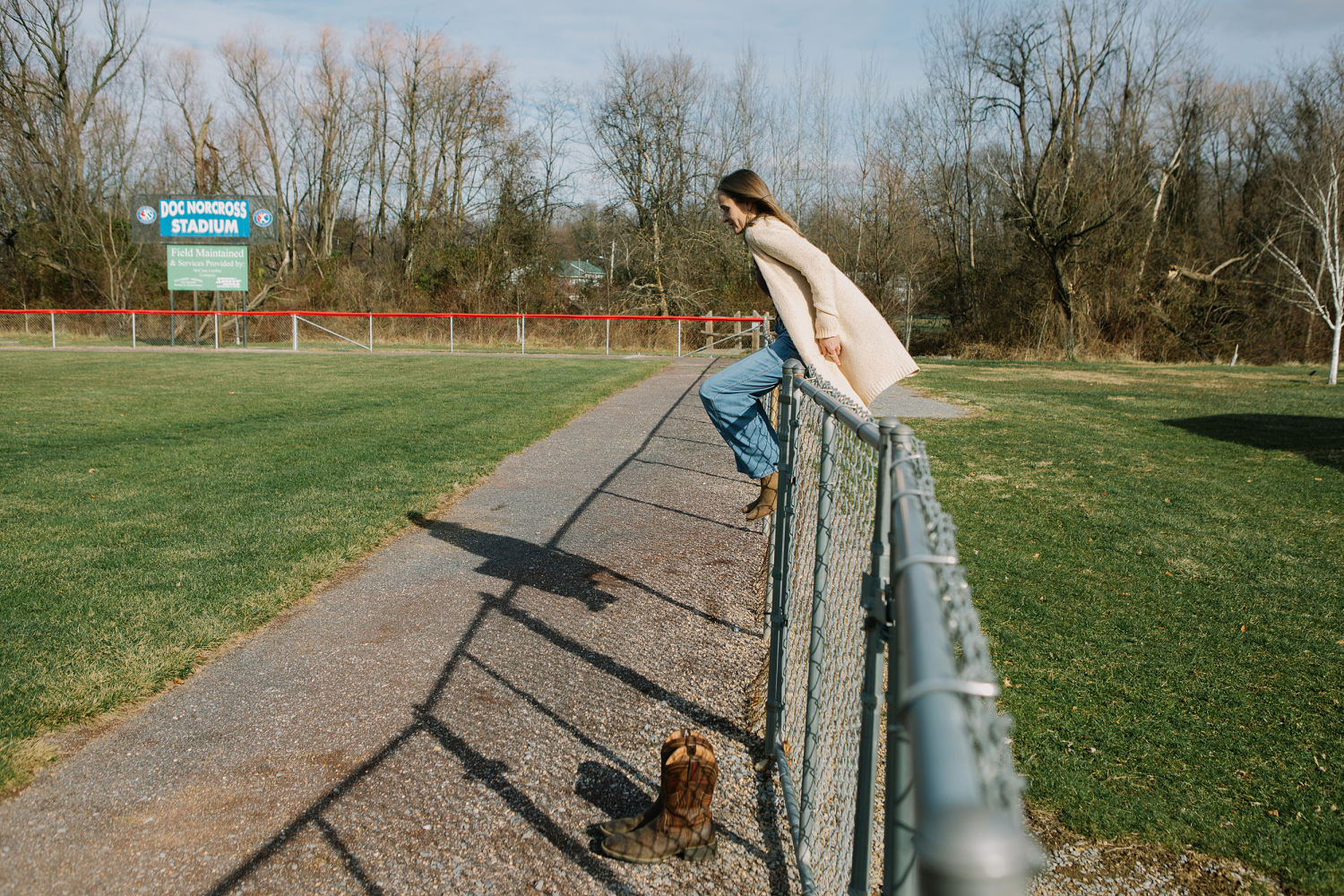

© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News

© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News
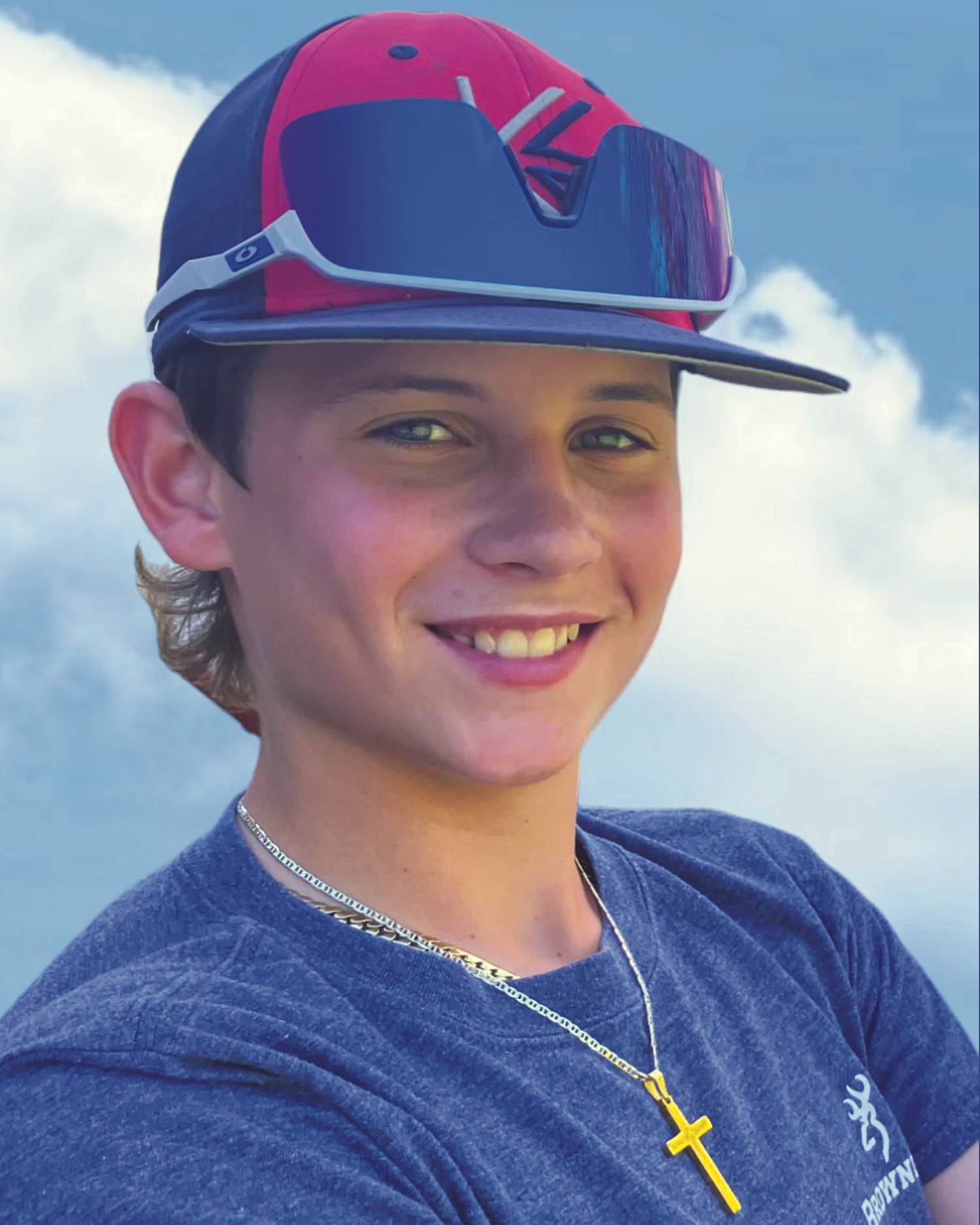

