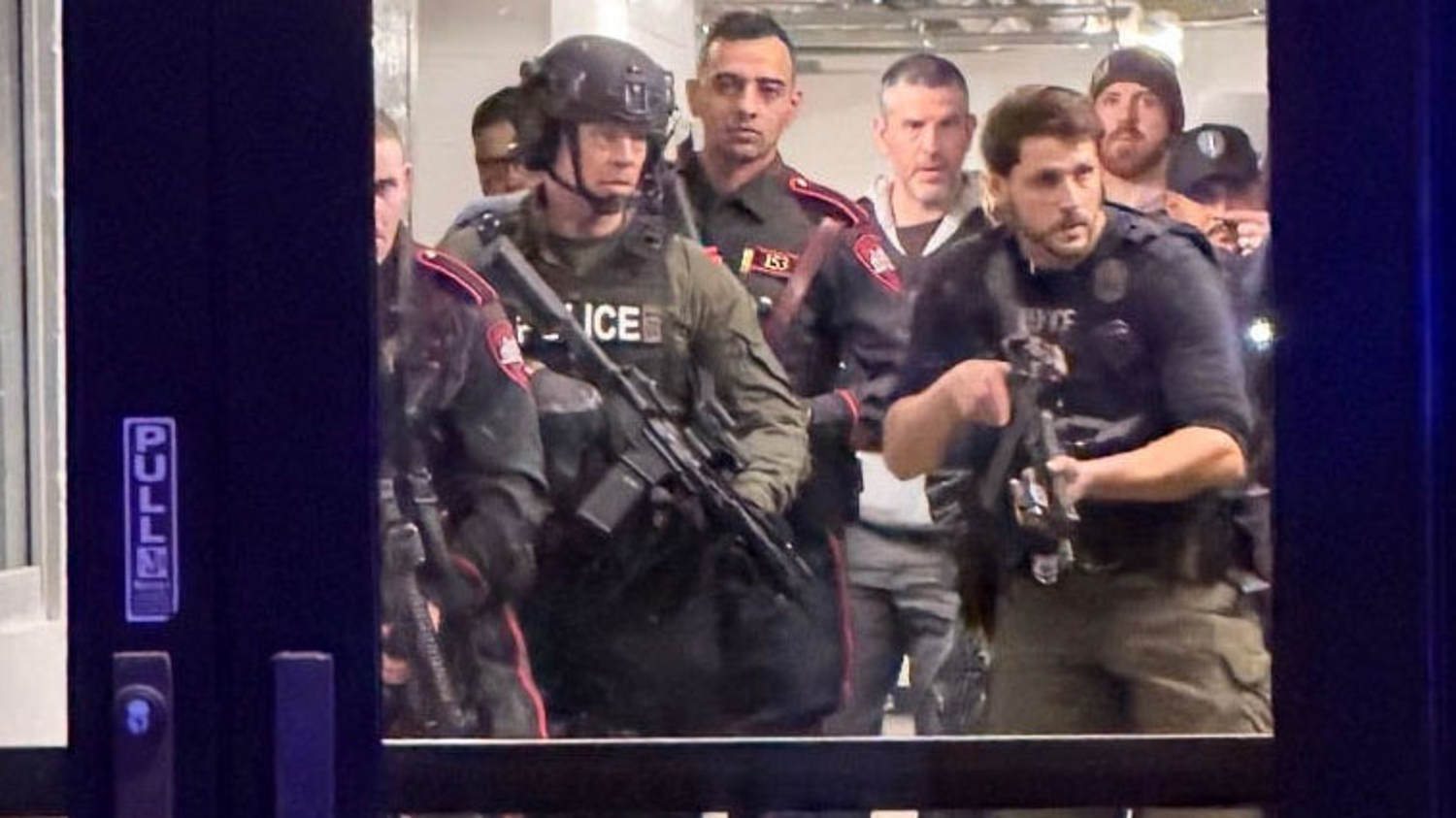
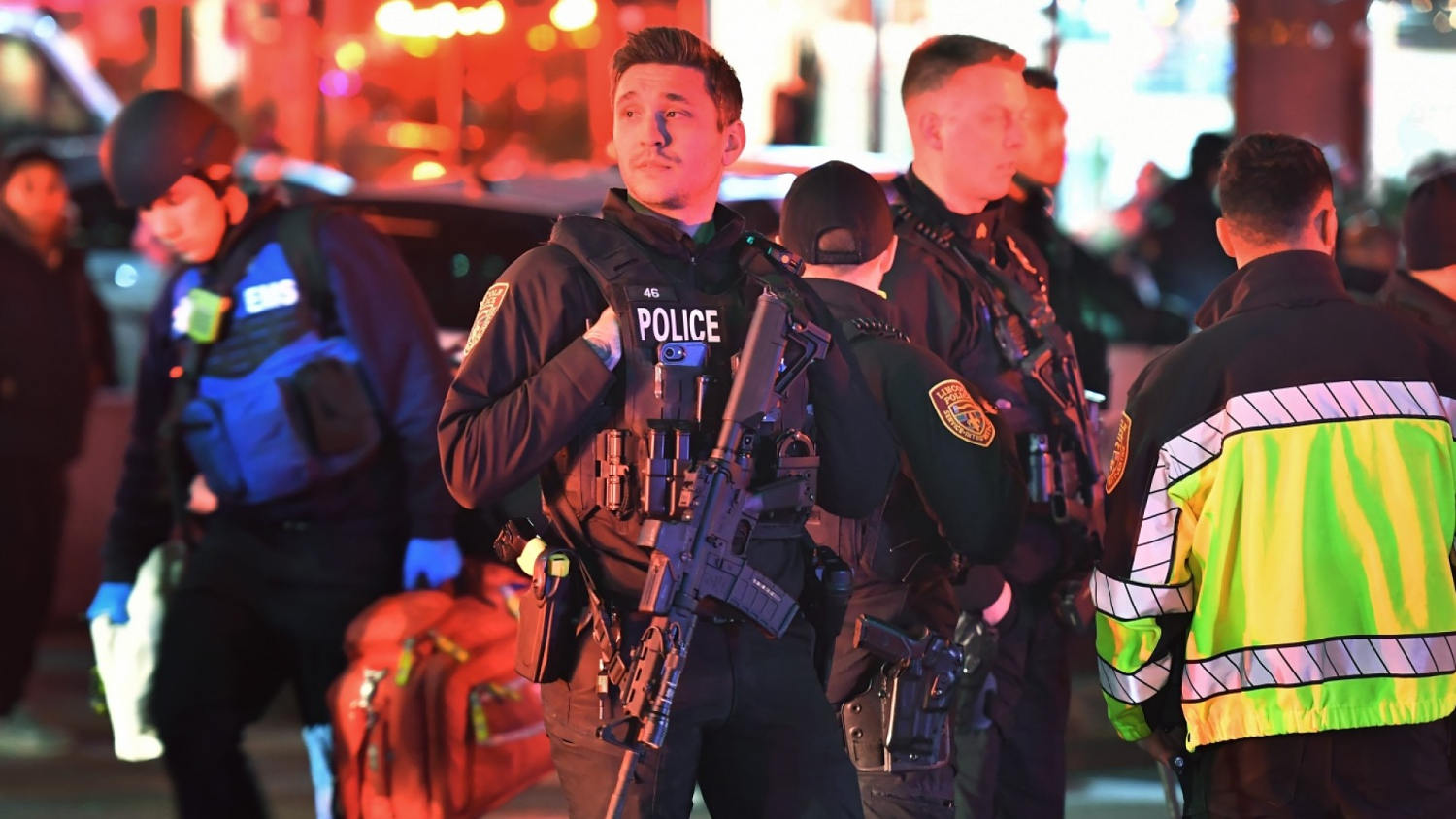
Brown University students describe uncertainty and fear in lockdown after shooting
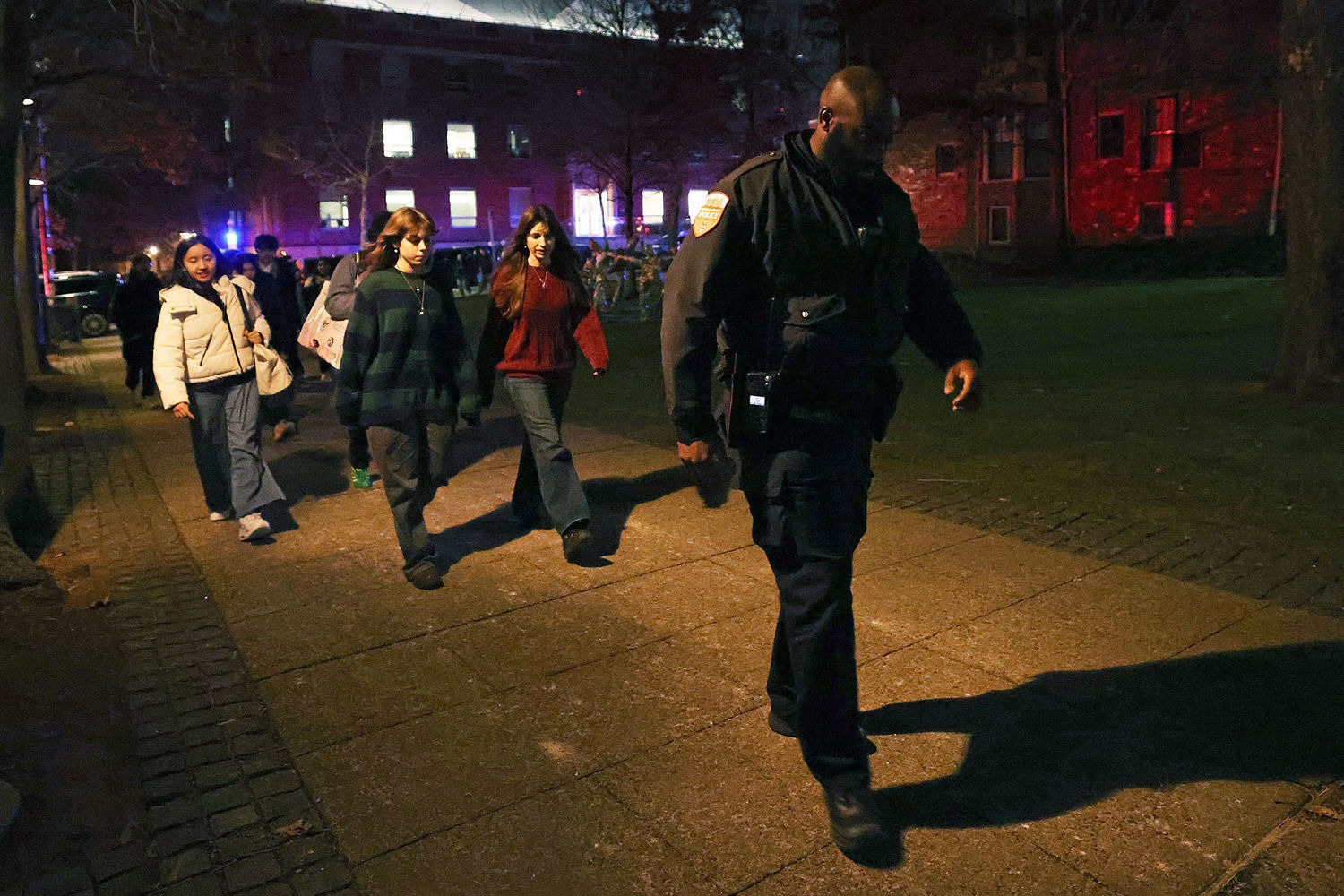