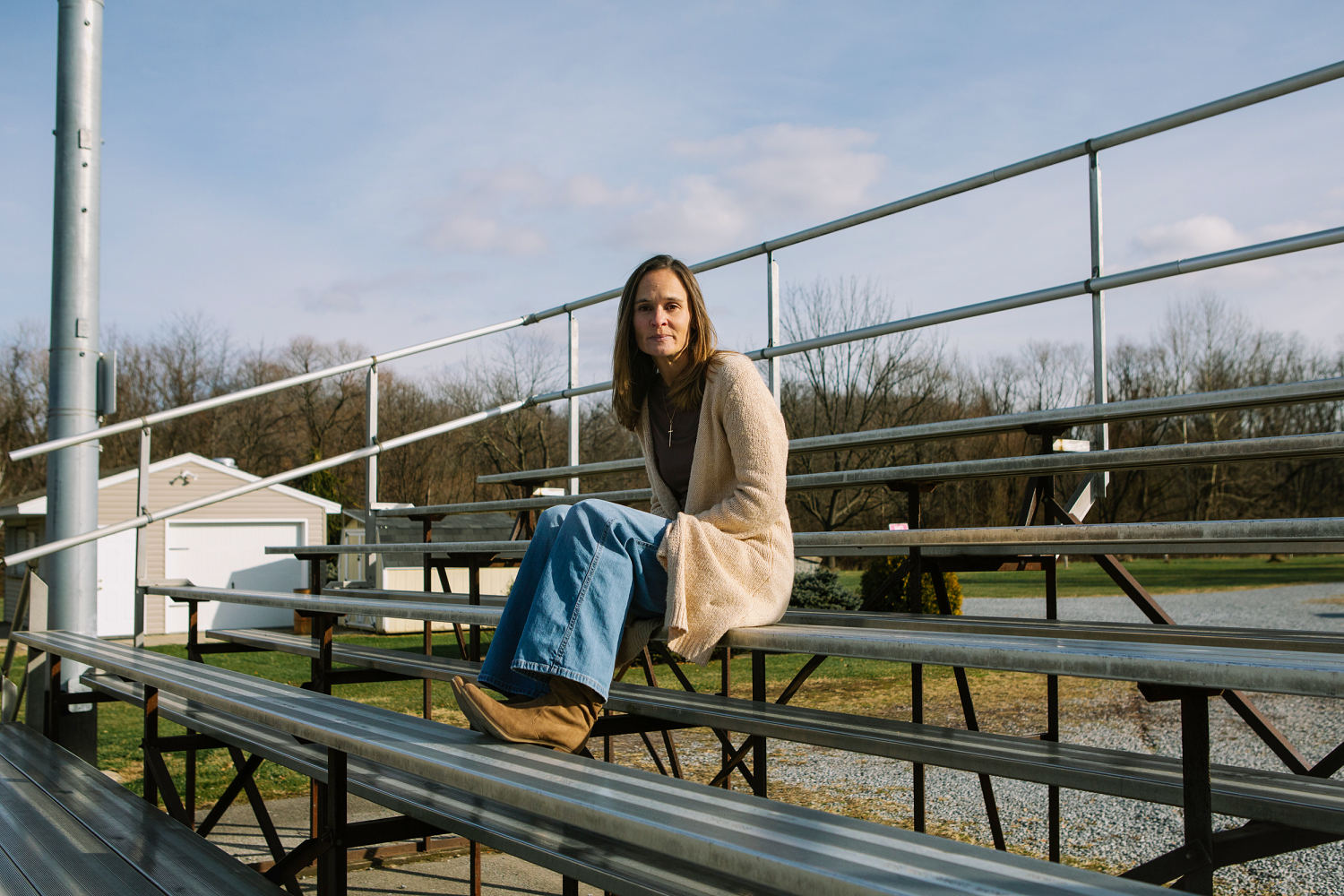
© Courtesy Tricia Maciejewski.
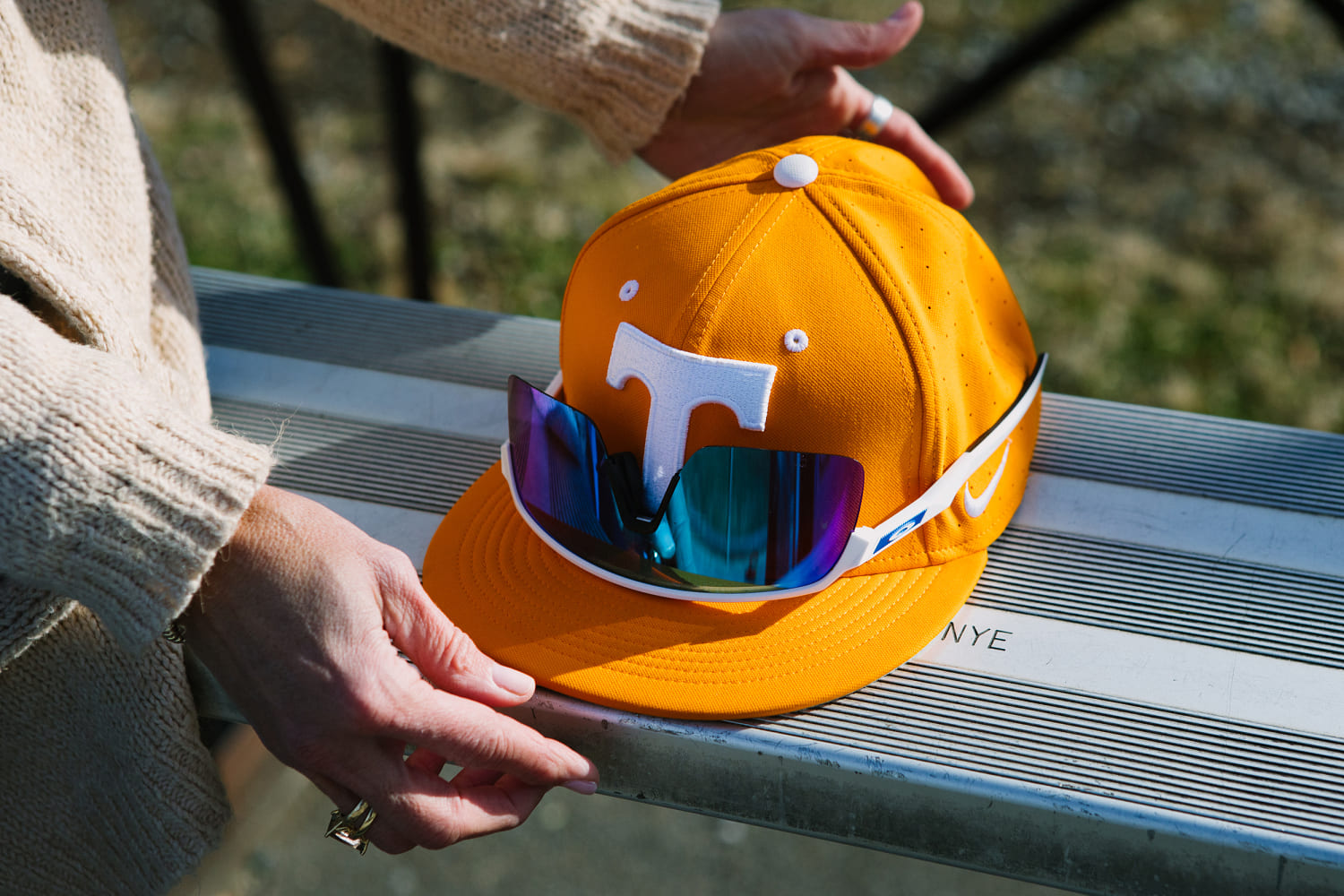

© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News

© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News

© Michelle Gustafson for NBC News

Read more of this story at Slashdot.