© Bing Guan

© Bing Guan

©
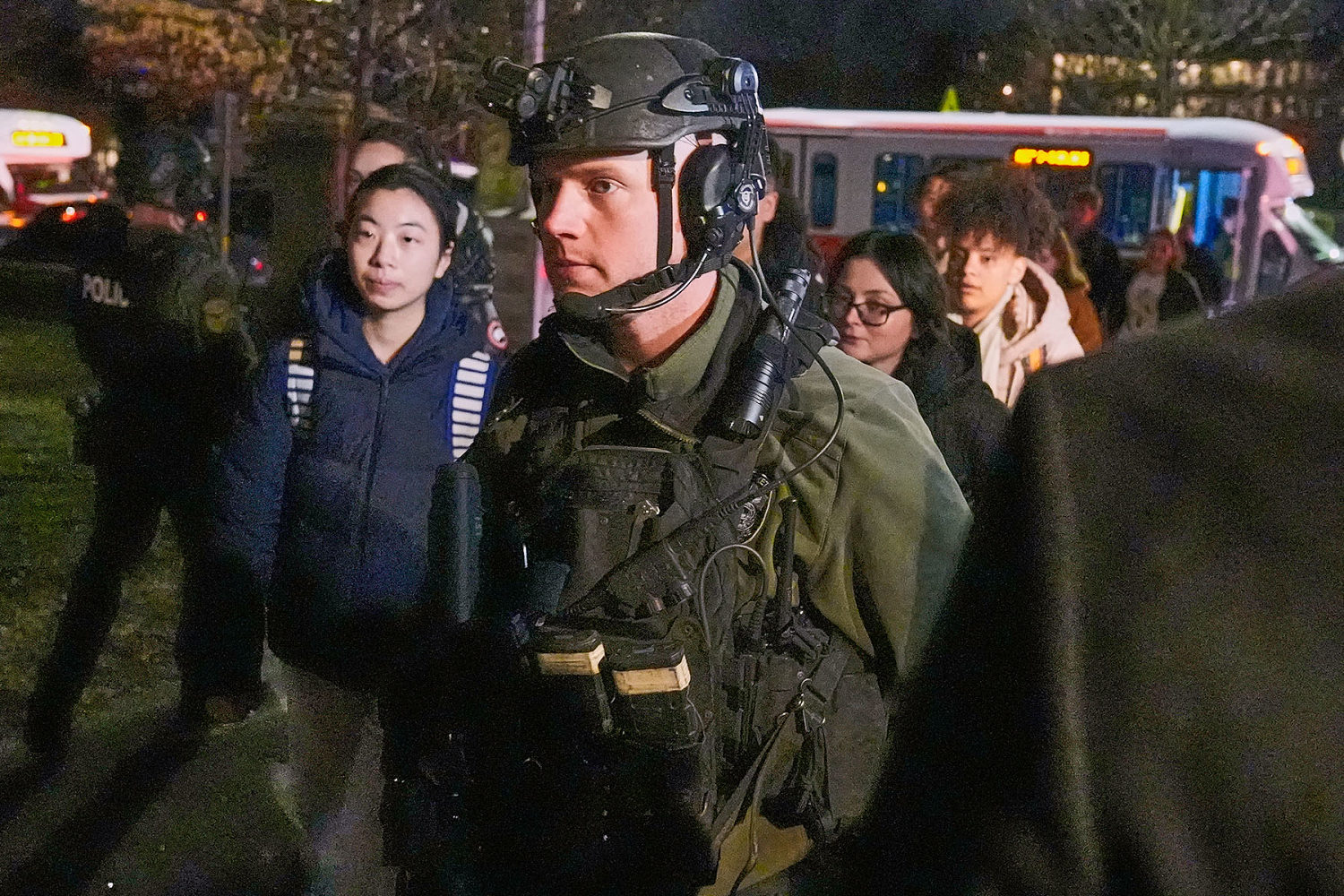


© Mark Patinkin
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

©

©

©
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Three weeks ago, I tested something that completely changed how I think about organic traffic. I opened ChatGPT and asked a simple question: "What's the best course on building SaaS with WordPress?" The answer that appeared stopped me cold. My course showed up as the first result, recommended directly by the AI with specific reasons why it was valuable.
I hadn't paid for advertising. I hadn't done any special promotion. The AI simply decided my content was the best answer to that question and served it to the user. This wasn't luck or a fluke. When I tested the same query in Perplexity, the same thing happened. My website ranked at the top of AI-generated responses, pulling in free traffic directly from AI models that millions of people now use as their primary search tool.
This represents a fundamental shift in how people discover content online. For years, we've optimized for Google's algorithm, carefully crafting meta descriptions and building backlinks to climb traditional search rankings. That work still matters, but a massive new traffic source has emerged that most content creators are completely ignoring. While everyone focuses exclusively on traditional SEO, AI Optimization is quietly becoming one of the most valuable skills for anyone who publishes content online.
The opportunity is enormous right now precisely because it's so new. Early adopters are claiming top positions in AI responses while their competitors remain oblivious to this emerging channel. But this window won't stay open forever. As more people recognize the value of appearing in AI results, competition will increase and optimization will become more sophisticated. The time to understand and implement AIO strategies is now, while the landscape is still relatively uncrowded.
In this comprehensive guide, I'll show you exactly how AI Optimization works, how it differs from traditional SEO, what specific tactics actually move the needle, and how to track your performance so you know what's working. More importantly, I'll explain why you can't afford to ignore this traffic source if you want to remain visible online as user behavior continues shifting toward AI-powered search.
Something profound has changed in how people find information online, and most website owners haven't noticed yet. The change isn't about a new Google algorithm update or a shift in social media platforms. It's about where people go when they have questions that need answering.
For twenty years, the pattern was predictable and universal. Someone needs information, they open Google, they type a query, they scan through ten blue links, they click a few results, they piece together answers from multiple sources. This process trained us to optimize for that journey. We focused on ranking in those ten blue links because that's where traffic came from. The entire SEO industry built around understanding and exploiting that single funnel.
But look at what's happening now. Someone needs information, they open ChatGPT or Claude or Perplexity, they ask a question in natural language, they receive a comprehensive answer immediately with sources cited. No clicking through multiple websites. No comparing different perspectives. No scanning search results pages. The AI synthesizes information and delivers a direct answer, fundamentally changing the discovery process.
The numbers tell the story. ChatGPT reached 100 million users faster than any consumer application in history, hitting that milestone in just two months after launch. By early 2025, ChatGPT alone processes over 10 million queries daily through its web browsing feature. Perplexity has grown to millions of daily users who rely on it as their primary search tool. Google has responded by launching AI Mode, available in over 180 countries, which provides AI-generated answers above traditional search results.
These aren't niche tools used by tech enthusiasts. They're mainstream applications that everyday people now use for research, planning, learning, and decision-making. When someone searches for "best productivity apps for small teams," they're increasingly likely to ask an AI rather than Google. When a business owner needs to understand a technical topic, they're prompting Claude instead of reading blog posts. When students research topics for papers, they're querying Perplexity instead of clicking through search results.
This behavioral shift creates a new visibility challenge. Your content might rank perfectly on Google, but if it's invisible to AI models when they're formulating answers, you're missing an enormous and growing segment of potential traffic. The users who discover information through AI tools never even see your traditional search rankings because they never visit a search results page.
The problem compounds because AI search is still in its explosive growth phase. Usage is doubling and tripling year over year as more people discover these tools and integrate them into their daily workflows. The traffic opportunity today is significant, but it's tiny compared to what it will become in the next few years as AI search becomes default behavior for entire demographics.
AIO stands for AI Optimization, and it represents the practice of optimizing your content to appear in AI-generated responses when people query language models. Think of it as SEO's younger sibling, similar in purpose but different in execution because the underlying mechanisms for how AI models select and cite sources differ fundamentally from how Google ranks web pages.
Traditional SEO focuses on signals that Google's algorithms evaluate when determining search rankings. You optimize title tags and meta descriptions. You build backlinks from authoritative sites. You ensure your site loads quickly and works on mobile devices. You create content that targets specific keywords with appropriate density and placement. These tactics work because they align with how Google's systems assess page quality and relevance.
AIO requires understanding how language models decide which sources to reference when answering questions. These models don't follow the same rules as search engine algorithms. They're not counting backlinks or analyzing page load speed. They're evaluating whether content provides clear, accurate, comprehensive answers to questions people actually ask. They're assessing credibility through different signals than traditional search engines use. They're making probabilistic decisions about which information best satisfies a query based on patterns learned during training and information retrieved during real-time web searches.
The distinction matters because tactics that boost Google rankings don't automatically improve your chances of being cited by AI models, and vice versa. A page optimized perfectly for SEO might never appear in AI responses if it doesn't align with how language models evaluate content. Conversely, content that AI models consistently cite might not rank highly in traditional search if it lacks conventional SEO signals.
This doesn't mean you should abandon SEO and focus exclusively on AIO. The two approaches are complementary, not competing. People still use Google extensively, and traditional search traffic remains valuable. The point is that comprehensive visibility requires optimizing for both channels. You need your content discoverable through conventional search engines and reliably cited by AI models. This dual approach captures traffic from users regardless of which discovery method they prefer.
The strategic value of AIO extends beyond just additional traffic. When an AI model cites your content, it provides context explaining why your resource is valuable. The model doesn't just list your URL like a search result—it summarizes your key points, extracts relevant information, and positions your content as a trusted source. This creates a stronger credibility signal than a traditional search result because the AI has effectively pre-vetted your content and endorsed it as worth reading.
Think about the user experience difference. In traditional search, someone sees your site listed among ten results and must decide whether to click based on a title and two-line description. In AI search, someone reads an answer that includes information from your content, sees your site cited as the source, and arrives at your page already understanding its value and relevance. The qualification happens before the click, resulting in higher-quality traffic with better engagement metrics.
Google's introduction of AI Mode represents a pivotal moment in search engine evolution and confirms that AI-generated answers are becoming a core component of how major platforms deliver information. Understanding this development helps contextualize why AIO matters and where organic discovery is headed.
AI Mode transforms Google's interface from a list of links into a conversational AI that provides direct answers. When you access AI Mode (available at google.com/ai or through the Google app), you interact with a language model that searches the web in real-time and synthesizes comprehensive responses to your questions. Instead of scanning through multiple websites, you receive curated information with sources cited, similar to ChatGPT with web search or Perplexity.
What makes this particularly significant is Google's market position. Despite the rise of alternative AI search tools, Google still processes billions of searches daily and serves as the primary discovery mechanism for most internet users. When Google integrates AI-generated answers into its core search experience, it's not experimenting with a niche feature—it's fundamentally changing how the world's most popular search engine works.
The financial implications validate this direction. Google reported that AI features contributed to a 10% increase in search revenue, reaching $50.7 billion in Q1 2025. This isn't a failing experiment that might be discontinued. It's a successful product innovation that's generating substantial revenue while improving user experience. Google has every incentive to expand AI Mode and integrate its capabilities more deeply into standard search.
Currently, AI Mode exists as a separate interface that users must access intentionally, but the trajectory is clear. Google has indicated that AI-generated answers will eventually become a more prominent part of standard search results. While they've walked back statements about making AI Mode the default search experience after initial concerns, the long-term direction remains toward greater AI integration. Traditional search results won't disappear, but AI-generated summaries will occupy increasingly valuable real estate on search result pages.