© Eric Lee for The New York Times
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

©
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
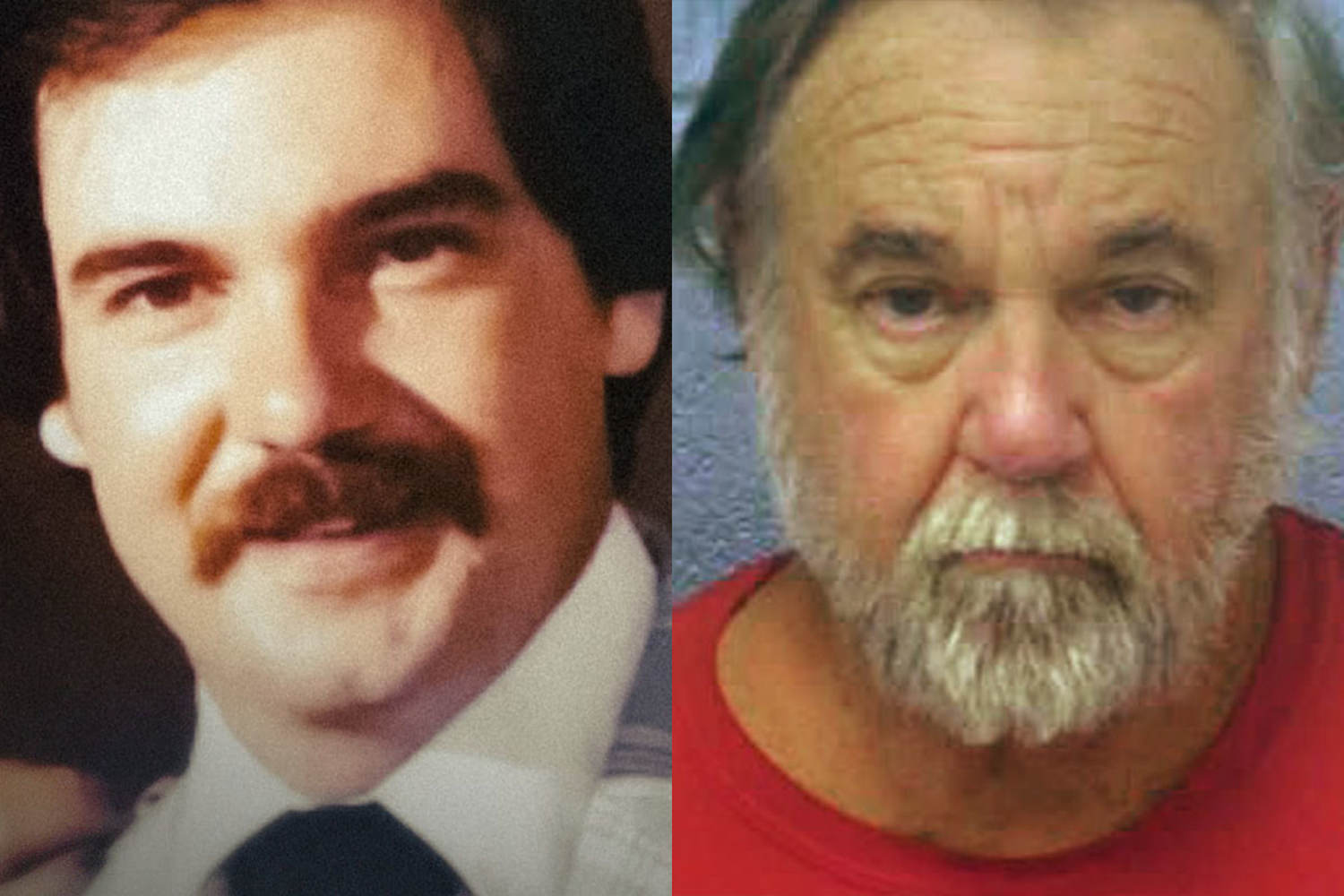