This evolution mirrors what happened with featured snippets and knowledge panels over the past decade. Google gradually introduced elements that answered questions directly on the search page rather than requiring clicks to external sites. AI Mode represents the next iteration of this trend—more comprehensive answers, synthesized from multiple sources, delivered conversationally rather than as extracted snippets.
For content creators, this creates both opportunities and challenges. The opportunity is that appearing in AI-generated responses places your content in a prominent, trusted position that provides context and drives qualified traffic. The challenge is that optimization strategies must adapt to capture this visibility. Content that ranks well in traditional search results won't automatically appear in AI Mode responses without deliberate optimization for how AI systems evaluate and select sources.
The global availability of AI Mode in over 180 countries means this isn't a gradual rollout that you can monitor and prepare for leisurely. It's happening now, and users worldwide are already accessing AI-powered search. Your competitors might be optimizing for these systems while you're still focused exclusively on traditional SEO, giving them an advantage in capturing traffic from this rapidly growing segment.
One of the biggest challenges with AI Optimization is measurement. Traditional SEO provides robust analytics through Google Search Console, showing exactly which queries trigger impressions, how often people click your results, and where you rank for specific keywords. These metrics make it straightforward to track SEO progress and identify opportunities for improvement.
AIO lacks this infrastructure. ChatGPT doesn't provide website owners with analytics showing how often their content appears in responses. Perplexity doesn't send performance reports. Google AI Mode doesn't have a Search Console equivalent yet. This creates a visibility problem—you can't optimize what you can't measure.
Several commercial tools have emerged to fill this gap, offering AIO tracking and monitoring services. Ahrefs introduced features for tracking AI visibility at $129 per month. SE Ranking offers similar capabilities starting at $95 monthly. First Answer provides specialized AIO tracking for $39 per month but limits you to just 10 query tests. Keyword.com offers competitive pricing with various tier options.
These tools work by systematically querying AI models with specific prompts and analyzing which sources appear in the responses. They help you understand whether your content shows up for relevant queries, how you compare to competitors, and how your visibility changes over time. For businesses with substantial budgets, these professional tools provide valuable insights with minimal setup effort.
However, the pricing creates barriers for smaller website owners, bloggers, and businesses just beginning to explore AIO. Spending $100-300 monthly on tracking tools makes sense when you're generating significant revenue from AI traffic, but it's prohibitive when you're still validating whether AIO is worth your investment. This gap between professional tools and budget-conscious creators leaves many people flying blind with no way to measure their AIO performance.
The solution is building your own tracking system using no-code automation tools. This approach requires more initial setup but provides ongoing monitoring at a fraction of commercial tool costs. The system I built uses Make.com, a no-code automation platform, to query AI models systematically, analyze responses, and track mentions over time. Make offers 1,000 operations monthly on their free tier, making it possible to start tracking without any monetary investment.
The tracking system consists of three automated scenarios that work together to provide comprehensive AIO monitoring. The first scenario handles query tracking and brand mentions, automatically sending prompts to ChatGPT and recording which sources appear in responses. The second scenario performs keyword performance analysis, tracking specific topics or phrases relevant to your business and monitoring whether you're gaining or losing visibility. The third scenario focuses on competitor tracking, identifying when competitors appear in AI responses and analyzing their positioning compared to yours.
Building this system requires understanding of Make.com's interface and basic automation concepts, but it's accessible to anyone willing to invest a few hours in setup. The difficulty level sits at intermediate—more complex than basic automation but far simpler than custom programming. Once configured, the system runs automatically on whatever schedule you set, collecting data and building a historical record of your AIO performance.
The workflow begins with identifying the queries you want to track. These are essentially "AIO keywords"—questions that people might ask AI models where your content should ideally appear in the answer. Unlike traditional SEO keywords, which are often short phrases, AIO queries tend to be longer, more conversational questions that reflect how people actually talk to AI assistants.
For example, instead of targeting the SEO keyword "WordPress hosting," you'd track the AIO query "What's the best WordPress hosting for SaaS applications?" or "Which hosting provider should I choose for a WordPress-based business site?" These natural language questions better represent how people interact with AI tools and help you optimize for actual usage patterns rather than keyword variations.
Finding these queries requires a different research approach than traditional keyword research. Rather than using tools that show search volume and competition metrics, you need to understand what questions your target audience actually asks AI models. This means thinking about their problems, concerns, and information needs, then formulating those as conversational queries. Tools like an LLM Query Generator can help by analyzing your content and suggesting relevant questions people might ask to find that information.
Once you've identified target queries, the automated system tests them periodically—daily, weekly, or on whatever schedule makes sense for your monitoring needs. Each test queries the AI model with your specified prompt, captures the response, parses which sources were cited, and records whether your content appeared. Over time, this builds a database showing your visibility trends, how often competitors appear for the same queries, and which topics you're gaining or losing ground on.
The data collected enables strategic decisions about content creation and optimization. If certain queries consistently show competitor sources but never yours, that signals an opportunity to create or improve content addressing that topic. If you're appearing reliably for some questions but not others in the same category, you can analyze what makes your successful content different and apply those lessons to underperforming pieces. If your visibility is declining over time, you know you need to refresh and strengthen your content to maintain AI citation rates.
This measurement foundation transforms AIO from guesswork into a data-driven practice. Instead of optimizing blindly and hoping AI models notice, you track actual performance and refine your approach based on concrete results. The initial investment in building or subscribing to tracking tools pays dividends through improved optimization efficiency and clearer understanding of what tactics actually work for your specific content and audience.
Understanding AIO conceptually is valuable, but implementation requires specific, actionable tactics that demonstrably improve your chances of appearing in AI-generated responses. These seven strategies have proven effective across different content types, industries, and AI platforms. They work because they align with how language models evaluate sources and decide which content to cite when formulating answers.
The first tactic centers on incorporating statistics, numbers, and verifiable proof throughout your content. AI models exhibit a strong preference for factual, data-backed information over general statements or opinions. When a model encounters two sources covering the same topic, one making vague claims and another providing specific numbers with citations, the statistical content almost always wins.
This doesn't mean stuffing your content with random numbers. It means grounding your claims in specific, verifiable data wherever possible. Instead of writing "Our tool is widely used," you'd write "Our tool has 150,000 monthly active users with a 4.7 out of 5 satisfaction rating based on 3,200 reviews." The specificity signals credibility to AI models, which learned during training that precise data indicates reliable sources.
The same principle applies to any factual claim. When discussing market trends, cite specific growth percentages and time periods. When mentioning company performance, include actual revenue figures or user counts. When describing product features, provide concrete specifications rather than abstract descriptions. Each piece of specific data you add increases the likelihood that AI models will view your content as authoritative and citation-worthy.
This approach requires sourcing and maintaining accurate information, which means you can't fabricate numbers or exaggerate metrics. AI models increasingly cross-reference claims across sources, and inconsistencies damage credibility. The data you include must be truthful and, where relevant, attributed to primary sources. But when you consistently provide specific, accurate information, you build a reputation as a reliable source that AI models return to repeatedly.
The second tactic involves active engagement on Reddit, Quora, and similar community forums. This strategy works for a less obvious reason than you might expect. It's not primarily about direct traffic from forum posts, though that can be valuable. It's about creating authentic mentions and discussions of your content across platforms that AI models frequently encounter during training and web searches.
Language models learn from vast datasets that include substantial amounts of community discussion content. Reddit threads, Quora answers, and forum posts represent genuine human conversations about real topics, making them high-value training data. When your content or expertise appears naturally in these discussions, it creates signals that AI models recognize and incorporate into their understanding of what resources exist and who's knowledgeable about specific topics.