© Obtained by NBC News
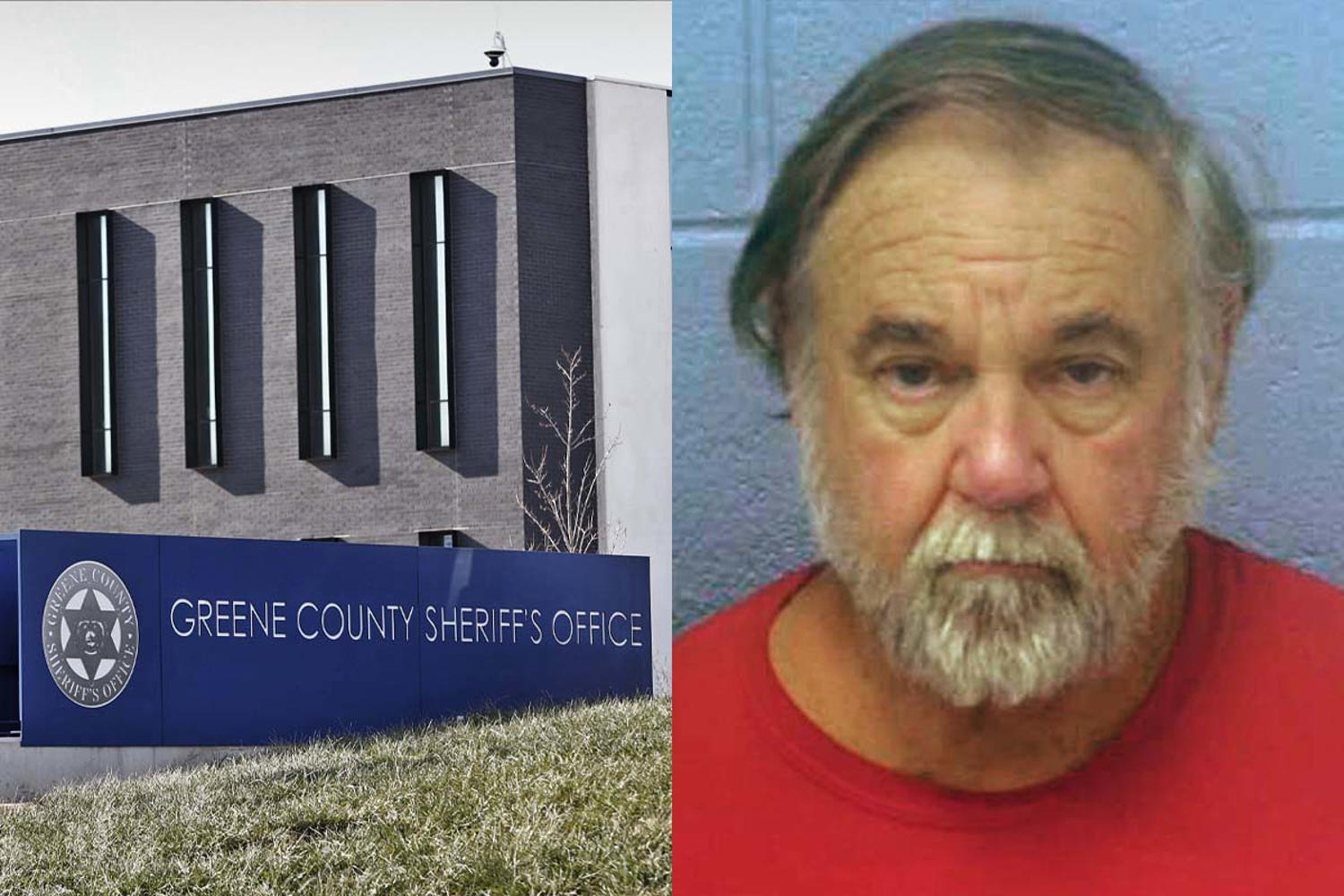

© STIDZ Media for NBC News; Greene County Sheriff's Office
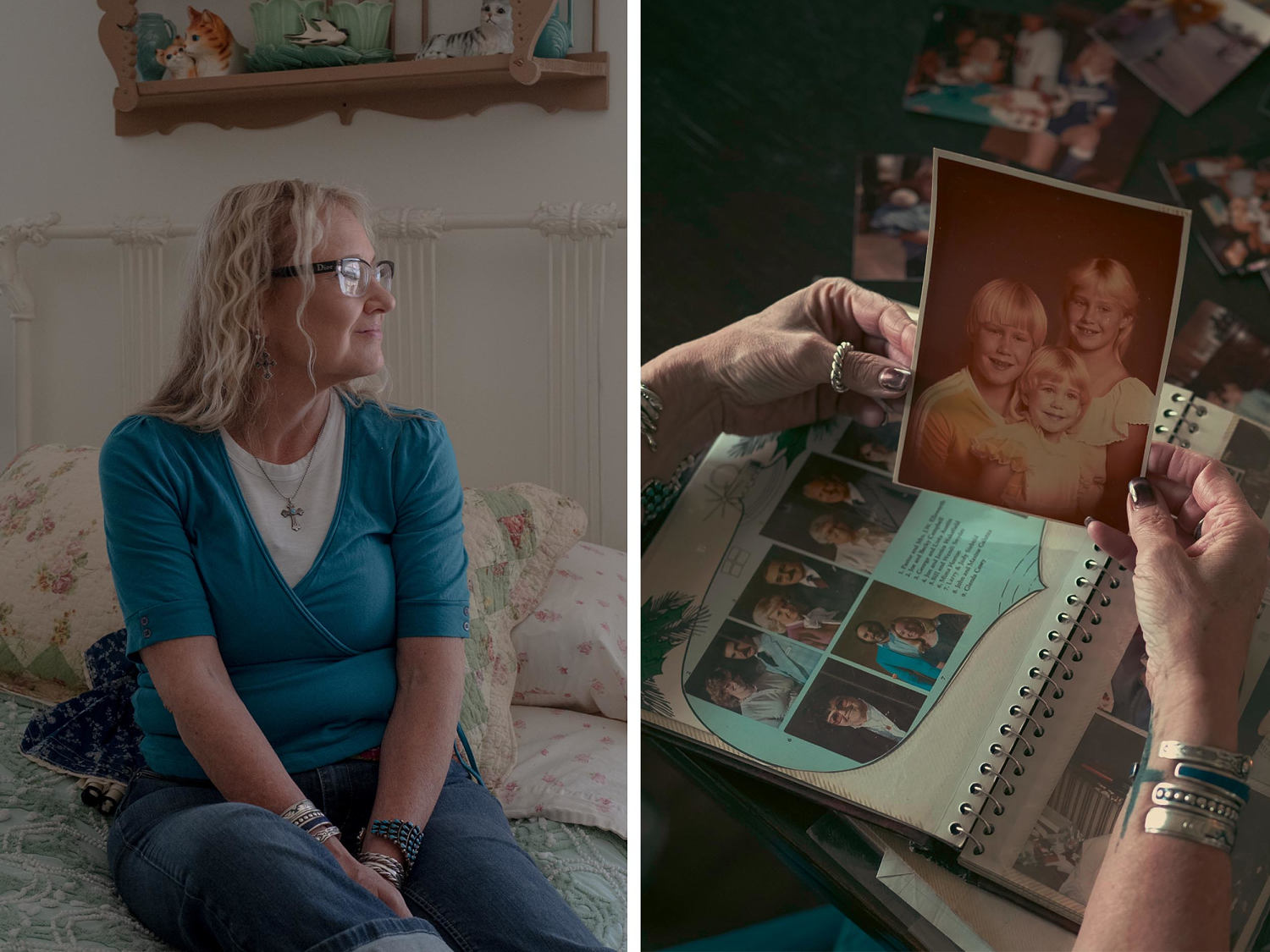
© September Dawn Bottoms for NBC News; Roberto Daza / NBC News
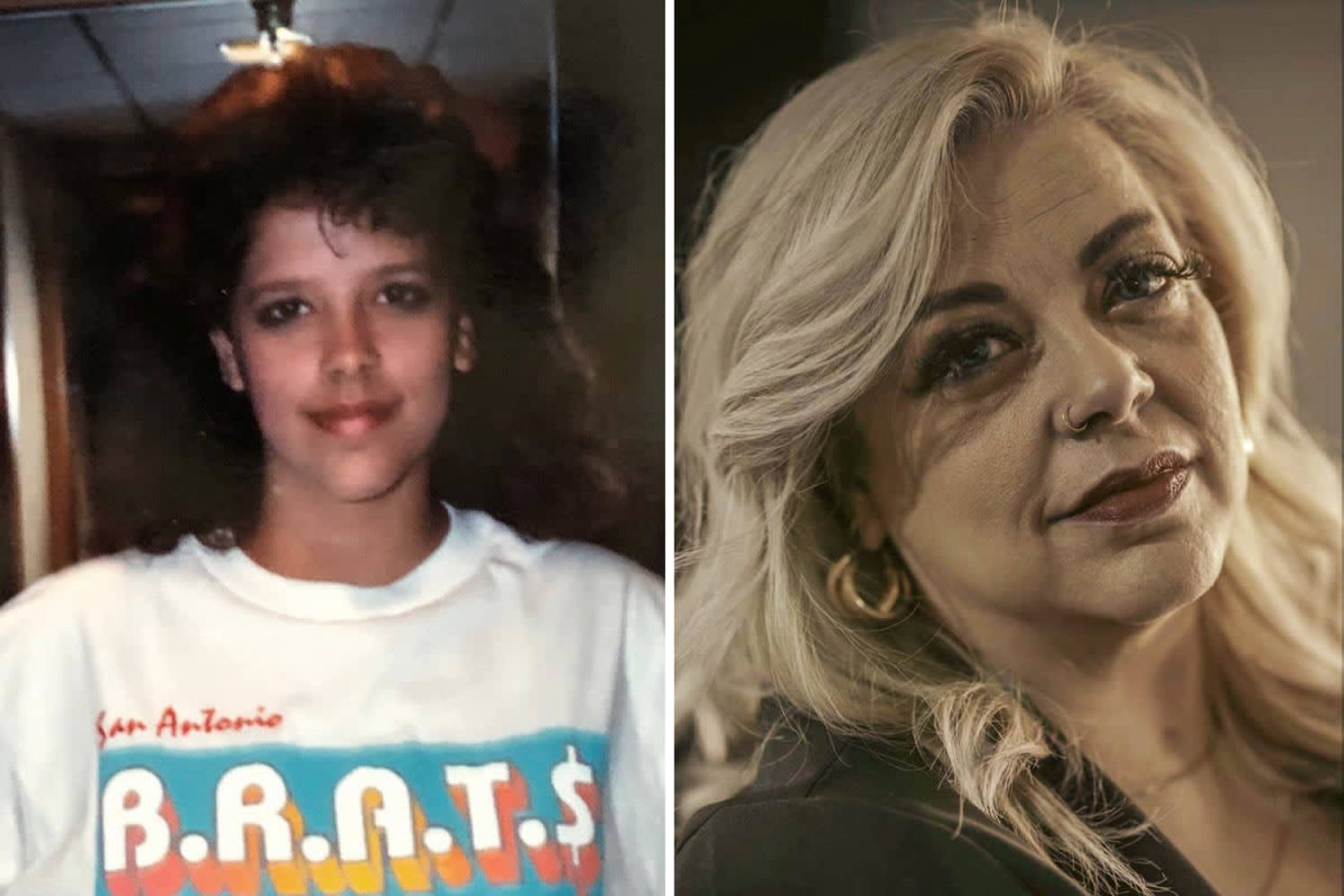