The key word here is "naturally." AI models have learned to recognize and discount obvious spam, self-promotion, and link-dropping. Simply posting your URL in relevant threads won't help and might actually hurt if it generates negative reactions or gets flagged as spam. Instead, you need to participate genuinely in communities where your expertise is relevant, providing real value in discussions and mentioning your content only when it truly addresses someone's question or adds to the conversation.
This means answering questions thoroughly, sharing insights from your experience, helping solve problems, and building a reputation as a knowledgeable contributor before you ever share links. When you do reference your content, it should be in the context of "I wrote a detailed guide about exactly this problem that covers X, Y, and Z" rather than "Check out my site." The former contributes to the discussion while the latter feels promotional.
Over time, this authentic participation creates a distributed network of references to your expertise and content across platforms that AI models access. These organic mentions, especially when they're accompanied by positive community response, signal that you're a legitimate authority worth citing. The impact accumulates gradually but compounds over months as you build a presence in relevant communities.
The third tactic focuses on optimizing for natural language queries rather than keyword stuffing. Traditional SEO often encourages optimizing for specific keyword phrases, sometimes at the expense of natural writing. You might structure sentences awkwardly to include exact keyword matches or repeat phrases more often than sounds natural. This approach can work for search engines that match keywords mechanically.
AI models process language differently. They understand semantic meaning and context, not just keyword matching. When people query AI tools, they ask complete questions in conversational language: "What's the best WordPress hosting for SaaS applications?" rather than "WordPress hosting SaaS." Your content needs to answer these natural questions directly and comprehensively to appear in AI responses.
This means structuring your content around questions your audience actually asks. Include FAQ sections that address common queries in full-sentence question format. Write subheadings as questions rather than just topics. Provide complete answers that someone could understand without additional context. Make your content readable and helpful to humans first, trusting that AI models will recognize and value that quality.
The practical implementation involves thinking about the conversation your audience wants to have rather than the keywords they might type. What are they trying to accomplish? What confuses them? What decisions are they facing? What objections or concerns do they have? When you address these elements in natural, conversational language, you simultaneously create content that people find valuable and that AI models recognize as comprehensive answers to common questions.
The fourth tactic requires creating comparison tables and structured data that AI models can easily parse and reference. Language models excel at processing structured information organized in clear, consistent formats. When they encounter well-formatted comparison tables, step-by-step lists, or data organized in predictable structures, they can extract and cite that information more reliably than when similar content appears in dense paragraphs.
This doesn't mean every piece of content should become a table or list. It means that when you're presenting information that naturally fits structured formats—comparisons between options, sequential steps in a process, multiple examples of a concept, sets of tips or recommendations—you should use formatting that makes that structure explicit and easy to process.
For example, if you're comparing different software tools, create an actual comparison table with columns for features, pricing, pros, and cons rather than describing each tool in paragraph form. If you're explaining a multi-step process, number the steps and use consistent formatting for each. If you're providing examples, use a predictable structure where each example follows the same pattern.
The benefit extends beyond AI optimization. Structured content is easier for human readers to scan and comprehend too. People increasingly skim content rather than reading every word, and clear structure helps them extract key information quickly. When you optimize for both AI processing and human scanning through better structure, you improve the experience for all visitors while increasing AI citation rates.
Implementation requires evaluating your existing content and identifying opportunities to add structure without forcing it artificially. Look for places where you're listing multiple items in prose that would be clearer as bullet points. Find sections comparing options that would benefit from table format. Identify processes that could be broken into numbered steps. These changes often improve content quality while making it more AI-friendly.
The fifth tactic involves building multi-platform authority by publishing consistent information across different channels. AI models, particularly those with web search capabilities, often cross-reference information across sources to verify accuracy and assess credibility. When they find the same core information presented consistently on your website, in your social media content, in articles you've published elsewhere, and in your responses on community platforms, it signals that you're a legitimate authority on that topic.
This doesn't mean duplicating content identically across platforms, which could create SEO problems and doesn't align with best practices for different mediums. It means maintaining consistent expertise, perspectives, and factual information while adapting the format and style to each platform's norms and audience expectations.
Your core message and expertise should be recognizable across a blog post on your website, a LinkedIn article, a Twitter thread, a YouTube video description, and a guest post on another site. The specific examples might vary, and the depth of coverage will differ based on format constraints, but the fundamental information should align. This consistency reinforces your authority and makes it easier for AI models to identify you as a reliable source on specific topics.
Building this multi-platform presence takes time and consistent effort. You can't create authority across channels overnight, but you can develop a systematic approach to repurposing and adapting your best content for different platforms. Each piece of substantial content you create should have a distribution plan that gets the core insights in front of audiences across multiple channels over time.
The strategic value compounds as your presence grows. Early on, you might only appear in AI responses when the model happens to encounter your website. As you build presence across platforms, the model has multiple opportunities to encounter your expertise from different angles, increasing the likelihood that it recognizes you as an authority worth citing.
The sixth tactic emphasizes showing fresh update signals throughout your content. AI models, especially those with real-time web access, demonstrate preference for current information over dated content. When choosing between two sources covering the same topic, with one clearly recent and another older, the fresher content usually gets cited unless there's a compelling reason to reference historical information.
This creates both an opportunity and a maintenance requirement. The opportunity is that regularly updating content can improve AI citation rates even if the core information hasn't changed dramatically. The requirement is that high-performing content needs periodic refreshes to maintain its competitive position as newer articles on the same topics emerge.
Making freshness obvious requires explicit signals that AI models can easily detect. The most straightforward approach is including "Last updated: [Date]" at the top of articles, making it immediately clear that the content reflects current information. This simple addition can significantly impact whether AI models view your content as relevant for queries about current state or recent developments.
Beyond update dates, freshness signals include referencing recent events, citing current statistics and data, mentioning the current year in context where relevant, and updating examples to reflect current tools and practices. These signals reassure both AI models and human readers that the information hasn't become outdated even if the core topic is relatively stable.
The practical challenge is balancing the benefit of updates against the time investment required. You can't refresh every piece of content constantly, so prioritize based on importance and competitive pressure. Content that generates significant traffic or ranks well in AI responses deserves regular attention to maintain those positions. Content about rapidly changing topics needs more frequent updates than evergreen material. Content facing new competition from recently published articles needs refreshing to remain competitive.
Implementing a content refresh schedule helps manage this systematically. Rather than updating randomly when you remember, establish a process where high-value content gets reviewed quarterly or semi-annually. During these reviews, update statistics, add recent examples, remove dated references, and add the new update date. This structured approach ensures your most important content remains fresh without requiring constant attention to every article.
The seventh tactic involves implementing JSON-LD structured data markup on your web pages. This technical optimization helps AI models understand your content's structure and purpose by providing machine-readable information about what your page contains, what type of content it is, and how different elements relate to each other.
Structured data uses a standardized format called Schema.org vocabulary implemented through JSON-LD script tags. These tags don't affect how your content appears to human visitors, but they provide clear signals to automated systems parsing your pages, including AI models determining whether your content answers specific queries.
Common structured data types relevant for most content include Article (marking blog posts and articles), HowTo (for step-by-step guides), FAQ (for question-and-answer sections), Person (for author bios), Organization (for company information), and Product (for product pages). Implementing appropriate schema markup for your content type helps AI models categorize and understand your content more accurately.
The technical implementation requires adding JSON-LD scripts to your page HTML, typically in the header section. Many content management systems, including WordPress, offer plugins that generate this markup automatically based on your content, eliminating the need for manual coding. For custom implementations, Schema.org provides documentation and examples for each data type.
While structured data implementation requires more technical knowledge than the other tactics, its value extends beyond AIO. Search engines like Google also use structured data to create enhanced search results like rich snippets, knowledge panels, and featured answers. This means the optimization work benefits both traditional SEO and AI visibility simultaneously.
The cumulative effect of implementing all seven tactics is substantial. Each strategy individually improves your chances of appearing in AI responses, but they work synergistically when combined. Content that includes specific statistics, appears in community discussions, answers natural language questions directly, presents information in structured formats, exists consistently across platforms, shows clear freshness signals, and implements proper schema markup sends multiple reinforcing signals that AI models recognize and value.
Understanding individual tactics is important, but sustainable success requires integrating AIO into your overall content strategy rather than treating it as a separate, occasional activity. This means developing systematic approaches that maintain and improve your AI visibility over time without requiring constant manual intervention.
The foundation of any sustainable strategy is creating content with AIO in mind from the beginning rather than retrofitting optimization after publication. This doesn't mean abandoning your audience's needs to serve AI algorithms—it means recognizing that content optimized for AI models is typically also better for human readers because both value clarity, structure, accuracy, and comprehensiveness.
When planning new content, start by identifying the questions your target audience asks AI models about your topic. These questions form the backbone of your content structure. If you're writing about project management tools, for example, you'd want to address questions like "What's the best project management software for small teams?", "How much do project management tools typically cost?", and "What features should I look for in project management software?" Each of these questions likely deserves a dedicated section with a clear, direct answer.
Your content outline should reflect these natural queries in your subheadings and section structure. This organizational approach simultaneously improves readability for humans scanning your content and makes it easier for AI models to identify which sections answer specific questions. When someone asks an AI about project management tool features, a model searching your content can quickly locate and cite the relevant section because you've structured it logically around that question.
The next consideration is information density and specificity. AI models favor content that provides concrete, actionable information over vague generalizations or superficial coverage. This means investing in depth rather than breadth for your most important topics. A comprehensive 3,000-word guide that thoroughly addresses a topic will typically perform better in AI citations than ten shallow 300-word articles that skim the surface.
This depth requirement influences content strategy decisions about volume versus quality. Rather than publishing something new every day with minimal research, you might publish twice weekly but ensure each piece provides genuine value with proper research, specific examples, and comprehensive coverage. The quality-focused approach generates better long-term results both for human audiences and AI visibility.
Maintenance and updates become critical components of sustainable strategy. AI models accessing the web in real-time naturally favor fresh content, so static articles gradually lose visibility even if they were initially successful. Building systematic content review and refresh processes prevents this decay and maintains your competitive position.
A practical maintenance schedule might review your top-performing content quarterly, your mid-tier content semi-annually, and your long-tail content annually. During these reviews, you update statistics and examples, add new sections covering recent developments, remove or update outdated information, and add a new "last updated" date to signal freshness. This regular maintenance keeps your content competitive and shows both AI models and human visitors that you're actively maintaining accuracy.
Competitive analysis should inform your ongoing strategy. Monitor which sources AI models cite for queries where you want visibility. Analyze what makes those sources effective—is it their structure? Their level of detail? Their use of data and statistics? Their freshness? Understanding your competition's strengths helps you identify gaps in your own content and opportunities to differentiate through superior quality or unique angles.
This competitive intelligence doesn't mean copying what others do well. It means understanding the bar you need to meet or exceed to compete for AI citations in your niche. If competing content provides basic overviews, offering in-depth analysis gives you an advantage. If competitors focus on theory, adding practical examples and case studies differentiates you. If everyone covers similar points, finding unique angles or addressing overlooked aspects of the topic creates competitive advantage.
Distribution and promotion strategies must extend beyond traditional channels to build the multi-platform presence that signals authority to AI models. This means systematically sharing your expertise across relevant communities, contributing to discussions on forums and social media, publishing on platforms like Medium or LinkedIn in addition to your own site, and building genuine relationships within your niche rather than just broadcasting content.
The goal isn't maximum reach across every possible platform—that's neither sustainable nor effective. Instead, identify the two or three platforms where your target audience genuinely spends time and where your expertise provides value. Focus your distribution efforts there, building consistent presence and contributing meaningfully over time. This focused approach generates better results than scattered efforts across a dozen platforms.
Collaboration and linking strategy matter differently for AIO than for traditional SEO. While backlinks remain important for search engine rankings, AI citation rates appear more influenced by the quality and relevance of the connection than purely by link volume. Being cited by a highly authoritative source in your niche can boost AI visibility even if it provides only one link, while dozens of low-quality directory links might not impact AI citations at all.
This suggests prioritizing genuine partnerships, guest posting on respected sites in your industry, and earning mentions from authoritative sources through excellent work rather than pursuing link-building tactics focused purely on volume. The relationship-based approach to link acquisition aligns well with AIO because it creates the kind of genuine authority signals that AI models recognize and value.
Understanding where AI search is headed helps you prepare for upcoming changes rather than constantly reacting to new developments. While predicting specific features or timeline is difficult, several clear trends are shaping the evolution of AI-powered discovery.
The most obvious trend is continued growth in AI search usage. As more people discover tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity, and as these tools improve their interfaces and expand capabilities, the percentage of information-seeking behavior flowing through AI models will increase. This doesn't necessarily mean traditional search engines will disappear, but it does mean the traffic pie is being redivided, with AI search claiming an expanding slice.
This growth trajectory suggests that early adoption advantages in AIO will compound over time. Establishing strong AI visibility now, while competition remains relatively light, positions you favorably as usage explodes and competition intensifies. The content creators building AI authority today will have structural advantages over those who wait until AI search is fully mainstream and optimization becomes more competitive.
Integration between different search modalities is accelerating. Google is bringing AI answers into traditional search results. Bing is integrating ChatGPT-powered features. New platforms are emerging that combine search, AI chat, and traditional browsing in unified experiences. This convergence means optimization strategies must account for hybrid discovery experiences where users might see both traditional results and AI-generated answers, potentially in the same interface.
The technical sophistication of AI models continues advancing rapidly, with implications for optimization strategies. Future models will better understand nuance, maintain longer context, cross-reference information more effectively, and potentially access real-time data more seamlessly. These improvements might make some current optimization tactics less important while creating new opportunities for differentiation.
For example, as models improve at understanding semantic meaning and context, exact keyword matching will matter even less than it does now. Conversely, models might become better at assessing content quality through subtle signals like writing sophistication, logical coherence, and comprehensive coverage. This evolution favors creators focused on genuine quality over those trying to game systems through technical tricks.
Personalization in AI search is emerging as models learn to consider individual user preferences, history, and context when formulating responses. This creates both opportunities and challenges for content visibility. The opportunity is that AI might recommend your content more prominently to users whose preferences align with your perspective or style. The challenge is that you might become invisible to users whose personalization profile doesn't match, even if your content is objectively relevant to their query.
Adapting to this personalized future likely requires building distinct brand identity and perspective rather than trying to be everything to everyone. If AI models categorize you clearly—as the practical, actionable advice source versus the theoretical deep-dive resource—you'll appear reliably for users whose preferences match that positioning. Trying to be too generic might result in appearing rarely for anyone as models route users to more distinctive alternatives.