© Courtesy Phaedra Creed; Roberto Daza / NBC News
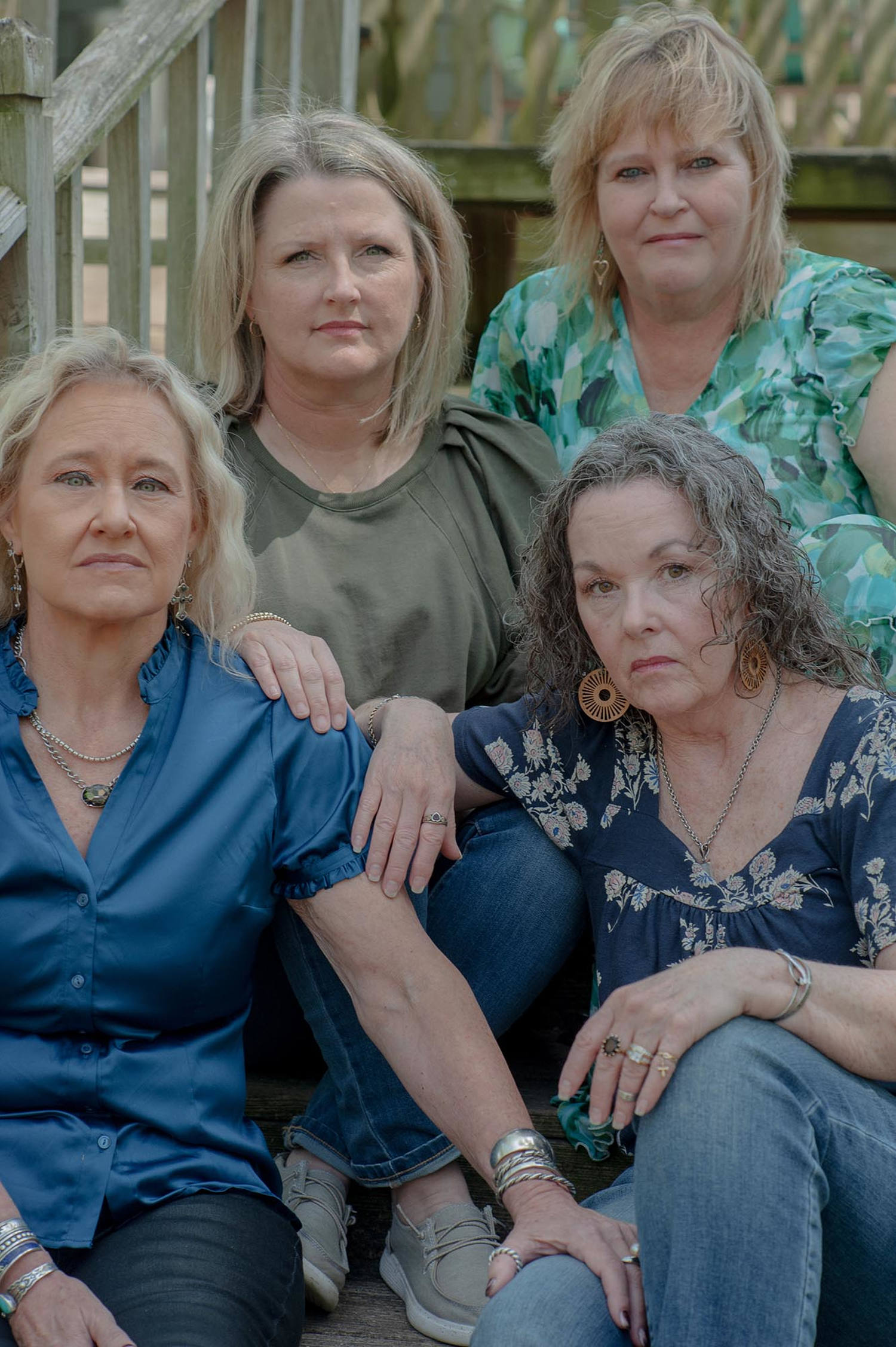

© September Dawn Bottoms for NBC News
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.
AirDrop is one of Apple's best features. I use it on a daily basis to share files between my various Apple devices, but it really shines when I'm sharing stuff with other people, or vice versa. It can be tricky to find a quick solution to send larger files. Emails have too low a file size limit, chat apps can compress files, and cloud storage can fill up fast, but AirDrop is simple, built-in, and reliable. It even works with Android now, albeit just the Pixel 10.
If AirDrop has one flaw, it's that it's not particularly easy to use with strangers. Apple has changed how this side of AirDrop works over the years. For the longest time, you had two AirDrop settings: "Contacts Only," which only lets your saved contacts find your device for AirDropping files, and "Everyone," which leaves your AirDrop open to anyone with an iPhone to send you stuff. This was convenient when you needed to share files with strangers, but inconvenient if you left it on: Anyone with an iPhone could see your iPhone and send you anything—like, say, a bomb threat while on an airplane. Not good.
Then, Apple changed this latter functionality to "Everyone for 10 Minutes." Ever since, if you want to open up your AirDrop to people outside your contacts, you have to manually enable this toggle, which will only stay open for, well, 10 minutes. After that, it switches back to "Contacts Only." That's an improvement in security, but not in convenience. If you're ever in a situation where you need to AirDrop something to someone relatively frequently but you don't want to add their contact to your iPhone, you'll be switching back to "Everyone for 10 Minutes" every 10 minutes.
iOS 26.2, Apple's newest iPhone update at the time of this writing, introduces a solution—AirDrop codes. This feature forces anyone not saved in your contacts who wants to share something with you via AirDrop to ask for a one-time code first. Once you share that code, that user is temporarily saved on your iPhone for 30 days, allowing you to AirDrop repeatedly without issue. After those 30 days are up, the user leaves your iPhone, and you don't need to worry about pruning your Contacts app down the line. (This same functionality also applies to AirDrop on iPadOS 26.2 and macOS 26.2.)
Here's how this new AirDrop experience works with strangers going forward. Let's say you're at a conference and you meet someone who wants to send you some relevant materials via AirDrop. You set your AirDrop settings to "Everyone for 10 Minutes," they see your contact, and attempt to send you the file.
On your end, you see the request, with a "Continue" option: Once you tap it, you'll see the AirDrop code on your iPhone, iPad, or Mac. You can tell the code to the sender, who can enter it on their device. If successful, the file will be shared like any other AirDrop interaction.
As stated above, this allows you to AirDrop with this contact for 30 days without needing to bother with another AirDrop code. But if you're done sharing with the stranger for good, you can remove their temporary contact early. Head to the Contacts app, hit the back button in the top left if applicable to head to Lists, then choose Other Known. Here, you'll see any temporary contacts generated from previous AirDrop sessions, which you can delete ahead of that 30 day deadline. Otherwise, your device will take care of it once that timeframe has elapsed.

Another PayPal phishing scam is circulating, this time with email notifications about recurring or automatic payments. The messages originate from a legitimate PayPal address, allowing them to evade some security filters and leave recipients worried that their accounts have been compromised—perhaps just enough to ignore the obvious red flags and call or email scammers back.
I personally have been targeted by this scam with at least five separate emails, though all have gone straight to my spam folder. Here's how scammers are exploiting PayPal settings to land in your inbox.
If you're targeted by this campaign, you may receive an email with the subject line "Your automatic payment status has changed" or "Recurring Payment Reactivated." The layout imitates a real PayPal notification and includes a message about a high-dollar payment being "successfully processed" along with a customer service email and phone number to contact PayPal support.
The email is full of red flags: It is addressed to a random name (or, in one of the messages I received, "Hello Update Invoice"), has poor spelling and wonky formatting, and simply doesn't make sense. You can easily spot oddities like bold text and Unicode characters, which BleepingComputer notes is a trick used to bypass spam filters and keyword detection.