Commercial considerations will shape AI search evolution as platforms figure out monetization beyond subscriptions. We're already seeing early experiments with citations including affiliate tracking, sponsored placements in AI responses, and premium content partnerships. The specific implementations will evolve, but the trajectory toward commercial integration seems certain.
For content creators, this commercial evolution might create new opportunities to monetize AI visibility beyond indirect traffic benefits. If platforms begin sharing revenue with cited sources, strong AI visibility could become directly profitable. If sponsored placements become normalized, there might be ways to amplify your organic visibility through paid promotion similar to how PPC complements SEO.
Regulation and AI model behavior around copyrighted content remains in flux, with implications for what content models can reference and how prominently different sources appear. Current legal frameworks are struggling to accommodate AI's information synthesis capabilities, and future regulations might significantly impact how models cite sources, what compensation creators receive, and what controls you have over whether AI systems can reference your content.
Staying informed about these regulatory developments and adjusting strategy accordingly will matter increasingly. The content creators who navigate this evolving landscape successfully will be those who remain flexible and adapt to changes rather than expecting today's rules to persist indefinitely.
Transforming AIO knowledge into actual improved visibility requires systematic implementation rather than sporadic efforts. Here's a practical framework for incorporating these strategies into your content workflow.
Start with an audit of your existing content to identify which pieces should be prioritized for AIO optimization. Not every article deserves equal attention—focus first on content that already performs well in traditional search, addresses important topics for your audience, or covers queries where you have genuine expertise to offer. These high-potential pieces are most likely to generate meaningful results from optimization efforts.
During the audit, evaluate each priority article against the seven optimization tactics. Does it include specific statistics and verifiable data? Could you add more? Is the content structured with clear headings that reflect natural language questions? Have you included an FAQ section addressing common queries? Is there a clear "last updated" date? Can you add comparison tables or other structured data? Does schema markup exist and is it appropriate for the content type?
Create a prioritized optimization checklist based on this audit, identifying which pieces need which improvements. Some content might only need a few additions like update dates and FAQ sections, while others might benefit from more substantial restructuring. This systematic approach prevents you from trying to fix everything at once and ensures you tackle the highest-impact improvements first.
Implement changes incrementally, testing as you go rather than making all modifications simultaneously. This allows you to learn which specific changes seem to impact your AI citation rates most significantly. While many factors influence visibility, you might discover that certain tactics work particularly well for your niche or content style, allowing you to prioritize those approaches for future content.
For new content creation, build AIO considerations into your standard workflow. Before writing, identify the key questions your content will answer and structure your outline around those questions. Plan to include specific data points and examples during research. Decide what structured elements (tables, step-by-step lists, comparisons) would enhance the content. Add these considerations to whatever content creation process you already use rather than treating AIO as a separate, optional step.
Establish monitoring routines to track your AI visibility over time. Whether you use commercial tracking tools or build your own system, schedule regular reviews of your performance. Monthly checks might suffice initially, though weekly monitoring makes sense if you're actively optimizing and want faster feedback on what's working.
When reviewing tracking data, look for patterns rather than obsessing over individual fluctuations. Is your visibility generally improving, declining, or stable? Which topics show stronger AI citation rates? Where are competitors consistently appearing instead of you? What queries used to show your content but no longer do? These patterns inform where to focus future optimization efforts and what's working well versus what needs adjustment.
Build a distribution schedule that ensures your content reaches the platforms where community discussion happens. Rather than sporadic promotion when you remember, systematically share new content and participate in relevant discussions on a regular cadence. This might mean dedicating 30 minutes daily to community engagement, or setting aside specific times weekly for distribution activities. The consistent approach yields better results than irregular bursts of activity.
Document what works as you implement and test different approaches. Keep notes on which tactics seem most effective for your content, which platforms drive the most engaged traffic, which topics generate the most AI citations. This knowledge base becomes increasingly valuable over time as you identify patterns specific to your niche and audience that might differ from general best practices.
Consider forming or joining groups of content creators in your niche who are also working on AIO to share insights and results. The field is new enough that collective learning accelerates progress for everyone involved. What you discover about effective tactics in your niche might help others, and their experiences can inform your strategy even if you're in slightly different spaces.
Plan for iterative improvement rather than expecting immediate perfection. AIO is still an emerging practice without definitive best practices etched in stone. You'll make mistakes, try things that don't work, and occasionally optimize for factors that turn out not to matter. This experimentation is part of the learning process. What matters is systematic iteration—trying approaches, measuring results, adjusting based on feedback, and gradually improving your effectiveness over time.
Set realistic timelines for seeing results. Unlike paid advertising where you can generate traffic immediately, organic visibility through either SEO or AIO builds gradually. You might see some quick wins from optimizing high-performing content, but establishing strong overall AI visibility typically takes months of consistent effort. Understand this going in to maintain motivation during the initial period where you're investing effort without dramatic visible results.
The opportunity in AI Optimization exists because most content creators haven't recognized its importance yet. Traditional SEO remains the primary focus, while this emerging traffic channel grows rapidly with relatively light competition. This window won't stay open indefinitely. As more people understand AIO's value, competition will intensify and optimization will become more sophisticated.
Your competitive advantage comes from starting now rather than waiting until AIO is fully mainstream. Begin with these immediate actions that require minimal investment but start building your foundation.
First, test your own AI visibility today. Open ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity and ask questions where your content should logically appear as a relevant source. Be honest in your queries—use the actual questions your audience would ask rather than phrasing things to favor your content. See whether AI models cite you, and if so, how prominently. This reality check shows you where you stand currently.
Second, identify your top five most important pieces of content—articles that address core topics for your audience or drive significant traffic currently. These become your initial optimization targets. Don't try to optimize everything at once. Focus on making these five pieces as strong as possible for AI citation.
Third, implement quick wins on those priority pieces. Add "Last updated: [current date]" to each. Create a simple FAQ section addressing three to five common questions related to each article's topic. Add specific statistics or data points if they're currently missing. These improvements take hours rather than days but can meaningfully impact AI visibility.
Fourth, set up basic tracking even if you don't build a comprehensive system immediately. Create a simple spreadsheet listing queries where you want visibility. Test those queries weekly in one or two AI platforms and note whether your content appears. This manual tracking takes just 15-30 minutes weekly but provides feedback on whether your optimization efforts are working.
Fifth, join one or two communities where your target audience discusses topics related to your content. You don't need to be everywhere—pick platforms where you can genuinely contribute value and commit to participating regularly. Start by reading and understanding the community culture before posting, then gradually engage in discussions where your expertise adds value.
The investment required isn't massive. You don't need expensive tools, extensive technical knowledge, or a large team. You need understanding of the principles, systematic implementation of practical tactics, and consistency over time. The same qualities that make someone successful with traditional content creation—providing genuine value, maintaining quality standards, and persisting through the gradual process of building authority—work for AIO as well.
The difference is timing. Traditional SEO is mature with intense competition and well-established players dominating many niches. AIO is emerging with room for newcomers to establish authority while the landscape is still taking shape. This timing advantage creates opportunities for content creators of all sizes to build significant AI visibility if they act now rather than waiting.
Start today. Audit your content. Implement quick optimizations. Begin tracking your performance. Engage in communities. Build the multi-platform presence that signals authority. Each small step compounds over time into substantial competitive advantage as AI search grows to represent an ever-larger percentage of how people discover information online.
The future of organic visibility includes AI citations alongside traditional search rankings. The question isn't whether to optimize for both—it's whether you'll start while competition is light or wait until fighting for AI visibility becomes as challenging as ranking in traditional search is today.
Choose wisely. The traffic is already flowing. The only question is whether it flows to you or your competitors.

©

Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

©
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
For the first time, global governments have agreed to widespread international trade bans and restrictions for sharks and rays being driven to extinction.
Last week, more than 70 shark and ray species, including oceanic whitetip sharks, whale sharks, and manta rays, received new safeguards under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. The convention, known as CITES, is a United Nations treaty that requires countries to regulate or prohibit international trade in species whose survival is threatened.
Sharks and rays are closely related species that play similar roles as apex predators in the ocean, helping to maintain healthy marine ecosystems. They have been caught and traded for decades, contributing to a global market worth nearly $1 billion annually, according to Luke Warwick, director of shark and ray conservation at Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), an international nonprofit dedicated to preserving animals and their habitats.


© Anadolu / Contributor


© Sora / Facebook
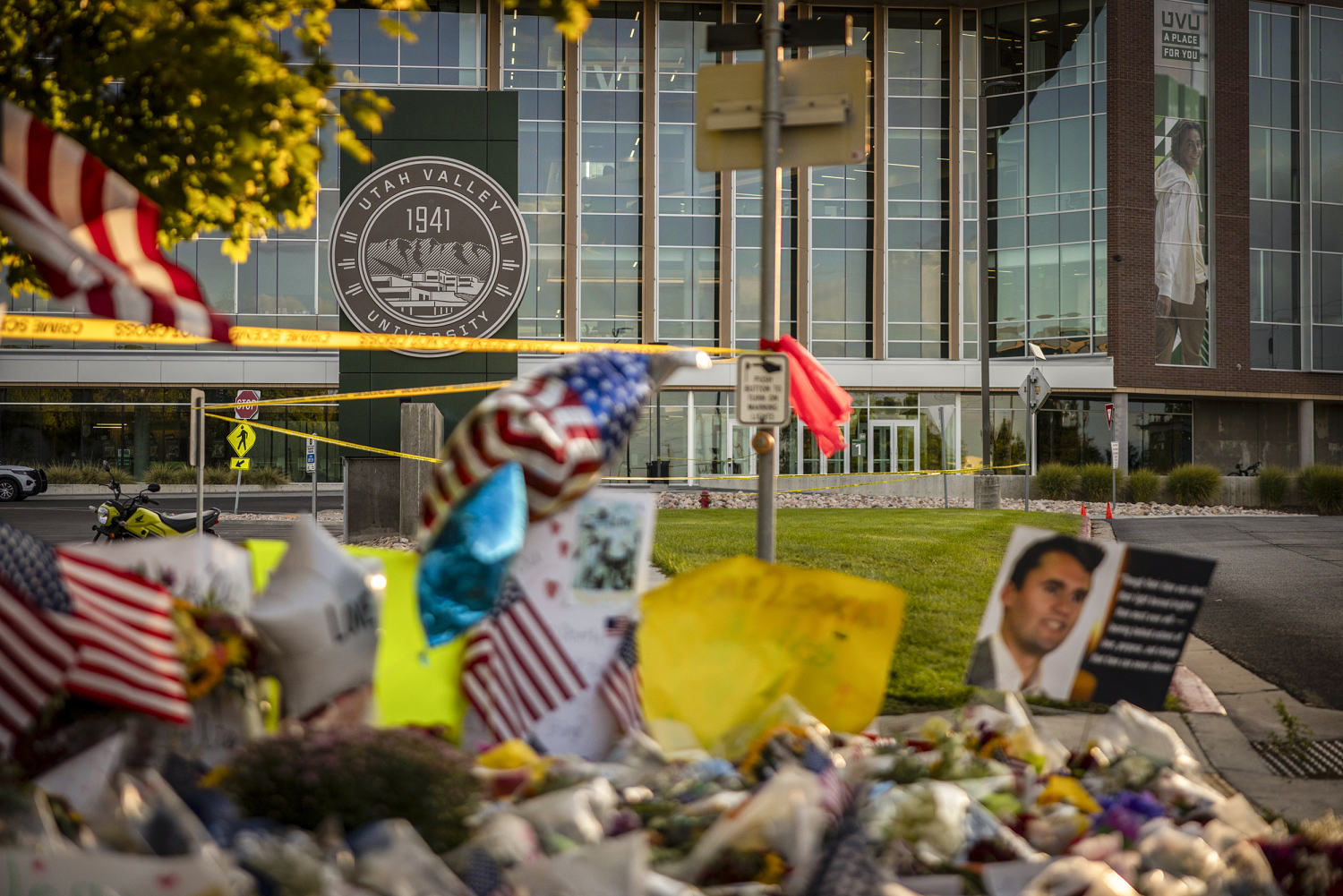
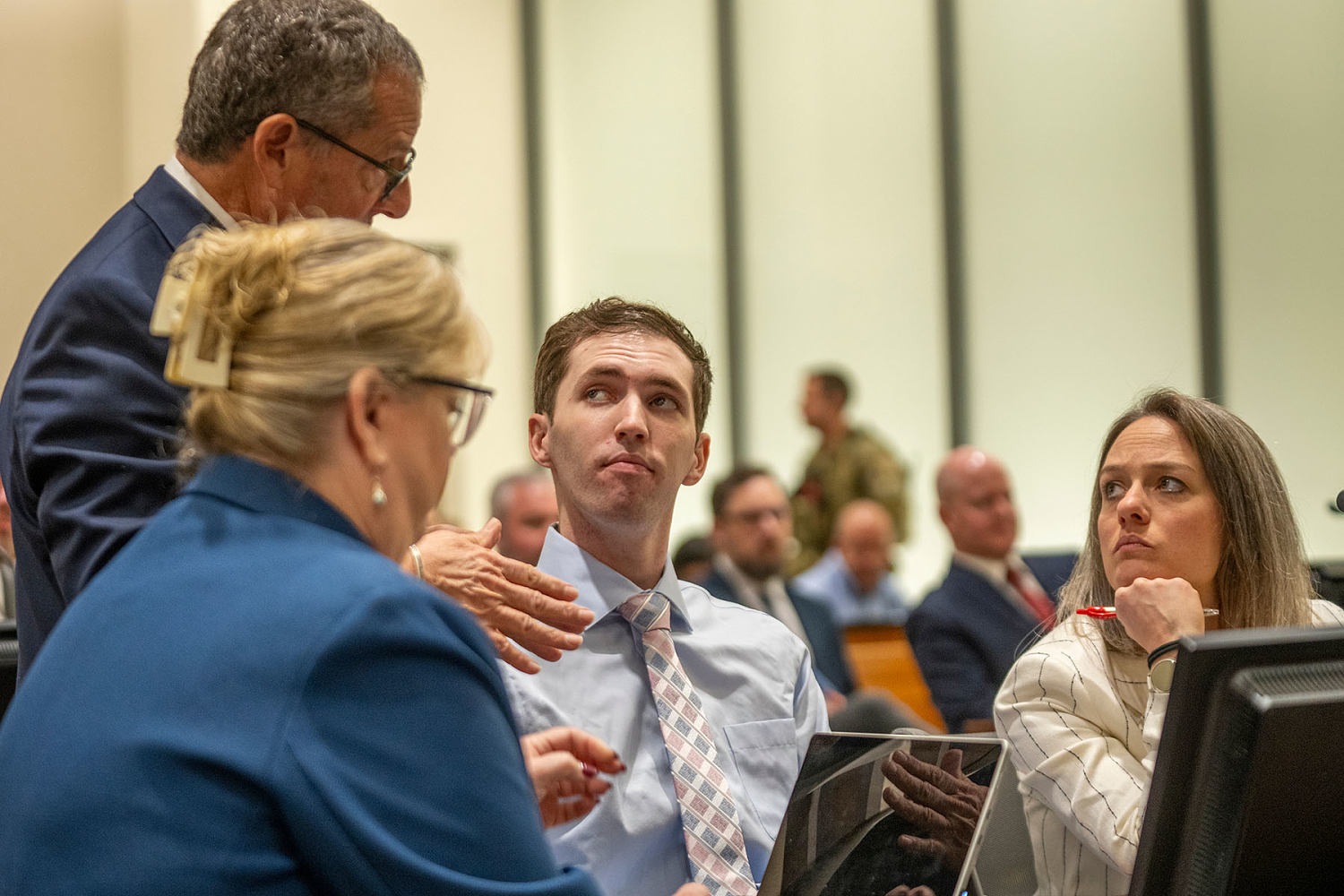



© Rick Egan

© Joe Raedle

© Tom Williams


The Post calls the podcast an "AI-powered tool" that turns its articles into an audio news digest.
(Image credit: The Washington Post)

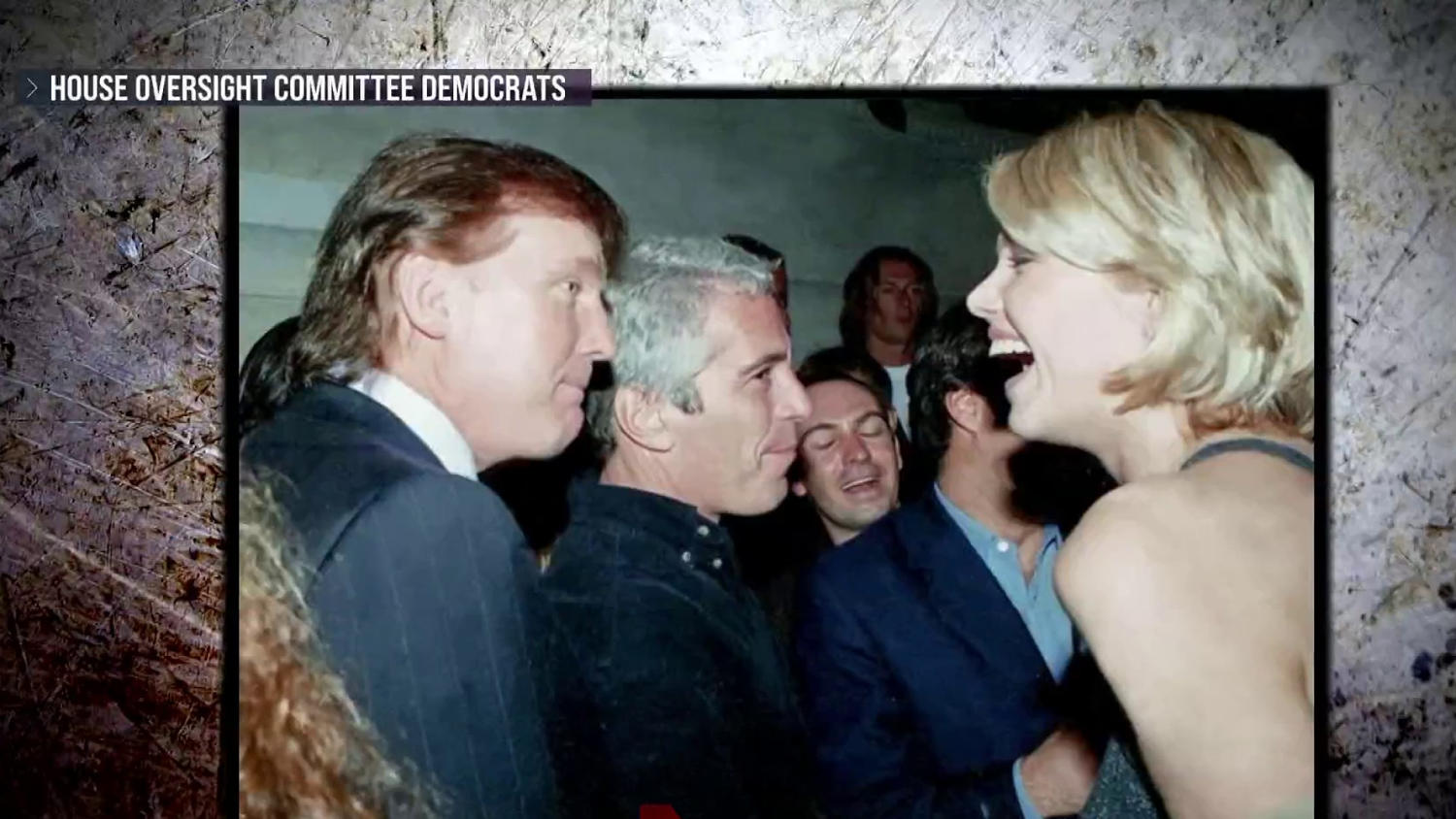
Sacks is the Trump administration's top advisor on tech and crypto policy. In recent weeks, he's faced questions about conflicts of interest and criticism over his drive to undo state AI laws.
(Image credit: Brendan Smialowski)
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.