Where the trick lies is in the sender field, as the email comes from service[at]paypal[dot]com, a legitimate PayPal address, and paypal.com is in the signed-by field. As Malwarebytes Labs describes, this is likely an abuse of PayPal's subscription billing feature. If a merchant pauses a customer subscription, the user will receive an automatic email from PayPal notifying them that their payment is no longer active. Scammers are likely setting up fake subscriber accounts using Google Workspace mailing lists, so automatic emails being generated are sent to everyone on those lists. If you look at the "To:" field, you'll see that the message isn't actually addressed to your email.
Exploiting these types of loopholes to make phishing emails seem legit is a common tactic, and I've covered several similar PayPal phishing campaigns already this year. According to a statement provided to BleepingComputer, PayPal is working on mitigating this specific flaw.
If one of these PayPal messages lands in your inbox, don't engage with it. Scammers frequently use emails, texts, and calls about account security and financial transactions to scare you into action, and the impersonation of trusted institutions is often pretty convincing.
If you are concerned about activity on your PayPal account, go directly to the app or website and log in to view alerts and check transactions. Do not use contact information or click any links in the original notification, as this increases the chances of compromising your information or downloading malware to your device.

There are fewer and fewer hardware differences between iPhones and Androids as the years go on, but back in the day, that was far from the case. At one point, many major Android devices came with dedicated LEDs that would shine whenever you received a notification. It was a passive way to know whether you had something on your phone to attend to, without having to actually wake up the display and risk getting unnecessarily sucked into your device.
iPhones have never had this specific feature, but Apple included a workaround for anyone interested in a similar experience. For years, you've been able to dive into Accessibility settings to turn your iPhone's LED flash into a notification light. Any time you received a text, app notification, or call, your camera flash would go off, ensuring you didn't miss an important update. This can be helpful both those who are hard of hearing, and who wouldn't be able to rely on audible alerts, or anyone who keeps their phone on silent, but would like a visual cue that they have a new notification.
For the first time in years, Apple is updating its flash alerts feature. With iOS 26.2, which the company released on Friday, you now have the option to have your iPhone's display itself flash for new alerts. You can choose to make the display the only light that flashes, or to use the feature in tandem with the LED flash, which I think makes the most sense for people who like this option. That way, it won't matter whether your iPhone is face up or face down: You'll always see a light flash for new alerts one way or another.
Display flash doesn't work like you might expect, especially if you've used LED flashes before. I thought my iPhone would flash a bright light on and off again a few times, mimicking how LED flash alerts works. Instead, when you get a new notification, the screen instantly increases the brightness for a few seconds, before lowering it again. It works—you're bound to notice your display jump in brightness if it isn't already maxed out—but it doesn't quite grab your attention as well as the LED flash.
To start, open the Settings app on your iPhone, then head to Accessibility. Scroll down to Hearing, then choose Audio & Visual. Scroll to the bottom of this page, then tap Flash for Alerts.
If you're running an older version of iOS, you'll only have the option to enable "LED Flash." However, those running iOS 26.2 and newer will also see an option for "Screen." Choose that option if you want the display to flash for new alerts, or "Both" to have both lights enabled.
You'll also find two choices that affect when these flash alerts go off, no matter which of the above options you pick. First, you can choose whether your iPhone will use flash alerts while locked. If you disable this option, you'll only see these light alerts when your iPhone is unlocked. Second, you can choose whether to use flash alerts in Silent Mode. I'd keep that setting enabled, since it seems most useful when your iPhone has no other way to alert you to new notifications.
It's also important to note that using an Apple Watch can complicate this feature a bit, at least in my experience. While giving this option a test, I had trouble getting alerts to come through on my locked phone without first going to my watch. If you have an Apple Watch, and its notifications mirror your iPhone's, you'll get the most out of this feature when your iPhone is unlocked.

We may earn a commission from links on this page. Deal pricing and availability subject to change after time of publication.
Sony's 1000X series have been around since 2016, improving on the previous iteration to eventually land on the Sony WH-1000XM6, the best over-ear headphones for audio quality currently on the market. But not everyone can (or needs to) drop nearly half a grand on headphones. The WH-1000XM5 are a generation older and were the best headphones for audio quality up until this year, when they were succeeded. They're currently $248 (originally $399.99), the lowest price they've ever been according to price-tracking tools, and they now come with free Sony WF-C700N earbuds. To put how good this deal is into perspective, the WH-1000XM4 are $100 more right now.
I have been a loyal customer of the 1000X line for many years; they're my go-to headphones for most activities. The WH-1000XM5 came out in May of 2022 to an "outstanding" review from PCMag for their top-notch audio quality, but also for their exceptional audio when using its best-in-class active noise-canceling (most headphones lose their audio quality when using ANC). The headphones are also well-designed to be comfortable for long sessions.
The ear controls use tapping and swiping, which aren't my favorite, but it's what all the modern headphones are moving toward. There's an app that comes with the headphones that lets you adjust your EQ settings to your liking, including what the swiping and tapping functions do on your headphones.
A great touch on these headphones that is often neglected is a Stereo 3.5mm connection, perfect for those who want to use a wired cable without worrying about battery life. Speaking of battery life, Sony says you can expect about 30 hours, but it will vary depending on your usage of ANC. They are compatible with AAC, LDAC and SBC codecs and have multipoint connection (you can pair them with more than one device at the same time).
The Sony WF-C700N earbuds are normally $119, and are "good" earbuds accorcing to PCMag's review. If you're looking for great headphones for audio quality with ANC with some free earbuds at a great price that arrives before Christmas, consider this deal.