© Alamy

© Craig Barritt

©

©

©
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
There’s a new Haiku monthly activity report, and this one’s a true doozy. Let’s start with the biggest news.
The most notable development in November was the introduction of a port of the Go programming language, version 1.18. This is still a few years old (from 2022; the current is Go 1.25), but it’s far newer than the previous Go port to Haiku (1.4 from 2014); and unlike the previous port which was never in the package repositories, this one is now already available there (for x86_64 at least) and can be installed via
↫ Haiku activity reportpkgman.
As the project notes, they’re still a few versions behind, but at least it’s a lot more modern of an implementation than they had before. Now that it’s in the repositories for Haiku, it might also attract more people to work on the port, potentially bringing even newer versions to the BeOS-inspired operating system. Welcome as it may be, this new Go port isn’t the only big ticket item this month.
Haiku can now gracefully recover from an app_server crash, something it used to be able to do a long time ago, but which was broken for a long time. The app_server is Haiku’s display server and window manager, so the ability to restart it at runtime after a crash, and have it reconnect with still-running applications, is incredibly welcome. As far as I can tell, all modern operating systems can do this by now, so it’s great to have this functionality restored in Haiku.
Of course, aside from these two big improvements, there’s the usual load of fixes and changes in applications, drivers, and other components of the operating system.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Alpine Linux maintainer Ariadne Conill has published a very interesting blog post about the shortcomings of both sudo and doas, and offers a potential different way of achieving the same goals as those tools.
Systems built around identity-based access control tend to rely on ambient authority: policy is centralized and errors in the policy configuration or bugs in the policy engine can allow attackers to make full use of that ambient authority. In the case of a SUID binary like
doasorsudo, that means an attacker can obtain root access in the event of a bug or misconfiguration.What if there was a better way? Instead of thinking about privilege escalation as becoming root for a moment, what if it meant being handed a narrowly scoped capability, one with just enough authority to perform a specific action and nothing more? Enter the object-capability model.
↫ Ariadne Conill
To bring this approach to life, they created a tool called capsudo. Instead of temporarily changing your identity, capsudo can grant far more fine-grained capabilities that match the exact task you’re trying to accomplish. As an example, Conill details mounting and unmounting – with capsudo, you can not only grant the ability for a user to mount and unmount whatever device, but also allow the user to only mount or unmount just one specific device. Another example given is how capsudo can be used to give a service account user to only those resources the account needs to perform its tasks.
Of course, Conill explains all of this way better than I ever could, with actual example commands and more details. Conill happens to be the same person who created Wayback, illustrating that they have a tendency to look at problems in a unique and interesting way. I’m not smart enough to determine if this approach makes sense compared to sudo or doas, but the way it’s described it does feel like a superior, more secure solution.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Some unexpected good news from the FDA: bemotrizinol, a sunscreen ingredient that has been used in Europe and Asia for decades, is finally being added to the allowable ingredients list for products sold in the U.S. Bemotrizinol is the active ingredient in sunscreens like Bioré Watery Essence, which has a cult following for being unlike anything we can get in the U.S.
I’ve tried Bioré UV Aqua Rich Watery Essence (that’s the full name of the product) in its original Japanese formulation. This sunscreen is a cult favorite on skincare and Asian beauty forums because of its non-greasy feel, and because it protects against both UVA and UVB rays without leaving a white cast. I got mine from a friend who had either picked it up while traveling or possibly ordered from overseas; you can’t buy it in U.S.-based stores.
I’ll explain why this is below, but first: it truly is nothing like anything we have locally. Even our most “non-greasy” sunscreens tend to feel a little goopy or sticky. This one really feels like nothing after you rub it in. I instantly understood why it’s so sought-after. Remembering that experience, I’m looking forward to what we might see in American sunscreens once manufacturers are allowed to include this ingredient.
Bemotrizinol has a lot of things going for it. One is that it “plays well with other sunscreen ingredients,” as one dermatologist told Women’s Health. You can make lighter, nicer-feeling sunscreens with it, hence the popularity of the Bioré formulation I tried. To see what I mean, check out this video where a dermatologist shows off the differences between Bioré's Japanese formulation and the version it sells in the U.S. The ingredients are different, and the texture just isn't the same.
It’s also more effective at broad-spectrum protection. With our current sunscreen formulations, all active ingredients protect against UVB rays (the rays that cause sunburn) but only a few can also provide protection against UVA rays (which contribute to wrinkling and aging of skin). UVB is considered to be the bigger risk for skin cancer, but both probably contribute to cancer risk. Right now, most broad-spectrum U.S. sunscreens use mineral components like zinc oxide. Mineral sunscreens work pretty well, but can leave a white cast on your skin when applied as thickly as you’re supposed to.
Bemotrizinol is a chemical UV filter, so it doesn’t leave that white cast. But it protects well against UVA rays in addition to UVB, and it’s more photostable than a lot of our existing chemical sunscreen ingredients so it can last longer on the skin. In other words, it’s a chemical sunscreen, but combines some of the best features of both chemical and mineral sunscreens.
It’s also considered to be one of the safest sunscreens. All sunscreens on the market are much safer than going without sunscreen, but all of our chemical sunscreen ingredients are currently undergoing a safety evaluation because regulators determined they are probably fine but need more research to know for sure. Currently only our two mineral sunscreen ingredients (zinc oxide and titanium dioxide) are considered GRAS, or generally recognized as safe and effective. Bemotrizinol will be the third.
If you're looking at ingredient lists on Asian or European sunscreens, be aware that it goes by several names. Tinosorb S is bemotrizinol; so is bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine.
Ask anyone in the skincare world what they think about U.S. sunscreens, and for decades now you’d get complaints that we’re missing out on the best sunscreens that the rest of the world uses. (Our last new sunscreen ingredient was approved in 1996.) In most countries, sunscreens are regulated as cosmetics, but in the U.S. they are regulated as drugs. That means the U.S. requires more rigorous testing and approval.
The CARES act, passed in 2020 for pandemic relief, provided a way for over-the-counter drugs to be sold without going through the complete approval process, so long as the FDA was satisfied they were safe and effective. Bemotrizinol met the criteria, thanks in large part to the fact that it’s been used safely since 2000 in Europe, Asia, and Australia. The FDA’s rule on bemotrizinol still needs to be finalized, but it seems likely we’ll see new sunscreens on shelves before the end of 2026.

Once again, there is a new feature available on Google's NotebookLM, the AI tool that functions like a personal assistant and only references material you provide for it. This one is a slide deck generator, which can be useful if you need to make a presentation in a hurry, but I've been using it a little differently to help myself retain new information.
First, you should know how to generate a deck. In case you're unfamiliar with NotebookLM, it's basically just like ChatGPT, but instead of pulling answers from the big, wide Internet, it only relies on PDFs, links, videos, and text you input as resources. This makes it the perfect tool for working on a specific project or studying for a class, since you don't run the risk of inadvertently getting misled by some random, unrelated source.
You can use the chat bot feature the way you would ChatGPT, asking questions and getting summaries of your materials. You can also automatically generate flashcards, videos, infographics, mind maps, fake podcasts, and much more.
To generate slides, it's the same process you'd follow to make those: In the left-side panel, select all of the sources you want the tool to pull from. In the right-side panel, select Slide Deck from the menu. After a few minutes, you'll get slides you can download as a PDF, the same as you would if you were downloading a PowerPoint, and you can upload those to Google Slides or PowerPoint to create a simple presentation.
I've mentioned before that while I love NotebookLM and use it every day for both work and personal pursuits, I can't stand its app. It just doesn't work nearly as well as the browser version, which is a shame because the browser version works so well. I pretty much ignore the app and don't use NotebookLM on mobile or, when I do, I use my mobile browser to access it, which we all know is an annoying workaround that never quite translates right on the smaller screen.

With the slide PDF, however, I get a ready-made study guide complete with visuals, which I can send to myself via iMessage and study on the go. When I generate my own study materials without NotebookLM, I almost always do it in Google Slides, then download the full PDF and review the slides like a giant study guide, so this new feature is taking a bunch of the work out of doing that for me.

With the popularity of AI coding tools rising among some software developers, their adoption has begun to touch every aspect of the process, including the improvement of AI coding tools themselves.
In interviews with Ars Technica this week, OpenAI employees revealed the extent to which the company now relies on its own AI coding agent, Codex, to build and improve the development tool. “I think the vast majority of Codex is built by Codex, so it’s almost entirely just being used to improve itself,” said Alexander Embiricos, product lead for Codex at OpenAI, in a conversation on Tuesday.
Codex, which OpenAI launched in its modern incarnation as a research preview in May 2025, operates as a cloud-based software engineering agent that can handle tasks like writing features, fixing bugs, and proposing pull requests. The tool runs in sandboxed environments linked to a user’s code repository and can execute multiple tasks in parallel. OpenAI offers Codex through ChatGPT’s web interface, a command-line interface (CLI), and IDE extensions for VS Code, Cursor, and Windsurf.


© Mininyx Doodle via Getty Images