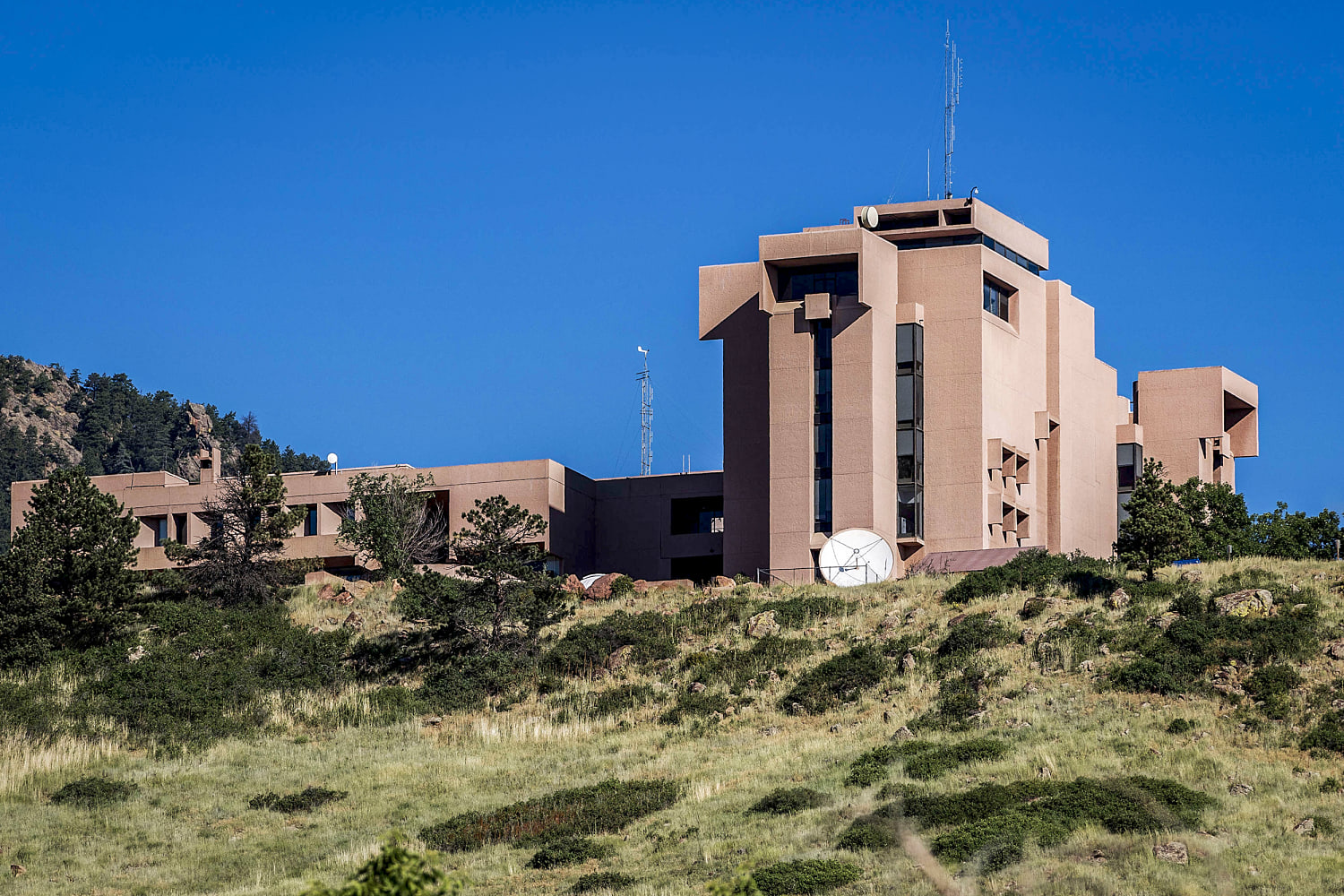
On Tuesday, the head of the Office of Management and Budget, Russell Vought, announced that a major climate research center will be “broken up.” The National Center for Atmospheric Research, or NCAR, is a significant contributor to research on the weather, climate, and other atmospheric phenomena. The move will be a crippling blow to climate research in the US and is being widely decried by scientists.
Vought initially gave a statement regarding NCAR to USA Today and later confirmed the outlet’s reporting on social media. Calling it “one of the largest sources of climate alarmism in the country,” Vought also decried what he termed “woke” activities at NCAR. These appear to be fairly typical efforts made to attract underrepresented groups to the sciences—efforts that were uncontroversial prior to the current administration.
NCAR is primarily based in a complex on the outskirts of Boulder, Colorado, and maintains a supercomputing center in Wyoming. Much of its funding comes from the National Science Foundation, but the day-to-day management is handled by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR), a nonprofit that represents 130 individual educational institutions. In addition to climate science, researchers based there study Earth and space weather, atmospheric chemistry, and their impacts on the environment and humans. NCAR hosts a series of webpages that explain its research and all the ways it helps society.
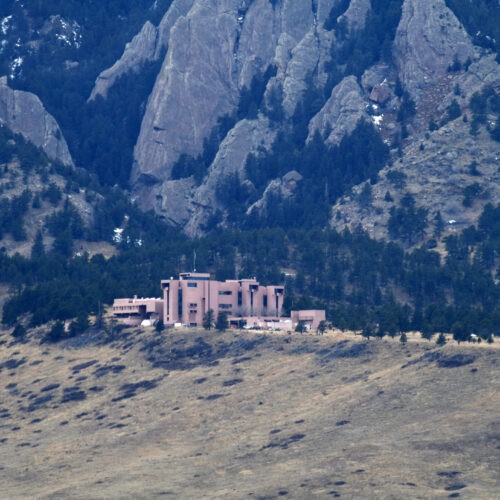
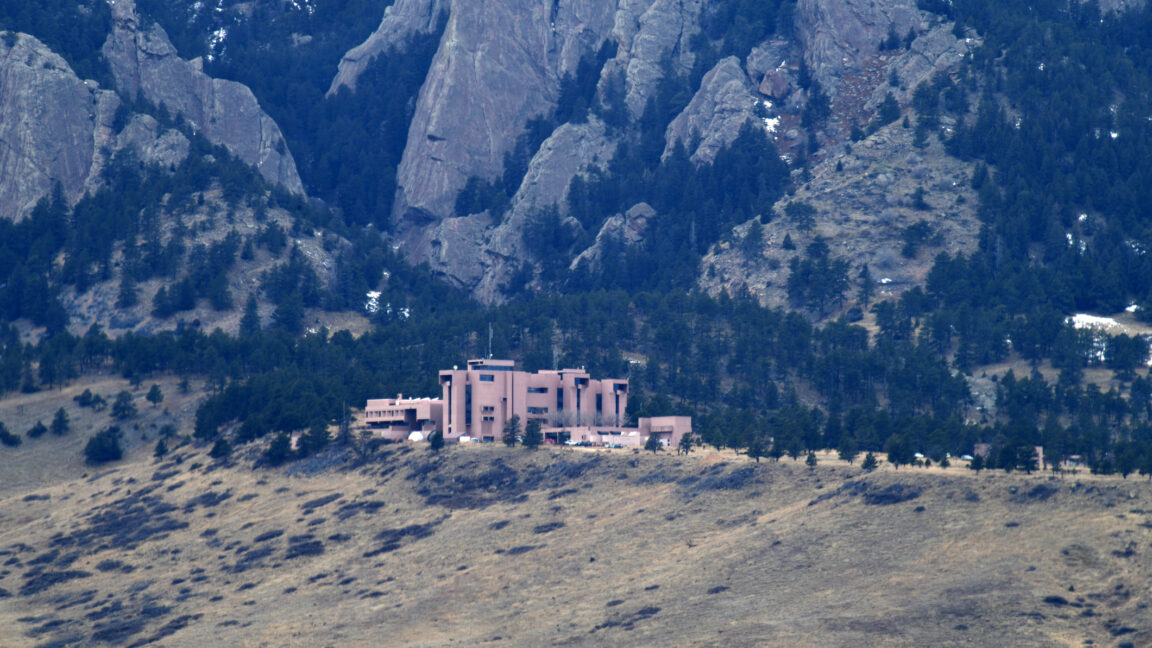


© Chris Rogers
Google began its transition to Gemini 3 a few weeks ago with the launch of the Pro model, and the arrival of Gemini 3 Flash kicks it into high gear. The new, faster Gemini 3 model is coming to the Gemini app and search, and developers will be able to access it immediately via the Gemini API, Vertex AI, AI Studio, and Antigravity. Google’s bigger gen AI model is also picking up steam, with both Gemini 3 Pro and its image component (Nano Banana Pro) expanding in search.
This may come as a shock, but Google says Gemini 3 Flash is faster and more capable than its previous base model. As usual, Google has a raft of benchmark numbers that show modest improvements for the new model. It bests the old 2.5 Flash in basic academic and reasoning tests like GPQA Diamond and MMMU Pro (where it even beats 3 Pro). It gets a larger boost in Humanity’s Last Exam (HLE), which tests advanced domain-specific knowledge. Gemini 3 Flash has tripled the old models’ score in HLE, landing at 33.7 percent without tool use. That’s just a few points behind the Gemini 3 Pro model.


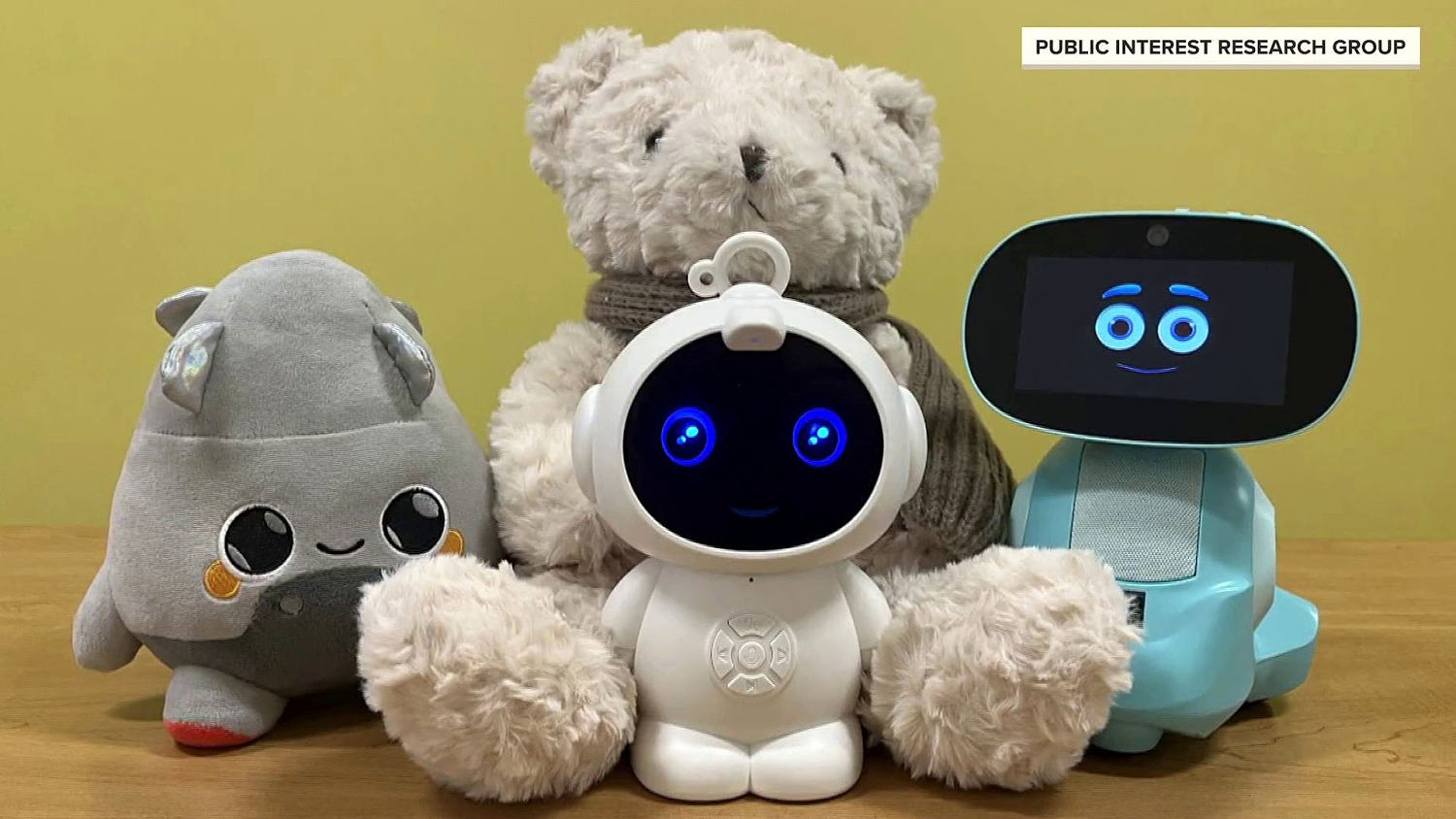
Browser extensions with more than 8 million installs are harvesting complete and extended conversations from users’ AI conversations and selling them for marketing purposes, according to data collected from the Google and Microsoft pages hosting them.
Security firm Koi discovered the eight extensions, which as of late Tuesday night remained available in both Google’s and Microsoft’s extension stores. Seven of them carry “Featured” badges, which are endorsements meant to signal that the companies have determined the extensions meet their quality standards. The free extensions provide functions such as VPN routing to safeguard online privacy and ad blocking for ad-free browsing. All provide assurances that user data remains anonymous and isn’t shared for purposes other than their described use.
An examination of the extensions’ underlying code tells a much more complicated story. Each contains eight of what Koi calls “executor” scripts, with each being unique for ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and five other leading AI chat platforms. The scripts are injected into webpages anytime the user visits one of these platforms. From there, the scripts override browsers’ built-in functions for making network requests and receiving responses.


© Getty Images
After federal clean vehicle tax credits ended in September, the electric vehicle industry reached a crossroads. Well, technically, it has been there since Trump took office. This is a weird period in automotive history; A chunk of the industry is full-steam ahead with EV development, another is cutting back, and the consumer is left wondering what the electrification landscape will look like next year, let alone in three, during the next administration.
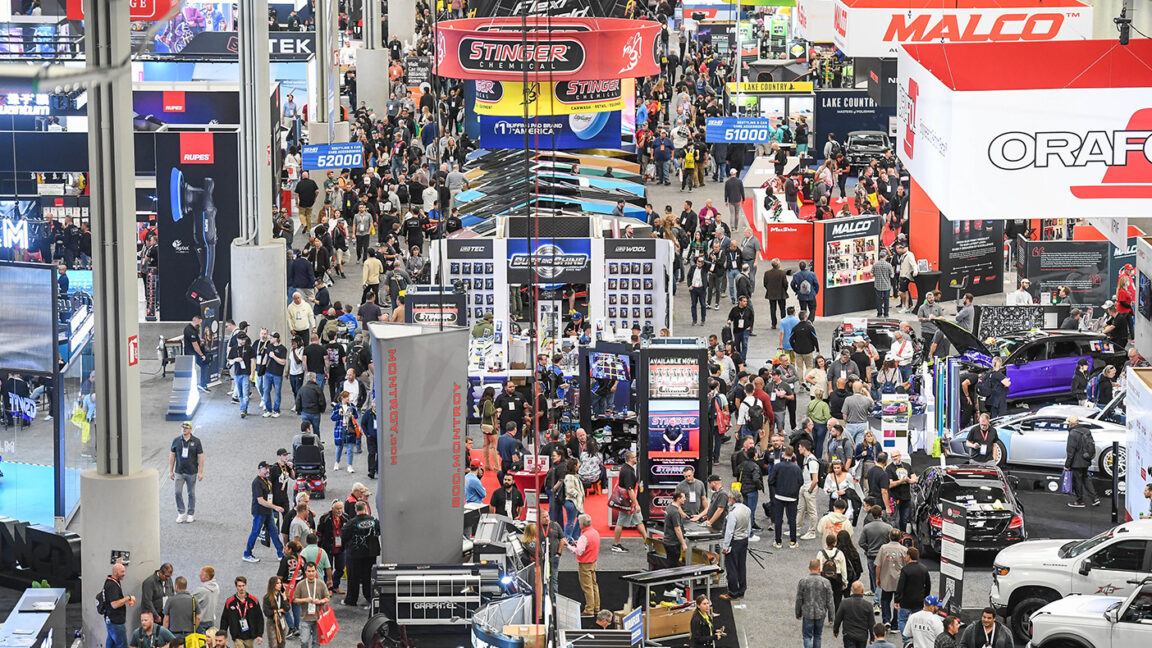
But what about the automotive aftermarket? Typically, this corner benefits from whatever progress is made on the OEM front—have Trump’s policies expanded or contracted its EV technological development? I recently spent some time chatting with personnel of the Specialty Equipment Market Association (SEMA) at its yearly tradeshow in Las Vegas to find out. I also hit the bricks (or, rather, bright carpeting) of the massive show itself, seeking out some new, unique developments in the space that behoove EV tech’s inherent benefits.
Above one of the show’s several sprawling halls, I met with Mike Spagnola, SEMA’s CEO, and Karen Bailey-Chapman, senior vice president, public and government affairs, to learn what the organization’s official stance is. First and foremost: It doesn’t want to be told what to do.


© Peter Nelson
On Tuesday, X Corporation, formerly known as Twitter, sued “Operation Bluebird,” the new startup that is seeking to reclaim the allegedly abandoned Twitter trademark and relaunch a new social media network under that name.
In its 43-page lawsuit, which was filed in federal court in Delaware, X Corporation alleges trademark infringement, adding that despite Bluebird’s “purported plan, it cannot bring Twitter ‘back’—Twitter never left and continues to be exclusively owned by X Corp.”
One of Bluebird’s leaders, Michael Peroff, told Ars in an email that Operation Bluebird was “fully expecting” a lawsuit from X Corporation and that “we planned for it.”


© Getty Images | Thomas Trutschel



Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.


Read more of this story at Slashdot.
